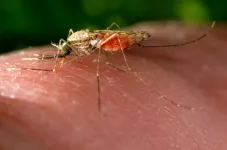
(Press-News.org) They are diligently stoking thousands of bonfires on the ground close to their crops, but the French winemakers are fighting a losing battle. An above-average warm spell at the end of March has been followed by days of extreme frost, destroying the vines with losses amounting to 90 percent above average. The image of the struggle may well be the most depressingly beautiful illustration of the complexities and unpredictability of global climate warming. It is also an agricultural disaster from Bordeaux to Champagne.
It is the loss of the Arctic sea-ice due to climate warming that has, somewhat paradoxically, been implicated with severe cold and snowy mid-latitude winters.
"Climate change doesn't always manifest in the most obvious ways. It's easy to extrapolate models to show that winters are getting warmer and to forecast a virtually snow-free future in Europe, but our most recent study shows that is too simplistic. We should beware of making broad sweeping statements about the impacts of climate change." Says professor Alun Hubbard from CAGE Center for Arctic Gas Hydrate, Environment and Climate at UiT The Arctic University of Norway.
Melting Arctic sea ice supplied 88% of the fresh snow
Hubbard is the co-author of a study in Nature Geoscience examining this counter-intuitive climatic paradox: A 50% reduction in Arctic sea-ice cover has increased open-water and winter evaporation to fuel more extreme snowfall further south across Europe.
The study, led by Dr. Hanna Bailey at the University of Oulu, Finland, has more specifically found that the long-term decline of Arctic sea-ice since the late 1970s had a direct connection to one specific weather event: "Beast from the East" - the February snowfall that brought large parts of the European continent to a halt in 2018, causing £1bn a day in losses.
Researchers discovered that atmospheric vapour traveling south from the Arctic carried a unique geochemical fingerprint, revealing that its source was the warm, open-water surface of the Barents Sea, part of the Arctic Ocean between Norway, Russia, and Svalbard. They found that during the "Beast from the East", open-water conditions in the Barents Sea supplied up to 88% of the corresponding fresh snow that fell over Europe.
Climate warming is lifting the lid off the Arctic Ocean
"What we're finding is that sea-ice is effectively a lid on the ocean. And with its long-term reduction across the Arctic, we're seeing increasing amounts of moisture enter the atmosphere during winter, which directly impacts our weather further south, causing extreme heavy snowfalls. It might seem counter-intuitive, but nature is complex and what happens in the Arctic doesn't stay in the Arctic." says Bailey.
When analyzing the long-term trends from 1979 onwards, researchers found that for every square meter of winter sea-ice lost from the Barents Sea, there was a corresponding 70 kg increase in the evaporation, moisture, and snow falling over Europe.
Their findings indicate that within the next 60 years, a predicted ice-free Barents Sea will likely become a significant source of increased winter precipitation - be it rain or snow - for Europe.
"This study illustrates that the abrupt changes being witnessed across the Arctic now, really are affecting the entire planet." says professor Hubbard.
INFORMATION:
Altering a mosquito's gut genes to make them spread antimalarial genes to the next generation of their species shows promise as an approach to curb malaria, suggests a preliminary study published today in eLife.
The study is the latest in a series of steps toward using CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology to make changes in mosquito genes that could reduce their ability to spread malaria. If further studies support this approach, it could provide a new way to reduce illnesses and deaths caused by malaria.
Growing mosquito resistance to pesticides, as well as malaria parasite resistance ...
Many consumers are willing to pay for improved environmental quality and thus non-market values of impacts of food production on e.g. water quality, C sequestration, biodiversity, pollution, erosion or GHG emissions may even be comparable to the market value of agricultural production. Diverfarming project elucidated how consumers value agroecosystem services enabled by diversification and provided consumer perspectives for developing future agricultural and food policies to better support cropping diversification.
The researchers quantified consumers' willingness to pay for the benefits of increased farm and regional scale diversity of cultivation practices and crop rotations. Three valuation scenarios were presented to a ...
Spain boasts the largest cultivated area of almond trees in the world, with more than 700,000 ha (MAPA, 2018), but ranks third in terms of production. How can this be? Actually it's easy to explain: most of the country's cultivated area of almond trees is comprised of traditional rainfed orchards and located in marginal areas featuring a low density of trees per hectare.
Over the last decade, however, the nut's surging prices havegiven rise to intensive almond tree plantations characterised bya high density of trees per hectare and the employment offertilisation and irrigation, yielding endless rows of white when the trees are in bloom. Knowing what the future of these plantations will be like in a ...
With summer around the corner, a project shows how implementing an evidence-based mindfulness program in a summer camp setting decreases emotional distress in school age children and empowers campers and counselors alike - enhancing camper-counselor relationships. Mindfulness - a state of consciousness that fosters awareness - has the potential to help regulate emotions and behaviors.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University's Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing implemented an eight-week program guided by the Mindful Schools© curricula in a large urban summer day camp program (ages 3 to seventh grade). Mindfulness-based practices are intentional exercises ...
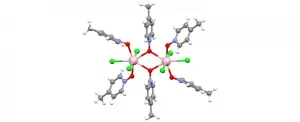
Light can be used to operate quantum information processing systems, e.g. quantum computers, quickly and efficiently. Researchers at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and Chimie ParisTech/CNRS have now significantly advanced the development of molecule-based materials suitable for use as light-addressable fundamental quantum units. As they report in the journal Nature Communications, they have demonstrated for the first time the possibility of addressing nuclear spin levels of a molecular complex of europium(III) rare-earth ions with light. (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22383-x)
Whether in drug development, communication, or for climate forecasts: Processing information quickly and efficiently is crucial in many areas. It is currently done using digital computers, ...
Imprinting is a popularly known phenomenon, wherein certain animals and birds become fixated on sights and smells they see immediately after being born. In ducklings, this can be the first moving object, usually the mother duck. In migrating fish like salmon and trout, it is the smells they knew as neonates that guides them back to their home river as adults. How does this happen?
Exposure to environmental input during a critical period early in life is important for forming sensory maps and neural circuits in the brain. In mammals, early exposure to environmental inputs, as in the case of imprinting, is known to affect perception and social behavior later in life. Visual imprinting has ...
New research led by a professor at NUI Galway is set to change how doctors treat some patients with high blood pressure - a condition that affects more than one in four men and one in five women.
The study by researchers at NUI Galway, Johns Hopkins University and Harvard Medical School found no evidence that diastolic blood pressure - the bottom reading on a blood pressure test - can be harmful to patients when reduced to levels that were previously considered to be too low.
Lead researcher Bill McEvoy, Professor of Preventive Cardiology at NUI Galway and a Consultant Cardiologist at University Hospital Galway, said the findings have the potential to immediately influence ...
New research by the University of Kent and the SWPS University has discovered that national narcissists are more likely to support greenwashing (misleading information about the environmental benefits of a product, a company or a policy) in order to improve their nation's public image.
Findings show that while national narcissists are not likely to support genuine pro-environmental campaigns, they are ready to support political greenwashing campaigns. In business greenwashing decreases consumers' trust and undermines both the image and the profits of the companies that use this strategy. In the realms of politics, it may garner ...
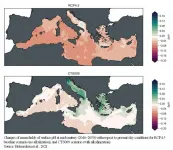
Is it possible to simultaneously address the increase of the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere and the resulting acidification of the oceans? The research of the project DESARC-MARESANUS, a collaboration between the Politecnico di Milano and the CMCC Euro-Mediterranean Center on Climate Change Foundation, explores the feasibility of this process, its chemical and environmental balance, and the benefits for the marine sector, focusing on the Mediterranean basin.
It is now widely recognized that in order to reach the target of limiting global warming ...
A five-year study of mule deer does and newborn fawns in western Wyoming shows that migrating deer have a lot to balance when it comes to birth timing.
The study led by University of Wyoming scientists challenges the long-held assumption that animals match offspring birth with the peak green-up of forage at the birth site. Instead, only deer that migrated long distances and followed the flush of spring green-up from low elevation winter ranges to higher-elevation summer ranges were able to match birth with peak green-up. Other deer migrated shorter distances and gave birth earlier, but birth was out of sync with green-up.
The researchers' work appears in the journal Ecology.
To ...