The role of hydrophobic molecules in catalytic reactions
2021-04-13
(Press-News.org) Electrochemical processes could be used to convert CO2 into useful starting materials for industry. To optimise the processes, chemists are attempting to calculate in detail the energy costs caused by the various reaction partners and steps. Researchers from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) and Sorbonne Université in Paris have discovered how small hydrophobic molecules, such as CO2, contribute to the energy costs of such reactions by analysing how the molecules interact in water at the interface. The team describes the results in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, PNAS for short, published online on 13 April 2021.
To conduct the work, Dr. Alessandra Serva and Professor Mathieu Salanne from Laboratoire PHENIX at Université Sorbonne collaborated with Professor Martina Havenith and Dr. Simone Pezzotti from the Bochum Chair of Physical Chemistry II.
Crucial role for small hydrophobic molecules
In many electrochemical processes, small hydrophobic molecules react at catalyst surfaces that often consist of precious metals. Such reactions often take place in an aqueous solution, whereby the water molecules form what are known as hydration shells around the other molecules: they accumulate around the other molecules. The water surrounding polar, i.e. hygroscopic molecules behaves differently compared to the water surrounding non-polar molecules, which are also referred to as hydrophobic. The Franco-German research team was interested in this hydrophobic hydration.
Using molecular dynamic simulations, the researchers analysed the hydrophobic hydration of small molecules such as carbon dioxide (CO2) or nitrogen (N2) at the interface between the gold and water. They showed that the interaction of water molecules in the vicinity of small hydrophobic molecules makes a crucial contribution to the energy costs of electrochemical reactions.
Model for calculating energy costs expanded
The researchers implemented these findings in the Lum-Chandler-Weeks theory. This allows the energy required to form water networks to be calculated. "The energy costs for hydrophobic hydration were calculated for the bulk in the previous model. This model has now been expanded here to hydrophobic molecules near interfaces. This case was not included before," explains Martina Havenith, the Speaker of the Ruhr Explores Solvation Cluster of Excellence, RESOLV for short, at RUB. The adapted model allows the energy costs for hydrophobic hydration to now be calculated at the interface between gold and water based on the size of the hydrophobic molecules. "Due to the water contribution, the size of the molecules plays an important role in the chemical reactions at these interfaces," says Dr. Simone Pezzotti from the Bochum Chair of Physical Chemistry II.
For instance, the model predicts that small hydrophobic molecules would tend to accumulate at the interface based on the interactions with the water, while larger molecules would remain further away in the solution.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-13
The time children and adolescents spend on screen time entertainment -computers, mobile phones, television and video games- adversely affects their eating habits. This is the main conclusion drawn from a research carried out by EpiPHAAN (Epidemiology, Physical Activity, Accelerometry and Nutrition) research group of the University of Malaga, which further establishes that parents' education level is also associated with the adherence to the Mediterranean diet.
This research was conducted within the PASOS Study -Physical Activity, Sedentarism, lifestyles and Obesity in Spanish youth- of Gasol Foundation, which analyzed more than ...
2021-04-13
Cancer patients from the UK were 1.5 times more likely to die following a diagnosis with COVID-19 than cancer patients from European countries.
This is the finding of a study of over 1000 patients - 924 from European countries and 468 from the UK - during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. The research team, led by Imperial College London, say the study highlights the need for UK cancer patients to be prioritised for vaccination.
The study tracked data between 27 February to 10 September 2020, across 27 centres in six countries: Italy, Spain, France, Belgium, Germany and the UK.
The results, published in the European Journal of Cancer, showed that 30 days after a COVID-19 diagnosis, 40.38 per cent of UK cancer patients had died, versus 26.5 per cent of ...
2021-04-13
Artificial intelligence could be one of the keys for limiting the spread of infection in future pandemics. In a new study, researchers at the University of Gothenburg have investigated how machine learning can be used to find effective testing methods during epidemic outbreaks, thereby helping to better control the outbreaks.
In the study, the researchers developed a method to improve testing strategies during epidemic outbreaks and with relatively limited information be able to predict which individuals offer the best potential for testing.
"This can be a first step towards society ...
2021-04-13
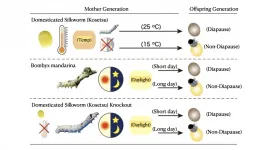
Diapause is a phenomenon in which animals and insects foresee changes in the environment and actively reduce metabolism, or halt regular differentiation and development. It is an adaptation strategy for adverse environments such as surviving winters, but also to encourage uniform growth of the generational group. By knocking out genes that allow the silkworm to detect temperature, researchers at Shinshu University et al. found that the silk moth diapause changes from temperature to photoperiod, or day length. This is not only valuable as an elucidation of the molecular mechanism in the environmental response mechanism of organisms such as insects, but also a very important finding in exploring the process of domestication of silk ...
2021-04-13
Scientists from the Skoltech Space Center (SSC) have developed nanosatellite interaction algorithms for scientific measurements using a tetrahedral orbital formation of CubeSats that exchange data and apply interpolation algorithms to create local maps of physical measurements in real time. The study presents an example of geomagnetic field measurement, which shows that these data can be used by other satellites for attitude control and, therefore, provided on a data-as-a-service basis. The research was published in the journal Advances in Space Research.
SSC is the research ...
2021-04-13
Despite increasing concern over the intrusion of algorithms in daily life, people may be more willing to trust a computer program than their fellow humans, especially if a task becomes too challenging, according to new research from data scientists at the University of Georgia.
From choosing the next song on your playlist to choosing the right size pants, people are relying more on the advice of algorithms to help make everyday decisions and streamline their lives.
"Algorithms are able to do a huge number of tasks, and the number of tasks that they are able to do is expanding practically every day," said Eric Bogert, a Ph.D. student in the Terry College of ...
2021-04-13
A recent case study from North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill demonstrates that, with training, neural control of a powered prosthetic ankle can restore a wide range of abilities, including standing on very challenging surfaces and squatting. The researchers are currently working with a larger group of study participants to see how broadly applicable the findings may be.
"This case study shows that it is possible to use these neural control technologies, in which devices respond to electrical signals from a patient's muscles, to help patients using robotic prosthetic ankles move more naturally and intuitively," says Helen Huang, corresponding author of the study. Huang ...
2021-04-13
The immune response to tuberculosis (TB) differs in adults and newborn babies due to the way immune cells use energy to kick into gear in a bid to kill the bacteria. This fresh discovery - just published in leading journal, Frontiers in Immunology - offers hope for improving treatments for what remains a deadly disease.
TB is still one of the biggest infectious killers in the world and babies are more likely than adults to get this infection and for it to spread outside of the lungs. Thanks to the work of scientists in Professor Joseph Keane's TB Immunology lab, based ...
2021-04-13
An observational study of patients in London hospitals suggests that the B.1.1.7. variant is not associated with more severe illness and death, but appears to lead to higher viral load, consistent with emerging evidence that this lineage is more transmissible than the original COVID-19 strain.
A separate observational study using data logged by 37,000 UK users of a self-reporting COVID-19 symptom app found no evidence that B.1.1.7. altered symptoms or likelihood of experiencing long COVID.
Authors of both studies acknowledge that these findings ...
2021-04-13
It has been long been known that cannabis users develop psychosis more often than non-users, but what is still not fully clear is whether cannabis actually causes psychosis and, if so, who is most at risk. A new study published in Translational Psychiatry by researchers at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) and King's College London helps shed light on both questions. The research shows that while cannabis users had higher rates of psychotic experiences than non-users across the board, the difference was especially pronounced among those with high genetic predisposition to schizophrenia.
"These results are significant because ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The role of hydrophobic molecules in catalytic reactions