(Press-News.org) One of the technical challenges the current data revolution faces is finding an efficient way to route the data. This task is usually performed by electronic switches, while the data itself is transferred using light confined in optical waveguides. For this reason, conversion from an optical to an electronic signal and back-conversion are required, which costs energy and limits the amount of transferable information. These drawbacks are avoidable with a full optical switch operation. One of the most promising approaches is based on microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), thanks to decisive advantages such as low optical loss and energy consumption, monolithic integration, and high scalability. Indeed, the largest photonic switch ever demonstrated uses this approach.
Commercialization
Until now, those MEMS photonic switches have been fabricated using nonstandard and complex processes in laboratory environments, which has made their commercialization difficult. But University of California Berkeley researchers initiated a collaboration that gathered engineers from different universities worldwide to demonstrate that the difficulties could be overcome. They created a photonic MEMS switch using a commercially available complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) fabrication process without modification. The use of this well-known microfabrication platform represents a huge step toward industrialization because it is compatible with most current technologies, cost-effective, and suited for high-volume production.
Switch fabrication
In their research, END
Photonic MEMS switches going commercial
Switch that uses existing fabrication method a step toward integration in data communication networks
2021-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How to build a city that prioritizes public health
2021-04-14
Most people by now have memorized the public health guidelines meant to help minimize transmission of COVID-19: wash your hands, wear a mask, keep six feet apart from others. That part is easy.
What some may not realize is that upholding these guidelines in certain urban areas can present new challenges.
For example, how are you supposed to stay six feet apart from other people when the standard width of a sidewalk is only four feet? What do you do when you want to cross an intersection that requires pressing a button to activate the pedestrian signal, but you are avoiding touching any surfaces?
The COVID-19 pandemic has drastically altered the way individuals interact with other people and their environment, but some public health guidelines meant to protect ...
RNA holds the reins in bacteria: U-M researchers observe RNA controlling protein synthesis
2021-04-14
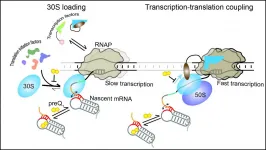
To better understand how RNA in bacteria gives rise to protein--and along the way, target these processes in the design of new antibiotics--researchers are turning their attention to the unique way this process happens in bacteria.
In eukaryotic cells, transcription (the process by which information in a DNA strand is copied into messenger RNA) and translation (the process by which a protein is synthesized by the ribosome from the mRNA) are two successive steps. In bacteria, they occur simultaneously: As the RNA is being synthesized by RNA polymerase, the ribosome comes in to make the proteins.
This synchronicity ...
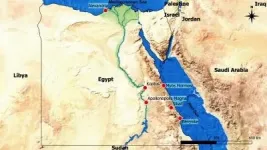
New evidence regarding emerald production in Roman Egypt coming from Wadi Sikait
2021-04-14
"New evidence of the importance of the Roman/Byzantine Mons Smaragdus settlement within the emerald mining network"
A new paper published in the END ...
How to gain a sense of well-being, free and online
2021-04-14
In 2018, when Professor Laurie Santos introduced her course "Psychology and the Good Life," a class on the science of happiness, it became the most popular in the history of Yale, attracting more than 1,200 undergraduate enrollees that first semester. An online course based on those teachings became a global phenomenon. By latest count, 3.38 million people have enrolled to take the free Coursera.org course, called "The Science of Well Being."
But the popularity of the course posed an interesting question. Does taking the course and participating in homework assignments -- which include nurturing social connections, compiling a gratitude list, and meditation -- really help improve a sense of well-being?
The answer is yes, according to two new studies that measured the psychological impact ...
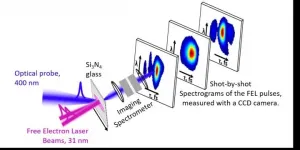
New method measures super-fast, free electron laser pulses
2021-04-14
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., April 14, 2021--New research shows how to measure the super-short bursts of high-frequency light emitted from free electron lasers (FELs). By using the light-induced ionization itself to create a femtosecond optical shutter, the technique encodes the electric field of the FEL pulse in a visible light pulse so that it can be measured with a standard, slow, visible-light camera.
"This work has the potential to lead to a new online diagnostic for FELs, where the exact pulse shape of each light pulse can be determined. That information can help both the end-user and the accelerator scientists," said Pamela Bowlan, Los Alamos National Laboratory's lead researcher on the project. The paper was published April 12, ...
New research provides insight into COVID-19 vaccine reluctancy among social media users
2021-04-14
New research has found that the most reliable indicators of willingness to be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, are rejection of conspiracy suspicions about COVID-19 and a positive attitude towards vaccines in general. The study by King's College London and the University of Bristol is published in the leading peer-reviewed journal Psychological Medicine.
The researchers' analysis was based on a large representative sample survey carried out in November-December 2020. They looked at a range of factors that previous ...
Using sound waves to make patterns that never repeat
2021-04-14
Mathematicians and engineers at the University of Utah have teamed up to show how ultrasound waves can organize carbon particles in water into a sort of pattern that never repeats. The results, they say, could result in materials called "quasicrystals" with custom magnetic or electrical properties.
The research is published in Physical Review Letters.
"Quasicrystals are interesting to study because they have properties that crystals do not have," says Fernando Guevara Vasquez, associate professor of mathematics. "They have been shown to be stiffer than similar periodic or disordered materials. They can also conduct electricity, ...
Mediterranean diet with lean beef may lower risk factors for heart disease
2021-04-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Eating red meat may have a bad reputation for being bad for the heart, but new research found that lean beef may have a place in healthy diets, after all.
In a randomized controlled study, researchers found that a Mediterranean diet combined with small portions of lean beef helped lower risk factors for developing heart disease, such as LDL cholesterol.
Jennifer Fleming, assistant teaching professor of nutrition at Penn State, said the study suggests that healthy diets can include a wide variety of foods, such as red meat, and still be heart friendly.
"When you create a healthy diet built on fruits, vegetables, and other plant-based foods, it leaves room for moderate amounts of other foods like lean beef," Fleming said. "There are still ...
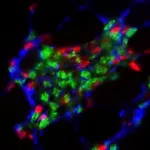
New discovery could lead to therapies for patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy
2021-04-14
Irvine, CA - April 14, 2021 - A new study, led by the University of California, Irvine (UCI), reveals how chronic inflammation promotes muscle fibrosis, which could inform the development of new therapies for patients suffering from Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), a fatal muscle disease.
Titled, "A Stromal Progenitor and ILC2 Niche Promotes Muscle Eosinophilia and Fibrosis-Associated Gene Expression," the study was published today in Cell Reports.
Chronic inflammation is a major pathological process contributing to the progression and severity of several degenerative disorders, including Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Studies directed at establishing a causal link between muscular ...
Guide for science outreach
2021-04-14
What are scientists passionate about? What do they actually do, and why does it matter? Answering questions like these is often part of public outreach efforts that, through demystifying the world of science for non-scientists, can increase appreciation for science and boost support for important research initiatives. Outreach can also make the sciences attractive and accessible to a broader diversity of people, who, in turn, can bring new ideas and perspectives.
"Science is having challenges in terms of getting the general public to support it and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
[Press-News.org] Photonic MEMS switches going commercialSwitch that uses existing fabrication method a step toward integration in data communication networks