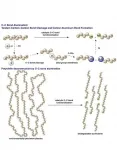
Long-term survival rates for immunotherapies could be misinterpreted
2021-04-15
(Press-News.org) Immune checkpoint inhibitors have transformed cancer care to the point where the popular Cox proportional-hazards model provides misleading estimates of the treatment effect, according to a new study published April 15 in JAMA Oncology.
The study, "Development and Evaluation of a Method to Correct Misinterpretation of Clinical Trial Results With Long-term Survival," suggests that some of the published survival data for these immunotherapies should be re-analyzed for potential misinterpretation.
The study's senior author, Yu Shyr, PhD, the Harold L. Moses Chair in Cancer Research and chair of the Department of Biostatistics at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, and colleagues, Chih-Yuan Hsu, PhD, and Emily Lin, MD, PhD, have proposed an adjustment to convert the inappropriate Cox proportional-hazards model to the appropriate cure model. The adjustment utilizes the Cox-TEL (Cox PH-Taylor expansion for long-term survival data) method.
"The Cox proportional-hazards model has become ingrained as the preferred choice for survival analysis in clinical trials for many reasons, including its robustness; however, researchers should not blindly use this in immunotherapy trials," Shyr said.
"Because the model's proportional hazards assumption is clearly violated in some immunotherapy trials, the results and conclusions based on this model are inaccurate and misleading. We wanted to create an approach that would not only correct the hazard ratio of the Cox proportional-hazards model, but also be interpretable and practical for both clinicians and statisticians. We believe Cox-TEL will be used widely to avoid misinterpretation of clinical trials with long-term survival."
The team of researchers initiated their work because of the common observance of long tails and crossovers in survival curves with immune checkpoint inhibitors. These observances violate the proportional hazards assumption in the widely-used Cox proportional-hazards model. The researchers looked at simulated data and real-world data from published immune checkpoint inhibitor trials. In comparing the Cox proportional-hazards model to the Cox-TEL adjustment method, they determined that the Cox-TEL adjustment method was more accurate in assessing long-term survival. The Cox-TEL adjustment is user friendly and freely available as a package in the statistical software R.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-15
Scientists at the University of Southampton have conducted a study that highlights the importance of studying a full range of organisms when measuring the impact of environmental change - from tiny bacteria, to mighty whales.
Researchers at the University's School of Ocean and Earth Science, working with colleagues at the universities of Bangor, Sydney and Johannesburg and the UK's National Oceanography Centre, undertook a survey of marine animals, protists (single cellular organisms) and bacteria along the coastline of South Africa.
Lead researcher and postgraduate student ...
2021-04-15
The dynamics of the neural activity of a mouse brain behave in a peculiar, unexpected way that can be theoretically modeled without any fine tuning, suggests a new paper by physicists at Emory University. Physical Review Letters published the research, which adds to the evidence that theoretical physics frameworks may aid in the understanding of large-scale brain activity.
"Our theoretical model agrees with previous experimental work on the brains of mice to a few percent accuracy -- a degree which is highly unusual for living systems," says Ilya Nemenman, Emory professor of physics and biology and senior author of the paper.
The ...
2021-04-15
Scientists at the Institute for Cooperative Upcycling of Plastics (iCOUP), an Energy Frontier Research Center led by Ames Laboratory, have discovered a chemical process that provides biodegradable, valuable chemicals, which are used as surfactants and detergents in a range of applications, from discarded plastics. The process has the potential to create more sustainable and economically favorable lifecycles for plastics.
The researchers targeted their work on the deconstruction of polyolefins, which represents more than half of all discarded plastics, and includes nearly every kind of product imaginable-- toys, food packaging, pipe systems, water ...
2021-04-15
A new review published in EPJ H by Clara Matteuzzi, Research Director at the National Institute for Nuclear Physics (INFN) and former tenured professor at the University of Milan, and her colleagues, examines almost three decades of the LHCb experiment - from its conception to operation at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) - documenting its achievements and future potential.
The LCHb experiment was originally conceived to understand the symmetry between matter and antimatter and where this symmetry is broken - known as charge conjugation parity (CP) violation. Whilst this may seem like quite an obscure area of study, it addresses one of the Universe's most fundamental questions: how it came to be dominated ...
2021-04-15
As the world's energy demands grow, so too does growing concern over the environmental impact of power production. The need for a safe, clean, and reliable energy source has never been clearer. Fusion power could fulfil such a need. A review paper published in EPJ H examines the 6-decade history of neutral particle analysis (NPA), developed in Ioffe Institute, Saint Petersburg, Russia, a vital diagnostic tool used in magnetic plasma confinement devices such as tokamaks that will house the nuclear fusion process and generate the clean energy of the future.
As ...
2021-04-15
Investigators in China and the United States have injected human stem cells into primate embryos and were able to grow chimeric embryos for a significant period of time--up to 20 days. The research, despite its ethical concerns, has the potential to provide new insights into developmental biology and evolution. It also has implications for developing new models of human biology and disease. The work appears April 15 in the journal Cell.
"As we are unable to conduct certain types of experiments in humans, it is essential that we have better models to more accurately study and understand human biology and disease," says senior author Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte, a professor in the Gene Expression ...
2021-04-15
LA JOLLA--(April 15, 2021) The ability to grow the cells of one species within an organism of a different species offers scientists a powerful tool for research and medicine. It's an approach that could advance our understanding of early human development, disease onset and progression and aging; provide innovative platforms for drug evaluation; and address the critical need for transplantable organs. Yet developing such capabilities has been a formidable challenge.
Researchers led by Salk Professor Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte have now come one step closer toward this goal by demonstrating a new integration of human cells into animal tissue. Published in the journal Cell on April 15, 2021, the new study builds upon previous work by the Izpisua Belmonte lab to take the next step in chimeric ...
2021-04-15
Illustration
A lot of attention has been paid in recent years to the carbon footprint of the foods we eat, with much of the focus on the outsize contribution of meat production and especially beef.
But much less is known about the implications of individual U.S. dietary choices on other environmental concerns, such as water scarcity.
In a study scheduled for online publication April 15 in the journal Nature Food, researchers from the University of Michigan and Tulane University present a water scarcity footprint that measures the water-use impacts of U.S. diets, taking into ...
2021-04-15
Coral reefs provide many services to coastal communities, including critical protection from flood damage. A new study led by researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz, and the U.S. Geological Survey reveals how valuable coral reefs are in protecting people, structures, and economic activity in the United States from coastal flooding during storms.
Published April 15 in Nature Sustainability, the study found that coral reefs offer more than $1.8 billion in annual flood protection to coastal communities. Losing 1 meter of reef height would cause 100-year flooding zones to increase by 23%, impacting 53,800 more people (a 62% increase) and 90% more property and increasing damages by $5.3 billion.
The study also found that the United States has ...
2021-04-15
In a novel laboratory investigation of the initial atmospheres of Earth-like rocky planets, researchers at UC Santa Cruz heated pristine meteorite samples in a high-temperature furnace and analyzed the gases released.
Their results, published April 15 in Nature Astronomy, suggest that the initial atmospheres of terrestrial planets may differ significantly from many of the common assumptions used in theoretical models of planetary atmospheres.
"This information will be important when we start being able to observe exoplanet atmospheres with new telescopes and advanced instrumentation," said first author Maggie Thompson, a graduate student in astronomy and astrophysics at UC Santa Cruz.
The early atmospheres of rocky planets are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Long-term survival rates for immunotherapies could be misinterpreted