Reliable COVID-19 short-term forecasting
A new model developed at Texas A&M has proved successful in predicting COVID-19 infection rates two to three weeks in advance
2021-04-15
(Press-News.org) A new study by Texas A&M University researchers published in END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
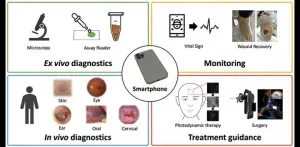
Medically savvy smartphone imaging systems
2021-04-15
Smartphones get smarter every day. These "Swiss Army knives" of mobile computing become even more useful with specialized attachments and applications to improve healthcare. Based on inherent capabilities like built-in cameras, touchscreens, and 3D sensing, as well wearable peripheral devices, custom interfaces for smartphones can yield portable, user-friendly biomedical imaging systems to guide and facilitate diagnosis and treatment in point-of-care settings.
What are the most effective ways to leverage and augment smartphone capabilities? Helpful guidelines are provided in a critical review of emerging smartphone-based imaging systems END ...
Imaging agent enables better monitoring of patients with bacterial infections
2021-04-15
An imaging agent allows scientists to better visualize Enterobacterales infections in patients, helping to address pathogens that can be life-threatening and frequently resist antibiotics. The agent was safe in 26 patients and differentiated infections from either sterile inflammation or COVID-19-linked pneumonia in hamsters. Enterobacterales is the largest group of disease-causing bacteria in humans, and includes common pathogens such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. These species have become increasingly resistant to common antibiotics, which has led the Centers for Disease Control to label some drug-resistant strains as urgent threats to human health. However, scientists still lack tools that can rapidly ...
FSU College of Medicine research links Parkinson's disease and neuroticism
2021-04-15
New research from the Florida State University College of Medicine has found that the personality trait neuroticism is consistently associated with a higher risk of developing the brain disorder Parkinson's disease.
The research by Professor of Geriatrics Antonio Terracciano and team, published in Movement Disorders, found that adults in the study who scored in the top quartile of neuroticism had more than 80% greater risk of Parkinson's, compared to those who scored lower on neuroticism.
"Some clinicians think that the anxiety and depression is just the result of Parkinson's," Terracciano said. "However, our findings suggest that some emotional vulnerability is present early in life, ...
Modelling ancient antarctic ice sheets helps us see future of global warming
2021-04-15
AMHERST, Mass. - Last month saw the average concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) climb to almost 418 parts-per-million, a level not seen on Earth for millions of years. In order to get a sense of what our future may hold, scientists have been looking to the deep past. Now, new research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst, which combines climate, ice sheet and vegetation model simulations with a suite of different climatic and geologic scenarios, opens the clearest window yet into the deep history of the Antarctic ice sheet and what our planetary future might hold.
The Antarctic ice sheet has attracted the particular interest of the scientific community because it is "a lynchpin in the earth's climate system, affecting everything from ...
Can financial stress lead to physical pain in later years?
2021-04-15
Financial stress can have an immediate impact on well-being, but can it lead to physical pain nearly 30 years later? The answer is yes, according to new research from University of Georgia scientists.
The study, published in Stress & Health, reveals that family financial stress in midlife is associated with a depleted sense of control, which is related to increased physical pain in later years.
"Physical pain is considered an illness on its own with three major components: biological, psychological and social," said Kandauda A.S. Wickrama, first author and professor in the College of Family and Consumer Sciences. "In older adults, it co-occurs with other health problems like limited physical functioning, loneliness and cardiovascular ...
FSU engineers improve performance of high-temperature superconductor wires
2021-04-15
Florida State University researchers have discovered a novel way to improve the performance of electrical wires used as high-temperature superconductors (HTS), findings that have the potential to power a new generation of particle accelerators.
An image of Bi-2212, bismuth-based superconducting wires. (Mark Wallheiser/FAMU-FSU College of Engineering)
Researchers used high-resolution scanning electron microscopy to understand how processing methods influence grains in bismuth-based superconducting wires (known as Bi-2212). Those grains form the underlying ...
Understanding the growth of disease-causing protein fibres
2021-04-15
Amyloid fibrils are deposits of proteins in the body that join together to form microscopic fibres. Their formation has been linked to many serious human diseases including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Type 2 diabetes.
Until today, scientists have been unable to reliably measure the speed of fibril growth, as there have been no tools that could directly measure growth rate in solution. However, researchers from the UK's University of Bath and the ISIS Neutron and Muon Source have now invented a technique that does just that. Results from their study are published in RSC Chemical Biology.
"This is an important breakthrough, ...
Small physician offices are seeing negative effects from virtual health care models
2021-04-15
In a newly released study, researchers found that remote and virtual care models can negatively impact small physician offices. Three researchers from END ...
Child Mind Institute's CRISIS survey yields insights to psychological impact of COVID-19
2021-04-15
To better understand the psychological and physical impact caused by the profound consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic - and also inform priorities for interventions and policy changes to address the mental health consequences of the pandemic -- researchers from the Center for the Developing Brain at the Child Mind Institute developed and deployed the CoRonavIruS health and Impact Survey (CRISIS). This questionnaire covered key topics relating to mental distress and resilience during the pandemic. According to a newly-published manuscript of the findings, perceived risk of COVID-19, prior mental health status, and lifestyle changes were key predictors of mental health during the pandemic in adults and children surveyed in the U.S. and U.K.
In the study, supported by the Morgan Stanley ...
Agricultural trade across US states can mitigate economic impacts of climate change
2021-04-15
URBANA, Ill. - Agricultural producers deal firsthand with changing weather conditions, and extreme events such as drought or flooding can impact their productivity and profit. Climate change models project such events will occur more often in the future. But studies of the economic consequences of weather and climate on agriculture typically focus on local impacts only.
A new study from the University of Illinois looks at how changes in weather - including extreme events - may decrease crop profit in one state while increasing profits in other states. The secret ingredient: U.S. interstate trade. It is expected to mitigate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
[Press-News.org] Reliable COVID-19 short-term forecastingA new model developed at Texas A&M has proved successful in predicting COVID-19 infection rates two to three weeks in advance