(Press-News.org) Faced with the tragic loss of the Arecibo observatory in Puerto Rico and the often prohibitive cost of satellite missions, astronomers are searching for savvy alternatives to continue answering fundamental questions in physics.
At a END
On the pulse of pulsars and polar light
Reimagined telescopes may fill the void left by Arecibo's collapse
2021-04-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Neural plasticity depends on this long noncoding RNA's journey from nucleus to synapse
2021-04-16
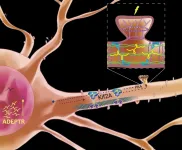
JUPITER, FL--Making memories involves more than seeing friends or taking photos. The brain constantly adapts to new information and stores memories by building connections among neurons, called synapses. How neurons do this--reaching out arm-like dendrites to communicate with other neurons--requires a ballet of genes, signaling molecules, cellular scaffolding and protein-building machinery.
A new study from scientists at Scripps Research and the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience finds a central role for one signaling molecule, a long, noncoding RNA that the scientists named ADEPTR.
Using a variety of technologies, including confocal and two-photon microscopy, they track ADEPTR's moves, watching as it forms, travels, amasses at the ...
A new guide for communicating plant science
2021-04-16
AMES, Iowa - A lot is riding on the continued advancement of plant sciences.
Take the food supply, for starters. Climate change and population growth will continue to pose challenges in the future, and crop production will require innovation and progress by plant scientists in order to keep pace. It isn't an overstatement to say that populations around the world will go hungry if plant science stagnates, said Gustavo MacIntosh, a professor in the Roy J. Carver Department of Biochemistry, Biophysics and Molecular Biology at Iowa State University.
"At the end of the day, either you eat plants or you eat food that ate plants," MacIntosh said. "Plants are the basis for the food we have."
MacIntosh predicts ...
The future of particle accelerators is here
2021-04-16
When the Electron Ion Collider received the go-ahead in January 2020, it became the only new major accelerator in the works anywhere in the world.
"All the stars aligned," said Elke-Caroline Aschenauer, Brookhaven National Laboratory Staff Scientist and a leader in developing the EIC plans. "We have the technology to build this unique particle accelerator and detector to do the measurements that, together with the underlying theory, can for the first time provide answers to longstanding fundamental questions in nuclear physics."
The EIC isn't the only Brookhaven project poised to reshape nuclear and particle physics. Forthcoming data from the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider could finally detect the elusive chiral magnetic effect. Meanwhile, planned accelerators could run on sustainable ...
Simulations reveal how dominant SARS-CoV-2 strain binds to host, succumbs to antibodies
2021-04-16
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., April 16, 2021 -- Large-scale supercomputer simulations at the atomic level show that the dominant G form variant of the COVID-19-causing virus is more infectious partly because of its greater ability to readily bind to its target host receptor in the body, compared to other variants. These research results from a Los Alamos National Laboratory-led team illuminate the mechanism of both infection by the G form and antibody resistance against it, which could help in future vaccine development.
"We found that the interactions among the basic building blocks of the Spike protein become ...
New understanding of the deleterious immune response in rheumatoid arthritis
2021-04-16
Researchers within the Biomedicine Discovery Institute at Monash University have made a breakthrough in understanding the role played by high-risk immune genes associated with the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
The findings, published in Science Immunology, were the result of a seven-year collaboration led by Monash University, involving Janssen Research and Development, USA and the Karolinska Institute, Sweden.
Certain immune system genes, called Human Leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR4, cause an increased susceptibility to RA. In this study, using mice genetically ...
The Trojan-Horse mechanism: How networks reduce gender segregation
2021-04-16
The social science literature has long viewed homophily and network-based job recruitment as crucial drivers of segregation. Researchers at Linköping University and ESADE, Ramon Llull University now show that this view must be revised. In their Science Advances article, they call attention to a previously unidentified factor, the Trojan-horse mechanism, which shows that network-based recruitment can reduce rather than increase segregation levels.
The segregation of labor markets along ethnic and gender lines is an important source of socio-economic inequalities. Therefore, the understanding the mechanisms that drive segregation ...
Science Advances publishes proteomics technology from Oblique Therapeutics AB
2021-04-16
Science Advances publishes proteomics technology from Oblique Therapeutics AB with a potential to bring several novel antibody medicines to large patient populations in multiple disease areas
Gothenburg, Sweden, April 16th, 2021 - Oblique Therapeutics AB, a Sweden-based biotech company, in collaboration with Karolinska Institutet (Stockholm, Sweden), Gothenburg University (Sweden) and several local biotechs published promising research results in the highly-acclaimed scientific journal Science Advances (AAAS) entitled: Rational Antibody design for Undruggable Targets using Kinetically Controlled Biomolecular ...
Female protective effect: Yale researchers find clues to sex differences in autism
2021-04-16
New Haven, Conn. -- It is well established that autism occurs much more frequently in boys than in girls, and that girls seem to have a greater resilience to developing the condition. It has been unclear, however, why that is.
In a new Yale-led study, researchers find that autism may develop in different regions of the brain in girls than boys and that girls with autism have a larger number of genetic mutations than boys, suggesting that they require a larger "genetic hit" to develop the disorder.
The findings appear in the April 16 edition of the journal ...
Researchers revise indicator of mobility limitation in older adults
2021-04-16
Aging entails a loss of muscle mass and strength, which in some cases impairs mobility, hinders walking or performance of day-to-day tasks, and exposes the elderly to the risk of falls and hospitalizations.
In clinical practice, handgrip measurement is the most widely used method to identify loss of overall muscular strength in older people. Values below 26 kg for men and 16 kg for women have for some time been considered an indication of risk-associated weakness, but these parameters are being revised.
Researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, collaborating with colleagues at other institutions in the same state such as the University of São Paulo's Ribeirão Preto Medical School (FMRP-USP), Nursing School ...
Study shows past COVID-19 infection doesn't fully protect young people against reinfection
2021-04-16
Although antibodies induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection are largely protective, they do not completely protect against reinfection in young people, as evidenced through a longitudinal, prospective study of more than 3,000 young, healthy members of the US Marines Corps conducted by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Naval Medical Research Center, published April 15 in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
"Our findings indicate that reinfection by SARS-CoV-2 in health young adults is common" says Stuart Sealfon, MD, the Sara B. and Seth M. Glickenhaus Professor of Neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and senior author of the paper. "Despite a prior COVID-19 infection, young people can catch the virus ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
Cloaked stem cells evade immune rejection in mice, pointing to a potential universal donor cell line
Growth in telemedicine has not improved mental health care access in rural areas, study finds
Pitt scientists engineer “living eye drop” to support corneal healing
Outcomes of older adults with advanced cancer who prefer quality of life vs prolonging survival
Lower music volume levels in fitness class and perceived exercise intensity
Of crocodiles, counting and conferences
AERA announces 2026 award winners in education research
Saving two lives with one fruit drop
Photonic chips advance real-time learning in spiking neural systems
[Press-News.org] On the pulse of pulsars and polar lightReimagined telescopes may fill the void left by Arecibo's collapse