(Press-News.org) UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- As vaccines that help protect against COVID-19 become available for more people across the United States, questions have been raised about whether institutions like schools and universities should require their students and staff to become vaccinated.
A new study by Simon Haeder, assistant professor of public policy at Penn State, found that a majority of those surveyed supported mandates that required students and teachers to be vaccinated against COVID-19. However, more people supported broader vaccine mandates that don't specifically include those against COVID-19.
Haeder said political partisanship, along with race and gender, helped account for these differences.
"Even if children are less likely to get severely ill, vaccination of students has been shown to have benefits such as lower numbers of community deaths, particularly among the elderly," Haeder said. "Mandates may serve as a crucial policy tool to help reign in COVID-19 and reach herd immunity, which we otherwise might not reach any time soon."
Haeder added that the findings -- recently published in the journal Vaccine -- suggest that while the majority of Americans would be supportive of COVID-19 vaccine mandates in educational settings, about one in five would be indifferent and another one in five would be opposed.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, policy makers have debated about how to determine whether educational institutions are safe enough for students to return in person. The development of safe and effective vaccines, Haeder said, offers a potential way for society to eventually return to normal.
He added that while making vaccines mandatory -- also known as vaccine mandates -- has been a strategy to control epidemics in the past, they have not been without controversy.
"Massachusetts mandated smallpox vaccinations in the early 1800s, Alaska and California used mandates in the 1970s to control measles, and in more modern times, there are often certain vaccine mandates for living in the dorms on some college campuses," Haeder said. "But these policies have often been met with vocal opposition from certain groups of Americans, and with the pandemic being so politicized, we were curious about how Americans felt about potential COVID-19 vaccine mandates."
For the study, Haeder developed and sent a survey to 2,404 participants in the fall of 2020. The nationally representative survey included questions about how the participants felt about requiring vaccines for students and teachers in three different educational settings: daycares, K-12 schools, and universities and colleges.
The survey also asked participants questions designed to measure political partisanship, political knowledge, and beliefs about whether schools are an appropriate place to deliver health care, as well as demographic information such as race, ethnicity, education and gender.
The researchers found that Democrats were consistently more supportive of vaccine mandates than moderates or Republicans. White Americans and people who believed schools were appropriate settings for providing health services were also more likely to support any vaccine mandate.
Haeder said there are several possible reasons for some of these differences.
"Partisanship has permeated everything related to COVID-19 and lots of misinformation has been spread, including from individuals in leadership positions," Haedaer said. "Additionally, there's a general growing distrust of science and its elites, which when combined with the novelty of the illness and vaccines, could contribute to this lack of support for vaccine mandates in certain groups."
Additionally, the researchers found that in daycare settings, about 70% of participants "definitely" or "probably" supported general vaccine mandates for students, a little over 50% supported COVID-19 vaccine mandates for students, and about 60% supported COVID-19 vaccine mandates for teachers.
For K-12 schools, about 68% supported general mandates for students, just over 50% supported COVID-19 vaccine mandates for students, and just under 60% supported COVID-19 vaccine mandates for teachers. For colleges and universities, the results were about 65%, 55% and 58%, respectively.
Haeder said that in addition to helping to guide policy makers as efforts continue to be made to control the pandemic, the findings have other implications, as well.
"Efforts to provide Americans with more information about the safety and effectiveness of the vaccines should be undertaken to help alleviate fears around the COVID-19 vaccines," Haeder said. "Also, efforts could be made to reduce potential barriers for vaccinations, including providing the vaccine free of charge, making scheduling appointments easier, avoiding long travel times, and offering convenient opening hours."
INFORMATION:
OKLAHOMA CITY -- With an overall survival rate of 9% for those diagnosed, pancreatic cancer remains exceedingly difficult to treat. However, the patient's primary tumor typically isn't what leads to death - it is the cancer's ability to evade detection and metastasize to other organs.
A team of researchers at the OU College of Medicine has published a new study in the journal Gastroenterology, the world's leading publication on GI tract disease, that sheds new light on the ability of pancreatic cancer cells to spread throughout the body. Understanding why metastasis occurs is crucial for developing a therapeutic strategy to stop the spread.
The study, led by scientist ...
The composition of the street drugs heroin and cocaine has dramatically changed at alarming speeds across the globe. No longer are these street drugs cut with benign materials such as lactose but now cut with up to 17 or more pharmaceutically active and potentially toxic adulterants.
A drug user may buy cocaine today but end up with a drug cocktail more dangerous then what was bought and assumed was cocaine. This has a profound effect on public health and safety as well as on the individual street drug users during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Selected by the Editor-in-Chief, Dr. Kenneth Blum as the Editor's Choice in the May 2021 issue of Current Psychopharmacology (CPSP), this work examined the alarming addition of multiple pharmaceutically active substances collectively ...
MIAMI--The Galápagos Islands have played a historic role since Charles Darwin's visit onboard the HMS Beagle in 1835. Today, a team of scientists, including from the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, studied a large eruption in the archipelago to get new insights into how volcanoes behave and could help forecast future events.
The study gives the first detailed description of a volcanic eruption from Sierra Negra found on Isla Isabela - the largest of the Galápagos Islands and home to nearly 2,000 people.
The findings, published in Nature Communications, reveal how the volcano inflated and fractured before it erupted and captures a new level of detail for any eruption from a volcano on the islands.
Networks ...
MIAMI--A new study led by scientists at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science provides evidence that humans are influencing wind and weather patterns across the eastern United States and western Europe by releasing CO2 and other pollutants into Earth's atmosphere.
In the new paper, published in the journal npj Climate and Atmospheric Science, the research team found that changes in the last 50 years to an important weather phenomenon in the North Atlantic--known as the North Atlantic Oscillation--can be traced back to human activities that impact the climate system.
"Scientists have long understood that human actions are warming the planet," said the study's lead author Jeremy ...
The results of coral beaching are obvious -- stark underwater forests of white coral skeletons -- yet the physiological processes of bleaching are not well understood. Now, KAUST researchers show that, long before signs of bleaching appear, prolonged spells of warm water cause heat stress that disrupts the nutrient cycling of the coral and its symbiotic algae.
Coral reefs occur in warm low-nutrient waters. Stony corals include the coral animal, which is a cnidarian host that lives in symbiosis with Symbiodiniaceae, single-celled algae that photosynthesize to help "feed" the coral in exchange for the ...
Varying severity of COVID-19 symptoms in patients is reflected by levels of a chemical biomarker in their body which scientists say could be used to better manage treatments and other interventions, including vaccinations.
In a new paper in International Journal of Infectious Diseases, medical experts in Italy and Australia examined levels of a chemical called serum amyloid A (SAA), a protein synthesised in the liver which can spike up to 1,000-fold within the first 24-48 hours of an infection.
In turn, an increase in SAA can further perpetuate inflammation and cause clot abnormalities and organ damage, researchers say, concluding SAA levels are associated ...
Solid-matrix catalysts called heterogeneous catalysts are among the most widespread industrial applications in reducing toxic gases, unburned fuel, and particulate matter in the exhaust stream from the combustion chamber. They are also used in energy, chemical, and pharmaceutical sectors, i.e., production of biodiesel, polymers, biomass/waste conversion into valuable products, and many others processes. All thanks to their active sites and high surface. Nevertheless, their high efficiency is limited by the astronomic price of noble metals, So, cost-effective substitutes with comparable effectivity seem to be a holy grail for the industry. A recent paper ...
OSAKA, Japan. Look at any piece of machinery and you will see a complex network of moving parts, or actuators, each with its own function, all working together for a common goal. From this perspective, the way most machines differ is in the way their actuators are powered: excavators rely on compressed liquid (hydraulic), the brake system in a car uses compressed air (pneumatic), and a printer has electricity.
What if the moving parts of a machine could be powered by light? A machine made up of photoactuators would not need direct contact with the power source to move. Among its many ...
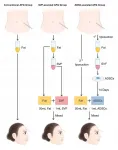
Durham, NC - A study released today in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine suggests a new way to correct facial atrophy of localized scleroderma (LoS) in patients. It shows how applying grafts made up of the patient's own fat enhanced with adipose?derived stem cells (ADSCs) is a safe, feasible and attractive alternative to conventional fat grafting or fat grafting combined with stromal vascular fraction in treating this condition.
LoS is a rare autoimmune disease caused when the body makes too much collagen, which results in the skin becoming stiff and hard. "Presenting mainly as subcutaneous tissue atrophy and hyperpigmentation, this disorder seriously ...
A COVID-19 vaccine that could provide protection against existing and future strains of the COVID-19 coronavirus, and other coronaviruses, and cost about $1 a dose has shown promising results in early animal testing.
Vaccines created by UVA Health's Steven L. Zeichner, MD, PhD, and Virginia Tech's Xiang-Jin Meng, MD, PhD, prevented pigs from being becoming ill with a pig model coronavirus, porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV). The vaccine was developed using an innovative approach that Zeichner says might one day open the door to a universal vaccine for coronaviruses, ...