(Press-News.org) Astronomers have discovered a pulsar--a dense and rapidly spinning neutron star sending radio waves into the cosmos--using a low-frequency radio telescope in outback Australia.
The pulsar was detected with the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) telescope, in Western Australia's remote Mid West region.
It's the first time scientists have discovered a pulsar with the MWA but they believe it will be the first of many.
The finding is a sign of things to come from the multi-billion-dollar Square Kilometre Array (SKA) telescope. The MWA is a precursor telescope for the SKA.
Nick Swainston, a PhD student at the Curtin University node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR), made the discovery while processing data collected as part of an ongoing pulsar survey.
"Pulsars are born as a result of supernovae--when a massive star explodes and dies, it can leave behind a collapsed core known as a neutron star," he said.
"They're about one and a half times the mass of the Sun, but all squeezed within only 20 kilometres, and they have ultra-strong magnetic fields."
Mr Swainston said pulsars spin rapidly and emit electromagnetic radiation from their magnetic poles.
"Every time that emission sweeps across our line of sight, we see a pulse--that's why we call them pulsars," he said. "You can imagine it like a giant cosmic lighthouse."
ICRAR-Curtin astronomer Dr Ramesh Bhat said the newly discovered pulsar is located more than 3000 light-years from Earth and spins about once every second.
"That's incredibly fast compared to regular stars and planets," he said. "But in the world of pulsars, it's pretty normal."
Dr Bhat said the finding was made using about one per cent of the large volume of data collected for the pulsar survey.
"We've only scratched the surface," he said. "When we do this project at full-scale, we should find hundreds of pulsars in the coming years."
Pulsars are used by astronomers for several applications including testing the laws of physics under extreme conditions.
"A spoonful of material from a neutron star would weigh millions of tonnes," Dr Bhat said.
"Their magnetic fields are some of the strongest in the Universe--about 1000 billion times stronger than that we have on Earth."
"So we can use them to do physics that we can't do in any of the Earth-based laboratories."
Finding pulsars and using them for extreme physics is also a key science driver for the SKA telescope.
MWA Director Professor Steven Tingay said the discovery hints at a large population of pulsars awaiting discovery in the Southern Hemisphere.
"This finding is really exciting because the data processing is incredibly challenging, and the results show the potential for us to discover many more pulsars with the MWA and the low-frequency part of the SKA."
"The study of pulsars is one of the headline areas of science for the multi-billion-dollar SKA, so it is great that our team is at the forefront of this work," he said.
INFORMATION:
MORE INFORMATION
ICRAR
The International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) is a joint venture between Curtin University and The University of Western Australia with support and funding from the State Government of Western Australia.
THE MURCHISON WIDEFIELD ARRAY
The Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) is a low-frequency radio telescope and is the first of four Square Kilometre Array (SKA) precursors to be completed. A consortium of partner institutions from seven countries (Australia, USA, India, New Zealand, Canada, Japan, and China) financed the development, construction, commissioning, and operations of the facility. The MWA consortium is led by Curtin University.
PUBLICATION:
'Discovery of a steep-spectrum low-luminosity pulsar with the Murchison Widefield Array', published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters on April 21st, 2021.
MULTIMEDIA:
Available from http://www.icrar.org/pulse
CONTACTS:
Dr Ramesh Bhat (ICRAR / Curtin University)
Ph: +61 430 910 055 E: Ramesh.Bhat@curtin.edu.au
Nick Swainston (ICRAR / Curtin University)
Ph: +61 402 566 321 E: Nicholas.Swainston@curtin.edu.au
Prof. Steven Tingay (ICRAR / Curtin University)
Ph: +61 401 103 635 E: S.Tingay@curtin.edu.au
Kirsten Gottschalk (Media Contact, ICRAR)
Ph: +61 438 361 876 E: Kirsten.Gottschalk@icrar.org
Lucien Wilkinson (Media Contact, Curtin University)
Ph: +61 413 070 925 E: Lucien.Wilkinson@curtin.edu.au
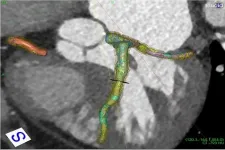
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common form of heart disease and is present in about END ...
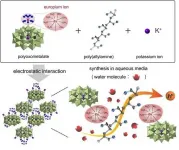
Protons are the next big thing when it comes to fuel cell technology. The subatomic exchange produces power on a scale that challenges contemporary solid-state fuel cell technology, used to help power space shuttles. To realize the proton-based technology sooner, an international team of researchers have developed a hybrid material that effectively transports protons at high temperatures and humidity -- two major challenges in past attempts.
The results were published on April 19 in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, a journal of the American Chemical Society.
The team, led by ...
A new Portland State study challenges the idea that youth with cognitive disabilities are unable or lack potential to pursue a career in science, technology, engineering and mathematics.
In a study using national data on more than 15,000 adolescents, the researchers found that undergraduates with medicated ADHD or autism appear to be more likely to major in STEM than youth without cognitive disabilities, and youth with autism have the most positive STEM attitudes.
Dara Shifrer, the lead author and an associate professor of sociology at PSU, says that increasing access to STEM fields for youth with disabilities depends not only on encouraging them to pursue STEM majors but also to enroll in college because STEM occupations often require bachelor's degrees at ...
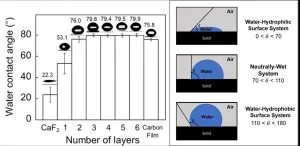
Graphene is a two-dimensional material in which carbon atoms are arranged in hexagonal structures, and it has unique physical and chemical properties such as sub-nanometer thickness, chemical stability, mechanical flexibility, electrical and thermal conductivity, optical transparency, and selective permeability to water. Due to these properties, various applications of graphene in transparent electrodes, desalination, electrical energy storage, and catalysts have been vigorously studied.
Because graphene is an extremely thin material, for practical uses, it has to be deposited on top of other materials that serve as substrate. One of the research subjects which is of great scientific ...
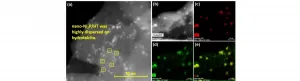
Osaka, Japan - Catalysts lie at the heart of a greener and more sustainable future for chemical production. However, many of the catalysts currently in widespread use have limitations that affect their efficiency. Researchers from Osaka University have reported a stable and reusable nickel phosphide nanoalloy catalyst for the hydrogenation of maltose to maltitol that outperforms conventional catalysts. Their findings are published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
Maltitol is a sugar alcohol that is widely used as a sweetener and food additive. It can be produced by hydrogenating maltose; however, the reaction must be selective to avoid generating ...
DALLAS, April 21, 2021 -- A smartphone-based electrocardiogram (ECG) screening accurately detected previously unknown atrial fibrillation in American Indians, and more than half who were diagnosed with the irregular heart rhythm were younger than the recommended screening age of 65, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association.
About one-third of ischemic strokes, those triggered by blood clots, are caused by atrial fibrillation, the most common heart rhythm disorder. Since many people don't have symptoms and are unaware of its presence, atrial fibrillation often goes undiagnosed. In some cases, a stroke is the first sign that a person has the ...
Volcanic eruptions deep in our oceans are capable of extremely powerful releases of energy, at a rate high enough to power the whole of the United States, according to research published today.
Eruptions from deep-sea volcanoes were long-thought to be relatively uninteresting compared with those on land. While terrestrial volcanoes often produce spectacular eruptions, dispersing volcanic ash into the environment, it was thought that deep marine eruptions only produced slow moving lava flows.
But data gathered by remotely operated vehicles deep in the North East Pacific and analysed by scientists at the University of Leeds, has revealed a link ...
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a stable high-conductivity polymer ink. The advance paves the way for innovative printed electronics with high energy efficiency. The results have been published in Nature Communications.
Electrically conducting polymers have made possible the development of flexible and lightweight electronic components such as organic biosensors, solar cells, light-emitting diodes, transistors, and batteries.
The electrical properties of the conducting polymers can be tuned using a method known as "doping". In this method, various dopant molecules are added to the polymer ...
Despite virtual reality (VR) technology being more affordable than ever, developers have yet to achieve a sense of full immersion in a digital world. Among the greatest challenges is making the user feel as if they are walking.
Now, researchers from the Toyohashi University of Technology and The University of Tokyo in Japan have published a paper to the journal Frontiers in Virtual Reality describing a custom-built platform that aims to replicate the sensation of walking in VR, all while sitting motionlessly in a chair.
"Walking is a fundamental and fun activity for human in everyday life. Therefore, it is very worthwhile to provide a high-quality walking experience in a VR space," says Yusuke Matsuda.
Matsuda is a project ...
Details:
Walking is a fundamental physical activity in humans. A research team at Toyohashi University of Technology, in collaboration with researchers at the University of Tokyo, has developed a virtual walking system for seated observers which allows them to experience walking without moving their limbs. A walking-avatar, in first-person and mirrored perspectives, enhanced illusory walking sensations by combining rhythmic foot vibrations to simulate footsteps. The "invisible" avatar, made of only hands and feet, also improved the illusion of walking. This system may provide virtual walking experience for people with walking disabilities. This study will be published in Frontiers in Virtual ...