Know your ally: Cooperative male dolphins can tell who's on their team
2021-04-22
(Press-News.org) When it comes to friendships and rivalries, male dolphins know who the good team players are. New findings, published in Nature Communications by University of Bristol researchers, reveal that male dolphins form a social concept of team membership based on cooperative investment in the team.
The Bristol researchers, with colleagues from the University of Zurich and University of Massachusetts, used 30 years of observational data from a dolphin population in Shark Bay, Western Australia, and sound playback experiments to assess how male dolphins responded to the calls of other males from their alliance network.
Dr Stephanie King, Senior Lecturer from Bristol's School of Biological Sciences who led the research, said: "Social animals can possess sophisticated ways of classifying relationships with members of the same species. In our own society, we use social knowledge to classify individuals into meaningful groups, like sports teams and political allies. Bottlenose dolphins form the most complex alliances outside humans, and we wanted to know how they classify these relationships."
Dr Simon Allen, Research Fellow at Bristol's School of Biological Sciences, who contributed to the study, added: "We flew drones above dolphin groups, recording their behaviour during the sound playbacks, tracking their movements underwater and revealing novel insights into how dolphins respond to the calls of other males in their network of allies."
Males responded strongly to all of the allies that had consistently helped them out in the past, even if they weren't currently close friends. On the other hand, they didn't respond strongly to males who hadn't consistently helped them out in the past, even if they were friends. What this shows is that these dolphins form social concepts of 'team membership', categorizing allies according to a shared cooperative history.
Dr King said: "Such concepts develop through experience and likely played a role in the cooperative behaviour of early humans. Our results show that cooperation-based concepts are not unique to humans, but also occur in other animal societies with extensive cooperation between non-kin."
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by The Branco Weiss Fellowship - Society in Science and the National Geographic Society.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-22
By cracking open a cellular membrane, Northwestern University synthetic biologists have discovered a new way to increase production yields of protein-based vaccines by five-fold, significantly broadening access to potentially lifesaving medicines.
In February, the researchers introduced a new biomanufacturing platform that can quickly make shelf-stable vaccines at the point of care, ensuring they will not go to waste due to errors in transportation or storage. In its new study, the team discovered that enriching cell-free extracts with cellular membranes -- the components needed to made conjugate vaccines -- vastly increased yields of its freeze-dried platform.
The work sets the stage to rapidly make medicines that address rising antibiotic-resistant bacteria as well as new viruses ...
2021-04-22
BOSTON -- Radiation therapy is used as a treatment for more than half of all cancer patients and can be highly effective at shrinking tumors and killing cancer cells. But radiation treatment can also damage healthy tissue, including tissue in the mouth and gastrointestinal tract. This tissue injury can lead to oral mucositis, esophagitis, and proctitis -- painful and sometimes debilitating tissue damage. It's estimated that these injuries occur in over 200,000 patients in the U.S. each year. In a new paper published in Advanced Science, investigators from Brigham and Women's Hospital, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital and ...
2021-04-22
Bottom Line: When given a choice, most individuals with an average risk of colorectal cancer said they would prefer a stool-based screening test for colorectal cancer over colonoscopy, the method most often recommended by health care providers.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Prevention Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Xuan Zhu, PhD, senior health services analyst at the Mayo Clinic Robert D. and Patricia E. Kern Center for the Science of Health Care Delivery
Background: Although colorectal cancer is the second most frequent cause of cancer-related death in the United States, about one-third of eligible American adults have never completed a colorectal cancer screening test, ...
2021-04-22
Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), astronomers found a rotating baby galaxy 1/100th the size of the Milky Way at a time when the Universe was only seven percent of its present age. Thanks to assistance by the gravitational lens effect, the team was able to explore for the first time the nature of small and dark "normal galaxies" in the early Universe, representative of the main population of the first galaxies, which greatly advances our understanding of the initial phase of galaxy evolution.
"Many of the galaxies that existed ...
2021-04-22
For elite runners competing in long-distance races, every second counts. So when Nike introduced "advanced shoe technology" in 2017, questions arose about whether the new design would significantly affect performances in professional sports. A new paper published in END ...
2021-04-22
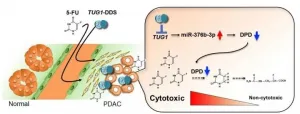
Nagoya University researchers and colleagues in Japan have uncovered a molecular pathway that enhances chemotherapy resistance in some pancreatic cancer patients. Targeting an RNA to interrupt its activity could improve patient response to therapy and increase their overall survival.
"Pancreatic cancer is one of the most aggressive human malignancies, with an overall median survival that is less than five months," says cancer biologist Yutaka Kondo of Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine. "This poor prognosis is partially due to a lack of potent therapeutic ...
2021-04-22
Robotics field aims at mimicking what natural biological entities have achieved throughout millennia of evolution - actions like moving, adapting to the environment, or sensing. Beyond traditional rigid robots, the field of soft robotics has recently emerged using compliant, flexible materials capable to adapt to their environment more efficiently than rigid ones. With this goal in mind, scientists have been working for years in the so-called biohybrid robots or biobots, generally composed of muscle tissue, either cardiac or skeletal, and an artificial scaffold, achieving crawling, ...
2021-04-22
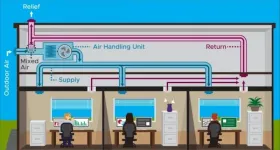
Vigorous and rapid air exchanges might not always be a good thing when it comes to addressing levels of coronavirus particles in a multiroom building, according to a new modeling study.
The study suggests that, in a multiroom building, rapid air exchanges can spread the virus rapidly from the source room into other rooms at high concentrations. Particle levels spike in adjacent rooms within 30 minutes and can remain elevated for up to approximately 90 minutes.
The findings, published online in final form April 15 in the journal Building and Environment, come from a team of researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. The team includes building and HVAC experts ...
2021-04-22
Diseases continue to be a major threat to coral reef health. For example, a relatively recent outbreak termed stony coral tissue loss disease is an apparently infectious waterborne disease known to affect at least 20 stony coral species. First discovered in 2014 in Miami-Dade County, the disease has since spread throughout the majority of the Florida's Coral Reef and into multiple countries and territories in the Caribbean. Some reefs of the northern section of Florida's Coral Reef are experiencing as much as a 60 percent loss of living coral tissue area.
A new study by researchers at Florida Atlantic University's Harbor ...
2021-04-22
INDIANAPOLIS -- A team from Regenstrief Institute leveraged OpenMRS, a global open-source electronic medical record (EMR), to create an emergency EMR for Indianapolis first responders preparing for a possible influx of COVID-19 patients. This process was completed in a week to allow Indianapolis Emergency Medical Services (IEMS) to register patients, collect basic clinical information, and send these encounters to Indiana's health information exchange, a crucial element to help the response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
IEMS asked Regenstrief research scientists for help ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Know your ally: Cooperative male dolphins can tell who's on their team