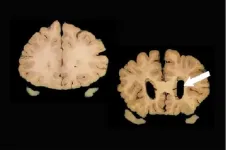
(Press-News.org) One of the biggest challenges in Alzheimer's research is to identify biomarkers that can identify people who are at risk of developing dementia. Biomarkers could be used to screen people so they might be helped before they develop dementia.
Researchers have focused primarily on three such biomarkers. Two are Alzheimer's-related proteins, amyloid and tau. Amyloid forms clumps in brains, and tau forms skeins of filaments called neurofibrillary tangles. Both can be detected in cerebral spinal fluid or by specialized positron emission tomography (PET) scans. The third marker, brain atrophy, can be seen with CT or MRI scans.
To guide researchers, the National Institute on Aging and the Alzheimer's Association have endorsed a research tool based on these three biomarkers called the AT(N) framework--A, for amyloid, T for tau, and (N) for neurodegeneration or atrophy. The hope was that the framework would provide a standard tool to assess an asymptomatic person's risk of developing dementia.
A new study by researchers in Seattle suggests a subset of people classified by this approach as having the highest risk for dementia will not develop dementia in their lifetime.
"We used autopsy data to approximate AT(N) biomarker categories from our well-characterized sample, and looked at dementia rates for people in each category," said END
Study evaluates biomarker criteria for assessing Alzheimer's risk
Community-based autopsy study of well-characterized older adults provides valuable data on influential research tool
2021-04-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
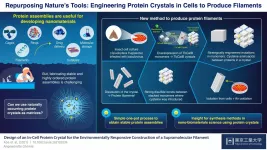
In-cell nano-3D printer: Synthesizing stable filaments from in-cell protein crystals
2021-04-26
Proteins are undoubtedly some of the most fascinating biomolecules, and they perform many of the functions that (in our eyes) separate life from inanimate matter. Multi-molecular protein assemblies even have large-scale structural functions, as evidenced by feathers, hair, and scales in animals. It should come as no surprise that, with progress in advanced nanotechnology and bioengineering, artificial protein assemblies have found applications in a variety of fields, including catalysis, molecular storage, and drug delivery systems.
However, producing ordered protein assemblies remains challenging. It is particularly difficult to get monomers, the building blocks of proteins, to assemble stably into the desired structures; this generally ...
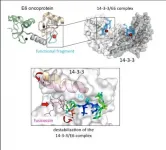
Biophysicists found an Achilles heel of a cancerogenic virus
2021-04-26
Although most oncological diseases are not infectious, some viruses can cause cancer. According to the World Health Organization, two HPV subtypes account for 70% of cervical cancer cases and pre-existing conditions. Moreover, HPV considerably increases the risks of other types of cancer. Within an infected cell, a viral protein called E6 binds with human proteins from the 14-3-3 family. 14-3-3 proteins are present in cells of all eukaryotic organisms and can interact with hundreds of other important players of intracellular processes to regulate cell division, gene activity, metabolism, cell death, and intracellular ...
Researchers identify the proteins that cause intestinal disease
2021-04-26
Researchers from Tel Aviv University have created an artificial intelligence platform that can identify the specific proteins that allow bacteria to infect the intestines - a method that paves the way for the creation of smart drugs that will neutralize the proteins and prevent disease, without the use of antibiotics. Participating in the study, which was published in the prestigious journal Science, were Ph.D. student Naama Wagner and Prof. Tal Pupko, head of the Shmunis School of Biomedicine and Cancer Research at the Faculty of Life Sciences and the new Center for Artificial Intelligence ...
Researchers complete high-precision time-frequency dissemination
2021-04-26
Prof. PAN Jianwei and his colleagues from the University of Science and Technology of China of the Chinese Academy of Sciences investigated the high-loss free space high-precision time-frequency dissemination experiment between remote locations, simulating the high-precision time-frequency high-orbit satellite-ground links in the channel loss, atmospheric noise, and transmission delay effects.
This link experiment exhibits that the instability of the time-frequency transfer via a satellite in middle-high earth orbits might reach E-18 at 10,000 s, enabling ...
Football Fitness gives an important boost to health in women treated for breast cancer
2021-04-26
The University of Southern Denmark (SDU), Rigshospitalet and the University of Copenhagen have come together to study the effects of Football Fitness on various health parameters and self-rated health following treatment for breast cancer.
The results of the project, called Football Fitness After Breast Cancer (ABC), have now been published in three scientific articles published in international sports medicine, cardiology and oncology journals.
"The main conclusion is that Football Fitness is an intense and good form of training for women treated for breast cancer, with beneficial effects on balance, muscle strength and bone density," says END ...
Pain patients and healthcare providers want CDC opioid guideline revoked
2021-04-26
The CDC's opioid prescribing guideline has failed to reduce addiction and overdoses, significantly worsened the quality of pain care in the United States and should be revoked, according to a large new survey of patients and healthcare providers by Pain News Network, an independent, non-profit news organization.
Nearly 4,200 patients and providers participated in the online survey, which was conducted as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention prepares to update and possibly expand its 2016 guideline, which discourages doctors from prescribing opioid ...
TBI: A new roadmap for advancing personalized treatment solutions
2021-04-26
NEW YORK, NY (April 26, 2021) -Brain research and advocacy nonprofit Cohen Veterans Bioscience (CVB) today announced the launch of a National TBI Precision Solutions Research Roadmap, with the advent of the first in a series of publications resulting from its Brain Trauma Blueprint framework program.
The Brain Trauma Blueprint is a framework that enables stakeholder groups across government, academia, foundations, and industry to advance precision diagnostics and treatments for brain trauma through a coordinated effort. The framework comprises a 12-step process to jointly identify unmet patient needs, associated research priorities, landscape state of the science, identify research gaps and barriers, and provide ...
Study looked at how nurses view touch as a form of care
2021-04-26
SPOKANE, Wash. - Touching patients while providing care is an important and unavoidable aspect of the nursing profession. Nurses can also transform touch into a useful therapeutic tool to improve patients'-- and their own--wellbeing.
That is the topic of a study, "'Permission to Touch': Nurses' Perspectives of Interpersonal Contact during Patient Care," published in the Western Journal of Nursing Research.The authors include two Washington State University College of Nursing faculty, Associate Professor Marian Wilson and Assistant Professor Tullamora Landis, former faculty member Michele Shaw, and lead author Enrico DeLuca, of Sapienza University of Rome, Italy, who visited WSU in 2018 to work with Wilson on the study.
Nurses touch patients frequently ...
Cell adaptation in critically ill could be difference between life and death
2021-04-26
Creating the best conditions for cells to make energy and survive critical illness is a challenge little understood in modern medicine. Now a new study led by scientists at the University of Plymouth, in collaboration with University College London and the Universities of Cambridge and Southampton, shows early signs that cells in some critically ill patients actually adapt to their conditions by producing energy more efficiently.
The research, published in the journal Redox Biology, took muscle and blood samples over seven days from 21 critically ill patients (ie those with two or more organs failing) in intensive care, and 12 healthy people, comparing cells' behaviour.
The study showed that all of the critically ill ...
Shopping online or locally - an individual choice
2021-04-26
The obstacles associated with shopping, such as shipping costs or the time needed to go to the shop, are crucial to the individual choice of where to shop. When deciding between online shopping and local shopping, personal opinion on purchasing security, environmental protection aspects, and work conditions plays a role. This is found by a study using microeconometric models at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT). Some of the results of the representative study funded by the German Research Foundation are reported in Papers in Applied Geography and Raumforschung und Raumordnung.
For the evaluations reported, data were collected in 2019, that is before local shopping was restricted due to the pandemic. "During the lockdowns, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
[Press-News.org] Study evaluates biomarker criteria for assessing Alzheimer's riskCommunity-based autopsy study of well-characterized older adults provides valuable data on influential research tool