INFORMATION:
Research gives trees an edge in landfill clean-up
2021-04-28
(Press-News.org) Rhinelander, Wis., April 28, 2021-- A research team from the USDA Forest Service and the University of Missouri has developed a new contaminant prioritization tool that has the potential to increase the effectiveness of environmental approaches to landfill clean-up.
Phytoremediation - an environmental approach in which trees and other plants are used to control leachate and treat polluted water and soil - hinges on matching the capability of different tree species with the types of contaminants present in soil and water. Identifying the worst contaminants within the dynamic conditions of a landfill has been challenging.
"Thousands of contaminants can be present in landfill leachate, and contamination can vary by location and over time, so it can be difficult to determine what needs to be, or even can be targeted with environmental remediation," said Elizabeth Rogers, a USDA Forest Service Pathways intern and the lead author of the study. "This tool allows site managers to prioritize the most hazardous contaminants or customize the tool to address local concerns."
Rogers and co-authors Ron Zalesny, Jr., a supervisory research plant geneticist with the Northern Research Station, and Chung-Ho Lin, a Research Associate Professor at the University of Missouri's Center for Agroforestry, combined multiple sources of data to develop a pollutant prioritization tool that systematically prioritizes contaminants according to reported toxicity values. The study, "A systematic approach for prioritizing landfill pollutants based on toxicity: Applications and opportunities," is available through the Northern Research Station at: https://www.nrs.fs.fed.us/pubs/62410
Knowing which contaminants are the most hazardous allows scientists like Zalesny to better match trees and tree placement in landfills. "Phytoremediation research has focused on discovering which trees work best in particular soils and sites," Zalesny said. "The ability to home in on specific contaminants will enhance phytoremediation outcomes."
The pollutant prioritization tool allows for greater transparency on the benefits of phytoremediation. "When you know what you are targeting, you can provide better information to your community on how long remediation will take and how effective it is," Lin said.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research delves into link between text anxiety and poor sleep
2021-04-28
LAWRENCE -- College students across the country struggle with a vicious cycle: Test anxiety triggers poor sleep, which in turn reduces performance on the tests that caused the anxiety in the first place.
New research from the University of Kansas just published in the International Journal of Behavioral Medicine is shedding light on this biopsychosocial process that can lead to poor grades, withdrawal from classes and even students who drop out. Indeed, about 40% of freshman don't return to their universities for a second year in the United States.
"We were interested in finding out what predicted students' performance in statistics classes ...
Novel late-stage colorectal cancer treatment proves effective in preclinical models
2021-04-28
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (04/28/2021) -- In a recent discovery by University of Minnesota Medical School, researchers uncovered a new way to potentially target and treat late-stage colorectal cancer - a disease that kills more than 50,000 people each year in the United States. The team identified a novel mechanism by which colorectal cancer cells evade an anti-tumor immune response, which helped them develop an exosome-based therapeutic strategy to potentially treat the disease.
"Late-stage colorectal cancer patients face enormous challenges with current treatment options. Most of the time, the patient's immune system cannot efficiently fight against tumors, even with the ...
Seasonal water resource on the Upper Indus
2021-04-28
Seasonally occurring fields of aufeis (icing) constitute an important resource for the water supply of the local population in the Upper Indus Basin. However, little research has been done on them so far. Geographers at the South Asia Institute of Heidelberg University have now examined the spreading of aufeis and, for the first time, created a full inventory of these aufeis fields. The more than 3,700 accumulations of laminated ice are important for these high mountain areas between South and Central Asia, particularly with respect to hydrology and climatology.
In the semi-arid Himalaya regions of India and Pakistan, meltwater from snow and glaciers plays an essential role for irrigation in local agriculture and hydropower generation. In ...
Using cosmic-ray neutron bursts to understand gamma-ray bursts from lightning
2021-04-28
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., April 28, 2021--Analysis of data from a lightning mapper and a small, hand-held radiation detector has unexpectedly shed light on what a gamma-ray burst from lightning might look like - by observing neutrons generated from soil by very large cosmic-ray showers. The work took place at the High Altitude Water Cherenkov (HAWC) Cosmic Ray Observatory in Mexico.
"This was an accidental discovery," said Greg Bowers, a scientist at Los Alamos National Laboratory and lead author of the study published in Geophysical Research Letters. "We set up this system to study terrestrial gamma-ray flashes - or gamma-ray bursts from lightning - that are ...
Epilepsy discovery reveals why some seizures prove deadly
2021-04-28
New research from the University of Virginia School of Medicine has shed light on the No. 1 cause of epilepsy deaths, suggesting a long-sought answer for why some patients die unexpectedly following an epileptic seizure.
The researchers found that a certain type of seizure is associated with sudden death in a mouse model of epilepsy and that death occurred only when the seizure induced failure of the respiratory system.
The new understanding will help scientists in their efforts to develop ways to prevent sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP). Based on their research, the UVA team has already identified potential approaches to stimulate breathing in the ...
COVID-19 may result in prolonged infection in immunocompromised children and young adults
2021-04-28
Children and young adults with compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing cancer treatment, may experience a prolonged period of infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, and the extended duration of infection may increase the incidence of mutations. This case study was conducted by investigators at Children's Hospital Los Angeles and is published in the journal EBioMedicine.
Most people are infectious for about 10 days after first showing COVID-19 symptoms. In this study, researchers describe two children and a young adult with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 for months. ...
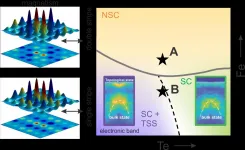
Mapping the electronic states in an exotic superconductor
2021-04-28
UPTON, NY--Scientists characterized how the electronic states in a compound containing iron, tellurium, and selenium depend on local chemical concentrations. They discovered that superconductivity (conducting electricity without resistance), along with distinct magnetic correlations, appears when the local concentration of iron is sufficiently low; a coexisting electronic state existing only at the surface (topological surface state) arises when the concentration of tellurium is sufficiently high. Reported in Nature Materials, their findings point to the composition range necessary for topological superconductivity. Topological superconductivity could enable more ...
Ludwig Cancer Research study shows pancreatic cancer cells reverse to advance malignancy
2021-04-28
APRIL 28, 2021, NEW YORK - A Ludwig Cancer Research study has identified a previously unrecognized mechanism by which cancer cells of a relatively benign subtype of pancreatic tumors methodically revert--or "de-differentiate"--to a progenitor, or immature, state of cellular development to spawn highly aggressive tumors that are capable of metastasis to the liver and lymph nodes.
The study, led by Ludwig Lausanne's Douglas Hanahan and published in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, also shows that engagement of the mechanism is associated with poorer outcomes in patients diagnosed with pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PanNETs). Further, its findings provide concrete evidence that such cellular de-differentiation, widely observed ...
Injectable dermal fillers don't just fill - they also lift, new study suggests
2021-04-28
April 28, 2021 - Injectable dermal fillers provide a minimally invasive approach to reduce facial lines and wrinkles while restoring volume and fullness in the face. More than 2.7 million dermal filler procedures were performed in 2019, according to the most recent statistics from the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
Even as the popularity of dermal fillers continues to skyrocket, plastic surgeons are still working out how to maximize their benefits for patients seeking nonsurgical facial rejuvenation. Most studies have used subjective rating systems, with little objective evidence on the outcomes achieved.
One recent study suggested that in addition to their "volumizing" effects, dermal fillers may also have variable "lifting" effects. Sebastian Cotofana, ...
Dynamic changes in early childhood development may lead to changes in autism diagnosis
2021-04-28
Philadelphia, April 28, 2021 - Researchers from the Center for Autism Research (CAR) at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) found that difficulties in diagnosing toddlers with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) might be due to the dynamic nature of the disorder during child development. Children with clinical characteristics that put them on the diagnostic border of autism have an increased susceptibility to gaining or losing that diagnosis at later ages. The findings were published online by The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry.
While most children diagnosed with ASD at early ages retain their diagnosis, a significant number of children have more dynamic presentations of clinical ...