New machine learning-based tool to help physicians determine best test for chest pain
2021-04-29
(Press-News.org) New Haven, Conn. -- The choice between two non-invasive diagnostic tests is a common dilemma in patients who present with chest pain. Yale cardiologist Rohan Khera, MD, MS, and colleagues have developed ASSIST©, a new digital decision-aiding tool.
By applying machine learning techniques to data from two large clinical trials, this new tool identifies which imaging test to pursue in patients who may have coronary artery disease or CAD, a condition caused by plaque buildup in the arterial wall.
The new tool, described in a study published April 21 in the European Heart Journal, focuses on the long-term outcome for a given patient.
"There are strengths and limitations for each of these diagnostic tests," said Khera, an assistant professor of cardiology at Yale School of Medicine. Patients may have calcium in their blood vessels or a more advanced stage of the disease than can be missed. "If you are able to establish the diagnosis correctly, you would be more likely to pursue optimal medical and procedural therapy, which may then influence the outcomes of patients."
Recent clinical trials have attempted to determine if one test is optimal. The PROMISE and SCOT-HEART clinical trials have suggested that anatomical imaging has similar outcomes to stress testing, but may improve long-term outcomes in certain patients.
"When patients present with chest pain you have two major testing strategies. Large clinical trials have been done without a conclusive answer, so we wanted to see if the trial data could be used to better understand whether a given patient would benefit from one testing strategy or the other," said Khera. Both strategies are currently used in clinical practice.
To create ASSIST, Khera and his team obtained data from 9,572 patients who were enrolled in the PROMISE trial through the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute and created a novel strategy that embedded local data experiments within the larger clinical trial.
"A unique aspect of our approach is that we leverage both arms of a clinical trial, overcoming the limitation of real-world data, where decisions made by clinicians can introduce bias into algorithms," said Khera
The tool also proved effective in a distinct population of patients in the SCOT-HEART trial. Among 2,135 patients who underwent functional-first or anatomical-first testing, the authors observed a two-fold lower risk of adverse cardiac events when there was agreement between the test performed and the one recommended by ASSIST. Khera said he hopes this tool will provide further insight to clinicians while they make the choice between anatomical or functional testing in chest pain evaluation.
Functional testing, commonly known as a stress test, examines patients for CAD by detecting reduced blood flow to the heart. The second option, anatomical testing, or coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA), identifies blockages in the blood vessels. Using machine learning algorithms ASSIST provides a recommendation for each patient.
"While we used advanced methods to derive ASSIST, its application is practical for the clinical setting. It relies on routinely captured patient characteristics and can be used by clinicians with a simple online calculator or can be incorporated in the electronic health record," said Evangelos Oikonomou, MD, DPhil, a resident physician in Internal Medicine at Yale and the study's first author.
INFORMATION:
ASSIST is part of a broader enterprise concept called Evidence2Health. Khera will present this new concept at the Yale Innovation Summit on May 19. Hosted by Yale Office of Cooperate Research, the Yale Innovation Summit is the largest gathering in Connecticut of venture capital and institutional investors from around the country.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-29
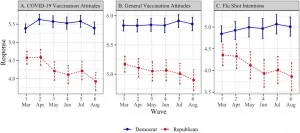
Individuals who self-identify as Republicans became more skeptical of a potential COVID-19 vaccine and other inoculations, such as the flu shot, over the course of the pandemic, reveals a new study by the University of California San Diego’s Rady School of Management.
The paper, published in PLOS ONE, measured general attitudes toward vaccines and assessed whether study participants would get a potential COVID-19 vaccine as well as the seasonal flu shot. It also gauged trust in media.
“We found Republicans became increasingly vaccine hesitant and less trusting of media from March to August of 2020, while Democrats’ views on ...
2021-04-29
LONDON, ON - In a published study, a team from Lawson Health Research Institute has found that a simple device can reduce swelling after kidney transplantation. The geko™ device, manufactured by Sky Medical Technology Ltd and distributed in Canada by Trudell Healthcare Solutions Inc., is a muscle pump activator which significantly improves blood flow by stimulating the body's 'muscle pumps.' Patients using the device following kidney transplantation experienced shorter hospital stays and reduced surgical site infections by nearly 60 per cent.
Kidney and simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantations ...
2021-04-29
Scientists have recreated the reaction by which carbon isotopes made their way into different organic compounds, challenging the notion that organic compounds, such as amino acids, were formed by isotopically enriched substrates. Their discovery suggests that the building blocks of life in meteorites were derived from widely available substrates in the early solar system.
Their findings were published online in Science Advances on April 28, 2021.
Carbonaceous meteorites contain the building blocks of life, including amino acids, sugars, and nucleobases. These ...
2021-04-29
Scientists from Stony Brook University and the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior have pieced together a timeline of how brain and body size evolved in mammals over the last 150 million years. The international team of 22 scientists, including biologists, evolutionary statisticians, and anthropologists, compared the brain mass of 1400 living and extinct mammals. For the 107 fossils examined--among them ancient whales and the oldest Old World monkey skull ever found--they used endocranial volume data from skulls instead of brain mass data. The brain measurements were then analyzed along with body size ...
2021-04-29
Within the past decade, next-generation sequencing technologies have revolutionized the way in which genetic data are generated and analyzed. In the field of phylogenetics, this has meant that researchers are rapidly reconstructing the tree of life, a goal that biologists have been working toward since Darwin sketched the first phylogeny in his notebook in 1837.
Yet despite the relative ease with which DNA can now be sequenced in large quantities, scientists must first extract that DNA from an organism, often relying on vast numbers of curated specimens ...
2021-04-29
DALLAS, April 29, 2021 -- Health care professionals should consider prescribing medication for patients with slightly elevated blood pressure if levels do not decrease after six months of healthy lifestyle changes, according to a new scientific statement from the American Heart Association. The statement, published today in the Association's journal Hypertension, fills a gap in guideline recommendations by addressing how to manage untreated, stage 1 high blood pressure - levels of 130-139/80-89 mm Hg - that was not fully addressed in the 2017 treatment guidelines.
The 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Blood Pressure Management ...
2021-04-29
Eye contact plays a fundamental role in human communication and relationships. When we look into each other's eyes, we show that we are paying attention to each other. However, we do not only look at each other but also at our four-legged companions. According to new research by Hungarian ethologists, at least four independent traits affect dogs' ability to establish eye contact with humans. Short-headed, cooperative, young, and playful dogs are the most likely to look into the human eye.
Dogs adapted uniquely well to live with humans, and communication plays a vital ...
2021-04-29
Less than one percent of people in the United States use kratom, a plant-based substance commonly used to manage pain and opioid withdrawal, according to a study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine. However, the use of kratom--which is legal but carries the risk of addiction and harmful side effects--is more prevalent among people who use other drugs, particularly those with opioid use disorder.
Derived from a tree native to Southeast Asia, kratom can be taken as a pill, capsule, or extract, or brewed as a tea. It acts on the brain's opioid receptors; at low doses, kratom is a stimulant, while at higher doses, it can relieve pain. Some people report using kratom as a substitute for opioids in an effort ...
2021-04-29
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Researchers have created a new, open-access tool that allows doctors and scientists to evaluate infant brain health by assessing the concentration of various chemical markers, called metabolites, in the brain. The tool compiled data from 140 infants to determine normal ranges for these metabolites.
Published in the journal NMR in Biomedicine, the study describes an easier and more reliable way to evaluate metabolite concentrations in the infant brain than was previously available, said study lead Ryan Larsen, a researcher at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.
Metabolites play an important role in normal brain growth, development and function, said study co-author ...
2021-04-29
When they go to the dentist to get a tooth pulled or another procedure, patients might not think that the prescription they receive to ease their pain could put them or their family at risk of an opioid overdose.
But a new study from the University of Michigan shows that overdose rates were two and a half times higher among patients who filled a prescription for an opioid medication after a dental procedure, compared with those who didn't fill such a prescription.
Overdose rates were also higher among the family members of such patients - possibly from misuse of the leftover pills.
The study is published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine by a team from the U-M Medical School and School of Dentistry. It used data from 8.5 million teen and adult ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New machine learning-based tool to help physicians determine best test for chest pain