(Press-News.org) Through T cell engineering, researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center show that it's possible to arrest tumor growth for a variety of cancers and squash the spread of cancer to other tissues. This research will be published in tomorrow's print edition of Cancer Research.
The paper builds on decades of research by study co-senior author Paul B. Fisher, M.Ph., Ph.D., a member of Massey's Cancer Biology research program, who discovered a protein called IL-24 that attacks a variety of cancers in several different ways.
In this latest study, Fisher teamed up with his colleague Xiang-Yang (Shawn) Wang, Ph.D., who co-leads the Developmental Therapeutics research program at Massey, to deliver the gene coding for IL-24, which is called MDA-7, to solid tumors using T cells.
"I think the beauty of what we've been involved in is that it expands the scope of immunotherapy," said Fisher, professor and chair of the Department of Human and Molecular Genetics at the VCU School of Medicine, director of the VCU Institute of Molecular Medicine (VIMM) and Thelma Newmeyer Corman Endowed Chair in Oncology Research. "Our approach is less dependent on cancer cells expressing something specific to target."
After all, this isn't the first time T cells have been engineered for cancer immunotherapy. FDA-approved chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell therapy - which is designed to destroy cancer cells expressing specific surface molecules - has shown tremendous success for treating advanced cancers of the blood and lymphatic systems.
But CAR-T has made limited progress on solid tumors, such as prostate cancer or melanoma, because the cells that make up those tumors aren't all the same, which blocks the engineered T cells from recognizing and attacking.
Wang and Fisher armed T cells with MDA-7/IL-24 to target cancer more broadly.
"Engineering T cells to produce MDA-7/IL-24 allows killing of cancer cells regardless of their expression of target molecules. This will help prevent cancer cells from escaping immune attack," said Wang, who is also a professor of human and molecular genetics at VCU, associate director of immunology in the VIMM and holds the Harry and Judy Wason Distinguished Professorship at Massey.
At the sub-cellular level, MDA-7/IL-24 binds to receptors on the surface of cells and instructs them to make and release more copies of the MDA-7/IL-24 protein. If the cell is normal, the protein is simply secreted and no damage occurs. But if the cell is cancerous, MDA-7/IL-24 causes oxidative stress damage and ultimately cell death, not only within the primary tumor but also among its distant metastases - the cause of death in 90% of patients.
As a result of this process, the immune system generates memory T cells that can theoretically kill the tumor if it ever comes back. At the whole tumor level, IL-24 also blocks blood vessel formation, starving tumors of the nutrients so badly needed to sustain their unchecked growth.
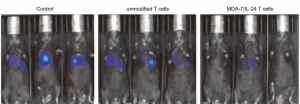
In mice with prostate cancer, melanoma or other cancer metastases, MDA-7/IL-24-expressing T cells slowed or stopped cancer progression better than unmodified T cells.
The researchers also discovered that arming T cells with MDA-7/IL-24 allowed them to survive better and multiply in the tumor microenvironment - the space right around the cancerous mass.
"The tumor site is often very hostile to immune cells," Wang said. "We discovered that MDA-7/IL-24 can help T cells to proliferate and outnumber cancer cells."
In the clinic, this approach would involve extracting the patient's own T cells from tumor samples, genetically engineering them to express MDA-7/IL-24, growing millions of copies of the cells in the lab and finally transplanting them back into the patient. With federally-mandated manufacturing standards, the procedure is generally safe and minimally invasive. CAR-T cells could also be engineered to express MDA-7/IL-24.
To be most effective, MDA-7/IL-24 T cells would likely be used in conjunction with other therapies.
Although it's never easy bringing a technology from the bench to the bedside, Fisher is optimistic that much of the groundwork has already been laid.
Clinical trials using different methods of delivering IL-24 are already underway for several cancers. A phase 1 trial using an adenovirus - similar to the common cold - to deliver MDA-7/IL24 to the tumor demonstrated about 44% efficacy against multiple forms of cancer and generally proved non-toxic.
"I think we have a head start and a running ramp that could be really accelerated," Fisher said.
Together, Wang and Fisher recently secured a grant from the National Cancer Institute to optimize their technology for the treatment of solid tumors and cancer metastases, in anticipation of future human trials.
INFORMATION:
Funding for this project was provided by the Department of Defense Prostate Cancer Research Program (grants W81XWH-11-1-0481 and W81XWH-13-1-0162), the National Foundation for Cancer Research, the National Cancer Institute (grants R01CA229812, R01CA099326 and R01CA259599), VCU Massey Cancer Center Research Development Funds and an NCI Cancer Center Support Grant to VCU Massey Cancer Center (grant P30CA16059).
Additional authors on the study include Zheng Liu, Ph.D., Xiaofei Yu, Ph.D., Anjan Pradhan, Ph.D., Xia Li, Ph.D., Yanxia Ning, M.D., Shixian Chen, M.D., and Wenjie Liu, Ph.D., of the VCU School of Medicine; and Chunqing Guo, Ph.D., Swadesh Das, Ph.D., Jolene Windle, Ph.D., Harry Bear, M.D., Ph.D., and Masoud Manjili, Ph.D., D.V.M., of the VCU School of Medicine and VCU Massey Cancer Center.
Boulder, Colo., USA: GSA's dynamic online journal, Geosphere, posts articles online regularly. Locations and topics studied this month include the Central Anatolian Plateau; the Southern Rocky Mountain Volcanic Field; petrogenesis in the Grand Canyon; and the evolution of the Portland and Tualatin forearc basins, Oregon.
A physical and chemical sedimentary record of Laramide tectonic shifts in the Cretaceous-Paleogene San Juan Basin, New Mexico, USA
Kevin M. Hobbs; Peter J. Fawcett
Abstract: Fluvial siliciclastic rocks bracketing the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) boundary ...
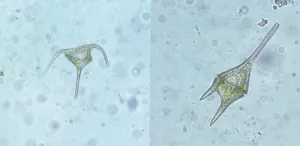
The genome of single-celled plankton, known as dinoflagellates, is organized in an incredibly strange and unusual way, according to new research. The findings lay the groundwork for further investigation into these important marine organisms and dramatically expand our picture of what a eukaryotic genome can look like.
Researchers from KAUST, the U.S. and Germany have investigated the genomic organization of the coral-symbiont dinoflagellate Symbiodinium microadriaticum. The S. microadriaticum genome had already been sequenced and assembled into segments known as scaffolds but lacked a chromosome-level assembly.
The team used a technique known as Hi-C to detect interactions in the dinoflagellate's ...
WILMINGTON, Del. (April 30, 2021) - Social, economic, and demographic factors that can influence health did not affect families' acceptance of telehealth for their children's cardiac care during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a study presented at the Pediatric Academic Society 2021 Virtual Meeting. The study, by research team members at the Nemours Children's Health System, suggests that telehealth is a feasible tool for families regardless of household income, language, or insurance type.
"When we saw that the use of telehealth would be necessary for maintaining children's cardiac care ...
Key takeaways
The basis of the ACS Quality Verification Program rests on 12 standards; all of which are being reviewed in the medical literature to demonstrate evidence for the program.
Five principles key in on the role of data surveillance, standardized process, and systems; all are interrelated.
The most robust evidence has been identified around the standards for data and use of data.
CHICAGO (April 30, 2021): Evidence from the medical literature that contributes to adopting a new practice into clinical care is integral for surgical quality improvement. Part II of ...
A single dose of vaccine boosts protection against SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus variants, but only in those with previous COVID-19, a study has found.
In those who have not previously been infected and have so far only received one dose of vaccine the immune response to variants of concern may be insufficient.
The findings, published today in the journal Science and led by researchers at Imperial College London, Queen Mary University of London and University College London, looked at immune responses in UK healthcare workers at Barts and Royal Free hospitals following their first dose of the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine.*
They ...
WESTMINSTER, Colorado - April 30, 2021 - Palmer amaranth is a hard-to-control noxious weed that can significantly reduce crop yields. It was first introduced in Minnesota in 2016 through contaminated seed mixes used for conservation plantings.
Fortunately, Minnesota regulators were prepared. They had already declared Palmer amaranth a prohibited noxious weed in 2015, and they quickly added the weed's seed to their prohibited list by emergency order. As a result, they were able to take prompt action to identify and eradicate newly emerged infestations.
A research paper featured in the journal Weed Technology documents Minnesota's experiences, including the timeline ...
For many of us, adding salt to a meal is a perfectly normal thing to do. We don't really think about it. But actually, we should. As well as raising our blood pressure, too much salt can severely disrupt the energy balance in immune cells and stop them from working properly.
Back in 2015, the research group led by Professor Dominik Müller of the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC) and the Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC) found that elevated sodium concentrations in the blood affect both ...
The detection of the axion would mark a key episode in the history of science. This hypothetical particle could resolve two fundamental problems of Modern Physics at the same time: the problema of Charge and Parity in the strong interaction, and the mystery of dark matter. However, in spite of the high scientific interest in finding it, the search at high radio frequency -above 6 GHz- has been almost left aside for the lack of the high sensitivity technology which could be built at reasonable cost. Until now.
The Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) will participate ...
A research team at the University of Cologne has discovered previously undescribed bacteria in amoebae that are related to Legionella and may even cause disease. The researchers from Professor Dr Michael Bonkowski's working group at the Institute of Zoology have named one of the newly discovered bacteria 'Pokemonas' because they live in spherical amoebae, comparable to Pokémon in the video game, which are caught in balls. The results of their research have been published in the journal Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.
Bacteria of the order Legionellales have long ...
Histology is the study of biological tissues at a microscopic level. Also called microscopic anatomy, histology is widely used to provide diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. For example, tissue samples obtained during surgery might help to determine whether further surgical action is needed, and further surgery may be avoided if a diagnosis can be rapidly obtained during an operation.
Traditional methods in histopathology are generally limited to thin specimens and require chemical processing of the tissue to provide sufficiently high contrast for imaging, which slows the process. A recent advance in histopathology eliminates the ...