(Press-News.org) A year into the COVID-19 pandemic, mass vaccinations have begun to raise the tantalizing prospect of herd immunity that eventually curtails or halts the spread of SARS-CoV-2. But what if herd immunity is never fully achieved - or if the mutating virus gives rise to hyper-virulent variants that diminish the benefits of vaccination?
Those questions underscore the need for effective treatments for people who continue to fall ill with the coronavirus. While a few existing drugs show some benefit, there's a pressing need to find new therapeutics.
Led by The University of New Mexico's Tudor Oprea, MD, PhD, scientists have created a unique tool to help drug researchers quickly identify molecules capable of disarming the virus before it invades human cells or disabling it in the early stages of the infection.
In a paper published this week in Nature Machine Intelligence, the researchers introduced REDIAL-2020, an open source online suite of computational models that will help scientists rapidly screen small molecules for their potential COVID-fighting properties.
"To some extent this replaces (laboratory) experiments, says Oprea, chief of the Translational Informatics Division in the UNM School of Medicine. "It narrows the field of what people need to focus on. That's why we placed it online for everyone to use."
Oprea's team at UNM and another group at the University of Texas at El Paso led by Suman Sirimulla, PhD, started work on the REDIAL-2020 tool last spring after scientists at the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) released data from their own COVID drug repurposing studies.
"Becoming aware of this, I was like, 'Wait a minute, there's enough data here for us to build solid machine learning models,'" Oprea says. The results from NCATS laboratory assays gauged each molecule's ability to inhibit viral entry, infectivity and reproduction, such as the cytopathic effect - the ability to protect a cell from being killed by the virus.
Biomedicine researchers often tend to focus on the positive findings from their studies, but in this case, the NCATS scientists also reported which molecules had no virus-fighting effects. The inclusion of negative data actually enhances the accuracy of machine learning, Oprea says.
"The idea was that we identify molecules that fit the perfect profile," he says. "You want to find molecules that do all these things and don't do the things that we don't want them to do."
The coronavirus is a wily adversary, Oprea says. "I don't think there is a drug that will fit everything to a T." Instead, researchers will likely devise a multi-drug cocktail that attacks the virus on multiple fronts. "It goes back to the one-two punch," he says.
REDIAL-2020 is based on machine learning algorithms capable of rapidly processing huge amounts of data and teasing out hidden patterns that might not be perceivable by a human researcher. Oprea's team validated the machine learning predictions based on the NCATS data by comparing them against the known effects of approved drugs in UNM's DrugCentral database.
In principle, this computational workflow is flexible and could be trained to evaluate compounds against other pathogens, as well as evaluate chemicals that have not yet been approved for human use, Oprea says.
"Our main intent remains drug repurposing, but we're actually focusing on any small molecule," he says. "It doesn't have to be an approved drug. Anyone who tests their molecule could come up with something important."
INFORMATION:
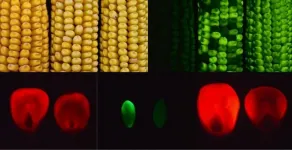
An abnormal build up of carbohydrates -- sugars and starches -- in the kernels and leaves of a mutant line of corn can be traced to one misregulated gene, and that discovery offers clues about how the plant deals with stress.
That is the conclusion of Penn State researchers whose previous study discovered the Maize ufo1 gene responsible for creating the mutant corn line. They now are assessing its effects and potential for inclusion in breeding new lines of corn better able to thrive in a warming world. The finding of higher sugar levels in plant tissues in their latest study is just ...
May 3, 2021
Using social values for profit cheapens them, a new study cautions.
Toronto - Businesses sometimes align themselves with important values such as a clean environment, feminism, or racial justice, thinking it's a win-win: the value gets boosted along with the company's bottom line.
But be careful, warns new research from the University of Toronto's Rotman School of Management.
Using these values primarily for self-interested purposes such as profit or reputation can ultimately undermine their special status and erode people's commitment to them.
"It sets a different norm for appropriate use of the value," says research author Rachel Ruttan, an assistant professor of organizational behaviour and human resources at the Rotman School, who ...
When it comes to batteries, lithium-ion are the best we have as far as energy density and convenience.
For now.
The Washington University in St. Louis lab of Peng Bai, assistant professor in the Department of Energy, Environmental & Chemical Engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering, has developed a stable sodium ion battery that is highly efficient, will be less expensive to make and is significantly smaller than a traditional lithium ion battery due to the elimination of a once-necessary feature.
"We've found that the minimal is maximum," ...
Hydraulic fracturing to extract trapped fossil fuels can trigger earthquakes. Most are so small or far from homes and infrastructure that they may go unnoticed; others can rattle windows, sway light fixtures and jolt people from sleep; some have damaged buildings.
Stanford University geophysicists have simulated and mapped the risk of noticeable shaking and possible building damage from earthquakes caused by hydraulic fracturing at all potential fracking sites across the Eagle Ford shale formation in Texas, which has hosted some of the largest fracking-triggered earthquakes in the United States.
Published ...
ATLANTA--An influenza vaccine that is made of nanoparticles and administered through the nose enhances the body's immune response to influenza virus infection and offers broad protection against different viral strains, according to researchers in the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University.
Recurring seasonal flu epidemics and potential pandemics are among the most severe threats to public health. Current seasonal influenza vaccines induce strain-specific immunity and are less effective against mismatched strains. Broadly protective influenza vaccines are urgently needed.
Intranasal vaccines are a promising strategy for combatting ...
BOSTON -- For the first time, researchers have shown how Mullerian inhibiting substance (MIS), also known as anti-Mullerian hormone, a key reproductive hormone, suppresses follicle development and prevents ovulation in females. "Understanding the mechanism of follicle development by MIS opens the door to creating novel approaches to contraception, preserving the eggs of young girls undergoing chemotherapy, enhancing the success of fertility treatment, and potentially delaying menopause," says David Pépin, PhD, an associate molecular biologist in the Department of Surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and senior author ...
Even under the most optimistic scenarios, most of the coral reef ecosystems on our planet - whether in Australia, the Maldives or the Caribbean - will have disappeared or be in very bad shape by the end of this century. That's because global warming is pushing ocean temperatures above the limit that single-cell algae, which are corals' main allies, can withstand. These algae live inside coral tissue for protection and, in exchange, provide corals with essential nutrients produced through photosynthesis. Because the algae contain a variety of pigments and therefore give coral reefs their famous colors, if they are lost the corals turn white, which is known as coral bleaching. But in spite of the real threat caused by global warming, corals in the ...
Abu Dhabi, UAE, May 3, 2021: Researchers from NYU Abu Dhabi's Center for Genomics and Systems Biology have successfully sequenced the genome of previously extinct date palm varieties that lived more than 2,000 years ago. They did so using date palm seeds that were recovered from archaeological sites in the southern Levant region and radiocarbon-dated from the 4th century BCE to the 2nd century CE. The seeds were germinated to yield viable, new plants. The researchers conducted whole genome sequencing of these germinated ancient samples and used this genome data to examine the genetics of these previously extinct Judean date palms. This study marks the first time researchers have sequenced the genomes of plants ...
First-of-its-kind model replicates human alveolar lung tissue
Allows researchers to study effects of COVID-19 on cell growth and development
Provides insight as to how various drugs impact viral spread
Globally, lung failure is one of the leading causes of death. Many conditions can affect and damage the lungs, including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, influenza, pneumonia, and, most recently, COVID-19. To better understand respiratory diseases and develop new drugs faster, investigators from Brigham and Women's Hospital designed a ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. --A new study found overlooked tsunami hazards related to undersea, near-shore strike-slip faults, especially for coastal cities adjacent to faults that traverse inland bays. Several areas around the world may fall into this category, including the San Francisco Bay area, Izmit Bay in Turkey and the Gulf of Al-Aqaba in Egypt.
The study led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign civil and environmental engineering professor Ahmed Elbanna and professor Ares Rosakis of the California Institute of Technology used the Blue Waters supercomputer at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications to model ...