Alzheimer's study: A Mediterranean diet might protect against memory loss and dementia
2021-05-06
(Press-News.org) In Alzheimer's disease, neurons in the brain die. Largely responsible for the death of neurons are certain protein deposits in the brains of affected individuals: So-called beta-amyloid proteins, which form clumps (plaques) between neurons, and tau proteins, which stick together the inside of neurons. The causes of these deposits are as yet unclear. In addition, a rapidly progressive atrophy, i.e. a shrinking of the brain volume, can be observed in affected persons. Alzheimer's symptoms such as memory loss, disorientation, agitation and challenging behavior are the consequences.
Scientists at the DZNE led by Prof. Michael Wagner, head of a research group at the DZNE and senior psychologist at the memory clinic of the University Hospital Bonn, have now found in a study that a regular Mediterranean-like dietary pattern with relatively more intake of vegetables, legumes, fruit, cereals, fish and monounsaturated fatty acids, such as from olive oil, may protect against protein deposits in the brain and brain atrophy. This diet has a low intake of dairy products, red meat and saturated fatty acids.
A nationwide study
A total of 512 subjects with an average age of around seventy years took part in the study. 169 of them were cognitively healthy, while 343 were identified as having a higher risk of developing Alzheimer's disease - due to subjective memory impairment, mild cognitive impairment that is the precursor to dementia, or first-degree relationship with patients diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease. The nutrition study was funded by the Diet-Body-Brain competence cluster of the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and took place as part of the so-called DELCODE study of the DZNE, which does nationwide research on the early phase of Alzheimer's disease - that period before pronounced symptoms appear.
"People in the second half of life have constant eating habits. We analyzed whether the study participants regularly eat a Mediterranean diet - and whether this might have an impact on brain health ", said Prof. Michael Wagner. The participants first filled out a questionnaire in which they indicated which portions of 148 different foods they had eaten in the past months. Those who frequently ate healthy foods typical of the Mediterranean diet, such as fish, vegetables and fruit, and only occasionally consumed foods such as red meat, scored highly on a scale.
An extensive test series
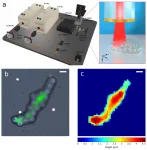
The scientists then investigated brain atrophy: they performed brain scans with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners to determine brain volume. In addition, all subjects underwent various neuropsychological tests in which cognitive abilities such as memory functions were examined. The research team also looked at biomarker levels (measured values) for amyloid beta proteins and tau proteins in the so-called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of 226 subjects.
The researchers, led by Michael Wagner, found that those who ate an unhealthy diet had more pathological levels of these biomarkers in the cerebrospinal fluid than those who regularly ate a Mediterranean-like diet. In the memory tests, the participants who did not adhere to the Mediterranean diet also performed worse than those who regularly ate fish and vegetables. "There was also a significant positive correlation between a closer adherence to a Mediterranean-like diet and a higher volume of the hippocampus. The hippocampus is an area of the brain that is considered the control center of memory. It shrinks early and severely in Alzheimer's disease," explained Tommaso Ballarini, PhD, postdoctoral fellow in Michael Wagner's research group and lead author of the study.
Continuation of nutrition study is planned
"It is possible that the Mediterranean diet protects the brain from protein deposits and brain atrophy that can cause memory loss and dementia. Our study hints at this," Ballarini said. "But the biological mechanism underlying this will have to be clarified in future studies." As a next step, Ballarini and Wagner now plan to re-examine the same study participants in four to five years to explore how their nutrition - Mediterranean-like or unhealthy - affects brain aging over time.
INFORMATION:
Original publication
Mediterranean Diet, Alzheimer Disease Biomarkers and Brain Atrophy in Old Age, Ballarini et al., Neurology® (May 2021), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000012067,
URL: https://n.neurology.org/lookup/doi/10.1212/WNL.0000000000012067
About Deutsches Zentrum für Neurodegenerative Erkrankungen (German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases, DZNE)
The DZNE investigates all aspects of neurodegenerative diseases (such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's and Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) in order to develop novel approaches of prevention, treatment, and health care. It is comprised of ten sites across Germany and cooperates closely with universities, university hospitals, and other research institutions on a national and international level. The DZNE is a member of the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centers. Website: http://www.dzne.de/en
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
Determining safe yet effective drug dosages for children is an ongoing challenge for pharmaceutical companies and medical doctors alike. A new drug is usually first tested on adults, and results from these trials are used to select doses for pediatric trials. The underlying assumption is typically that children are like adults, just smaller, which often holds true, but may also overlook differences that arise from the fact that children's organs are still developing.
Compounding the problem, pediatric trials don't always shed light on other differences that can affect recommendations for drug doses. There are many factors that limit children's participation in drug trials - for instance, some diseases simply ...
2021-05-06
AURORA, Colo. (May 6, 2021) - Scientists examining the remains of 36 bubonic plague victims from a 16th century mass grave in Germany have found the first evidence that evolutionary adaptive processes, driven by the disease, may have conferred immunity on later generations of people from the region.
"We found that innate immune markers increased in frequency in modern people from the town compared to plague victims," said the study's joint-senior author Paul Norman, PhD, associate professor in the Division of Personalized Medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. "This suggests these markers might have evolved to resist the plague."
The study, done in conjunction with the Max Planck Institute in Germany, was published online Thursday in the journal Molecular ...
2021-05-06
Ultrasound is an indispensable tool for the life sciences and various industrial applications due to its non-destructive, high contrast, and high resolution qualities. A persistent challenge over the years has been how to increase the resolution of an acoustic endoscope without drastically increasing the footprint of the probe, or risking the robustness of the ultrasonic transducer. In recent years, a host of all-optical ultrasonic imaging techniques have emerged - which generally utilise pulsed lasers and optical cavities to excite and detect ultrasound waves - without sacrificing device footprint, sensitivity, or the integrity of the transducer. Thus far these powerful techniques have achieved imaging resolutions on microscopic-mesoscopic length ...
2021-05-06
Researchers at the University of Eastern Finland have discovered previously unknown non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) involved in regulating the gene expression of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF), the master regulators of angiogenesis. The study, conducted by the research groups of Associate Professor Minna Kaikkonen-Määttä and Academy Professor Seppo Ylä-Herttuala, provides a better understanding of the complex interplay of ncRNAs with gene regulation, which might open up novel therapeutic approaches in the future. The results were published in the Molecular and Cellular Biology Journal.
Over the past years, the development of next generation ...
2021-05-06
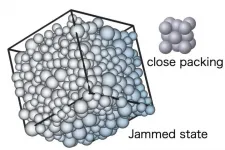
Researchers at Chinese Academy of Science and Osaka University show that, unlike the crystalline close packing of spheres, random close packing or jamming of spheres in a container can take place in a broad range of densities and anisotropies. Furthermore, they show that such diverse jammed states are all just marginally stable and exhibit common universal critical properties.
Osaka, Japan - Scientists at the theoretical institutes, Chinese Academy of Science and Cybermedia Center at Osaka University performed extensive computer simulations to generate and examine random packing of spheres. They show that the "jamming" ...
2021-05-06
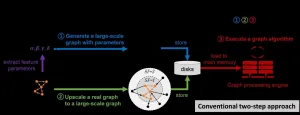
A KAIST research team has developed a new technology that enables to process a large-scale graph algorithm without storing the graph in the main memory or on disks. Named as T-GPS (Trillion-scale Graph Processing Simulation) by the developer Professor Min-Soo Kim from the School of Computing at KAIST, it can process a graph with one trillion edges using a single computer.
Graphs are widely used to represent and analyze real-world objects in many domains such as social networks, business intelligence, biology, and neuroscience. As the number of graph applications increases rapidly, developing and testing new graph algorithms is becoming more important than ever before. Nowadays, many industrial ...
2021-05-06
Trust, safety and security are the most important factors affecting passengers' attitudes towards self-driving cars. Younger people felt their personal security to be significantly better than older people.
The findings are from a Finnish study into passengers' attitudes towards, and experiences of, self-driving cars. The study is also the first in the world to examine passengers' experiences of self-driving cars in winter conditions.
The findings were published in Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour. The study was carried out in collaboration between the University of Eastern Finland and Tampere University.
Self-driving cars face huge expectations in Europe and the United States, which is why passengers' ...
2021-05-06
A new study has shown that most patients discharged from hospital after experiencing severe COVID-19 infection appear to return to full health, although up to a third do still have evidence of effects upon the lungs one year on.
COVID-19 has infected millions of people worldwide. People are most commonly hospitalised for COVID-19 infection when it affects the lungs - termed COVID-19 pneumonia. Whilst significant progress has been made in understanding and treating acute COVID-19 pneumonia, very little is understood about how long it takes for patients to fully recover and whether changes within the lungs persist.
In this new study, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, researchers from the University of Southampton worked with collaborators ...
2021-05-06
Children born in December are almost twice as likely to be diagnosed with a learning disorder as those born in January. ADHD was found not to affect the association between month of birth and the likelihood of a learning disability diagnosis.
The new, register based study included children born in Finland between 1996 and 2002. Of nearly 400,000 children, 3,000 were diagnosed with a specific learning disorder, for example, in reading, writing or math by the age of ten.
"We were familiar with the effects of the relative age to the general school performance, but there were no previous studies on the association between clinically diagnosed specific learning disorders and relative age, which is why we wanted to study it," says Doctoral Candidate, MD Bianca ...
2021-05-06
Research led by the University of Liverpool, in partnership with Johnson Matthey PLC and Loughborough University is making significant progress in the development of stable and practical electrolytes for lithium-oxygen batteries.
The lithium-oxygen (Li-O2) battery (or lithium-air battery), consisting of Li-metal and a porous conductive framework as its electrode's releases energy from the reaction of oxygen from the air and lithium. The technology is in its infancy, but in theory could provide much greater energy storage than the conventional lithium-ion battery.
In a paper published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials, Professor Laurence Hardwick from the University of Liverpool's Stephenson ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Alzheimer's study: A Mediterranean diet might protect against memory loss and dementia