Quantum mechanics paves the way for more stable organic solar cells
2021-05-11
(Press-News.org) Quantum mechanics can be used to create more stable and more easily produced organic solar cells. These are the findings of new research from the University of Gothenburg.
Organic solar cells have many advantages compared with traditional silicon-based solar cells. They can be manufactured cheaply at a large scale using printing presses, and they are light, malleable and flexible. The problem is that today's organic solar cells are not as stable and effective as silicon-based solar cells. In a new study, a research group has taken on this problem and found a way that can lead to more cost-effective solar cell technology.
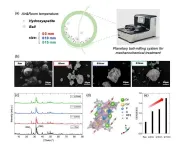
"There are excellent opportunities for utilising quantum efficiencies to change different chemical and material characteristics. In this study, we present a method that makes it possible to increase diffusion of energy in organic materials. This allows us to create organic solar cells with simpler structure," says Karl Börjesson, professor of physical chemistry at the University of Gothenburg and the main author of the study.
Basically, this is about making sure the energy in the solar cells is effectively transferred to the right place. Organic solar cells contain two materials, and the absorbed energy from the sun needs to be diffused - to travel - to the interface between the materials. But diffusion is an ineffective process since the energy travels slowly and risks being lost as heat before it reaches this interface. The solution has been to blend the two materials in solar cells to reduce the distance and so the energy reaches the interface more quickly. Unfortunately, this also leads to the solar cells not being in thermodynamic equilibrium, making design less durable over time than it could be.
The researchers show that the new method allows the energy to be transferred over a longer distance, which means that the complicated blending of materials in solar cells can be avoided. The key behind the method is quantum effects, where light and material are combined into hybrid light-matter states.
"When we couple light and matter strongly, the energy is spread out over the entire system. If the system - as in this case - consists of multiple materials, the energy can be channelled to the interface. We show in the study that the energy travels faster to the interfaces when the materials are strongly coupled. This means that the materials in solar cells do not need to be physically blended since they are blended at the quantum level. This also leads to the system being in thermodynamic equilibrium," says Karl Börjesson.
According to Börjesson, the discovery can influence how organic solar cells are manufactured, since it becomes possible to increase their durability while the solar cells can be made with a simple layered structure. He also notes that the research is really an outgrowth of a concept already found in nature.
"Nature uses strong coupling between molecules to effectively transfer solar energy in photosynthesis. In principle, we have shown that the same basic concept can be applied to organic solar cells."
INFORMATION:
Contact:
Karl Börjesson, professor of physical chemistry at the University of Gothenburg, Department of Chemistry and Molecular Biology, phone: +46 (0)31-786 90 99, +46 (0)766-22 90 99, email: karl.borjesson@gu.se
About the research:
Title: Polariton-assisted excitation energy channeling in organic heterojunctions
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-22183-3
Scientific journal: Nature Communications
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-11
The Sturtian Snowball Earth glaciation (717~660 million years ago) represents the most severe icehouse climate in Earth's history. Geological evidence indicates that, during this glaciation, ice sheets extended to low latitudes, and model simulations suggest global frozen ocean as well as a prolonged shut-down of the hydrological cycles. The Snowball Earth hypothesis poses that the Sturtian global glaciation is directly triggered by intense continental weathering that scavenges atmospheric CO2, while the global frozen condition is terminated by ...
2021-05-11
One of the most basic structural aspects of relativistic spacetime is the description of how time and distances are altered by motion. The theory of special relativity describes a spacetime framework for linear constant motion in which time dilates and lengths contract in response to motion. This framework is described by the Lorentz transformation, which encompasses mathematical formulas that describe how time and distance are altered between moving reference frames. The Lorentz transformation also describes how a stationary observer views time in the moving frame to be offset with distance. ...
2021-05-11
One of the most prominent evils of rapid industrialization has been the emission of toxic pollutants into the surrounding biosphere, with often disastrous consequences for human beings. Several industrial processes, such as chemical manufacturing and printing, along with facilities such as power plants emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that are known to be cancer-causing and raise an important environmental issue in need of a solution. Traditionally, VOCs are controlled via a process called "catalytic oxidation," in which they are converted into benign materials in the presence of noble metal (e.g. gold, silver, and platinum) ...
2021-05-11
A new study from the University of Surrey has revealed 'real world' factors that influence people's interest in adopting a dietary pattern called time-restricted feeding.
According to NHS England, 67 per cent of men and 60 per cent of women in the UK are overweight or obese - with more than 11,000 yearly hospital admissions directly attributable to obesity.
Time-restricted feeding, which is a type of intermittent fasting, is the practice of restricting the time between the first and last food intake each day - therefore prolonging the daily fasting period.
In a study published by the ...
2021-05-11
A new study from the University of Portsmouth calls for further government oversight to curb potential illegal activity through these zones.
This study demonstrates the attractive trading advantages offered by freeports to enable enterprise and innovation. Eight new freeports in England are due to enter operation in late 2021, which are hoped to drive investment, economic opportunities and growth to those regions.
However, researchers also advise that stronger regulation is needed to prevent Freeports being abused for money-laundering and tax-evasion purposes. The study, ...
2021-05-11
Young children in deprived areas see nature and outdoor spaces as being associated with "happy places", according to a new study published in the journal Child Indicators Research.
Researchers Dr Nicola Walshe and Dr Zoe Moula from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) asked 91 children aged seven and eight from two primary schools in areas of relatively high deprivation in the East of England to draw their happy place, before engaging them in group discussions about how they perceive their own wellbeing.
More than half of the children created drawings that included aspects of nature and outdoor spaces, such as trees, grass, parks, gardens, lakes, rivers, outdoor playgrounds, rainbows or sunlight. Trees, ...
2021-05-11
It was commonly assumed that wildlife products are exported from low-income countries to meet the demand of consumers in wealthy economies, and therefore, a widening wealth gap may drive up the volume of global trade and endanger wildlife.
Recently, a research team co-led by Research Division for Ecology and Biodiversity (E&B), Faculty of Science, the University of Hong Kong (HKU) and the Science Unit (SU) of Lingnan University (LU) corroborated this premise by analysing global wildlife trade databases. The research team includes Dr Jia Huan LIEW, Research Assistant Professor of SU, ...
2021-05-11
YouTube channels run by zoos focus on entertainment over education, according to a new study.
The videos also focus disproportionately on mammals, rather than reflecting the diversity of zoos' animals.
Conservation was the focus of just 3% of zoo videos in the study - but it found that conservation content in videos is gradually increasing.
The study evaluated the most recent and most-viewed videos, so the findings partly reflect the public's preference for certain species and content.
Of the animals that appeared in zoos' most-viewed videos, the top nine were mammals - with giant pandas ...
2021-05-11
Teamwork is becoming increasingly common in modern science. In this context, the effect of different characteristics of a team on its research performance has been studied extensively. Various factors such as team size, number of countries involved, universities, disciplines, and workload distribution have been found to have a significant contribution on the paper's role in advancing science.
The question of how the freshness of the team influences its research performance, however, has not been studied systematically. A research team may consist ...
2021-05-11
Most of us have imagined how free it would feel to float around, like an astronaut, in conditions of reduced gravity. But have you ever considered what the effects of reduced gravity might have on muscles? Gravity is a constant force on Earth which all living creatures have evolved to rely on and adapt to. Space exploration has brought about many scientific and technological advances, yet manned spaceflights come at a cost to astronauts, including reduced skeletal muscle mass and strength.
Conventional studies investigating the effects of reduced gravity on muscle mass and function have used a ground ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Quantum mechanics paves the way for more stable organic solar cells