INFORMATION:
Space-based system can provide seismic monitoring for large earthquakes and tsunamis
2021-05-11
(Press-News.org) Researchers have developed a global earthquake monitoring system that uses the Global Navigational Satellite System (GNSS) to measure crustal deformation.
The monitoring system within seconds can rapidly assess earthquake magnitude and fault slip distribution for earthquakes of magnitude 7.0 and larger, making it a potentially valuable tool in earthquake and tsunami early warning for these damaging events, Central Washington University geophysicist Timothy Melbourne and colleagues report in the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America.
GNSS can potentially characterize a large earthquake much more rapidly than the global seismic network, offering more time for evacuations, drop-and-cover and automatic shut-down of essential infrastructure. "The imperative for doing it quickly is really about saving lives," said Melbourne.
GNSS systems consist of Earth-orbiting satellites that send signals to receiver stations on Earth. The signals are used to determine the receivers' exact locations through time. Earthquakes move and deform the Earth's crust underneath the receivers, so changes in their locations after an earthquake can be used to monitor and characterize the ruptures.
Seismic monitoring by GNSS is a "very blunt tool," compared to seismometer-based networks capable of detecting minute seismic waves, Melbourne said.
A top-of-the-line seismometer is remarkably sensitive, he noted, able to detect seismic wave velocities as small as tens of nanometers per second.
GNSS is more coarse, only detecting displacements of centimeters or larger.
During a big earthquake, however, there is a trade-off between sensitivity and speed. Local seismic networks can be swamped with data during a large, complex event such as the 2016 magnitude 7.8 Kaikoura earthquake in New Zealand, where multiple faults are involved and waves from the initial event reverberate through the crust. To accurately determine magnitude and fault slip distribution, seismologists usually have to wait for the seismic wave data to reach distant stations before it can be accurately characterized, which involves tens of minutes of delay while the waves propagate across the planet.
The global system created by Melbourne and his colleagues is the first of its kind. It takes in raw GNSS data acquired at any Internet-connected receiver on Earth, positions these data, and then re-transmits the positioned data back to any Internet-connected device, within a second.
The researchers assessed their system over one typical week, using data from 1270 receiver stations across the world. They found that the average time it took data to travel from a receiver to the processing center at Central Washington University was about half a second--from anywhere in the world. It took an average of about one-200th of a second to convert that data into estimates of GNSS position.
This means that the GNSS global monitoring system can detect changes well before the earthquake itself is done rupturing, since it can take tens of seconds--or even minutes for the largest earthquakes--"for the fault to unzip and radiate all that energy into the planet," Melbourne said.
The speed of a global GNSS seismic monitoring system might be even more important for tsunami warnings, he noted. At the moment, an international monitoring program uses data from a global seismic network to determine an earthquake magnitude, combined with data from global tide gauges and buoys that detect a tsunami wave in the open ocean, to determine whether a tsunami advisory should be sent to the public.
The seismic network could take 15 minutes or more to determine the magnitude of an earthquake that causes a tsunami, said Melbourne, and the tidal gauges and buoys could take up to an hour to deliver data, depending on their proximity to the earthquake. GNSS receivers, on the other hand, could characterize an earthquake in tens of seconds with sufficient nearby stations.
"The real power of the GNSS for the tsunami is buying more time and greater accuracy from the get-go for the warnings that come out," Melbourne said.
GNSS receiver stations are proliferating around the world as more people use them, especially for surveying or monitoring in mining and construction. But the global GNSS monitoring system depends on open-source data, which has not expanded at the same rate. In some countries, data are sold to recover the costs of constructing and maintaining the receivers, Melbourne said, making their operators reluctant to make the data freely available.
"Part of what I do is trying to get countries in seismically active areas to open up their data sets for hazard mitigation purposes," said Melbourne.
For instance, GNSS operators in New Zealand, Ecuador, Chile and elsewhere partner with Melbourne's group, benefiting from the decade of work that the team has put into their GNSS positioning system. They send raw data from receivers in their countries to Central Washington, where Melbourne and colleagues position the data within a global reference frame and send it back within subseconds for further research and monitoring.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
COVID-19 alters gray matter volume in the brain, new study shows
2021-05-11
Covid-19 patients who receive oxygen therapy or experience fever show reduced gray matter volume in the frontal-temporal network of the brain, according to a new study led by researchers at Georgia State University and the Georgia Institute of Technology.
The study found lower gray matter volume in this brain region was associated with a higher level of disability among Covid-19 patients, even six months after hospital discharge.
Gray matter is vital for processing information in the brain and gray matter abnormality may affect how well neurons function and communicate. The study, published in the May 2021 issue of Neurobiology ...
Report: 'Safe System' approach could dramatically reduce road deaths while improving equity
2021-05-11
A new approach to road safety that relies on design and engineering principles--the "Safe System" approach--could lead to dramatic reductions in vehicle-related deaths and injuries if implemented in the U.S., according to a report from a consortium of experts convened by researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and the Institute of Transportation Engineers.
The Safe System approach engineers road systems so that they are safe when used intuitively, the way people tend to use them. A Safe System minimizes the chances for mistakes by drivers, pedestrians, and bicyclists, and reduces the intensity ...
A personalized anti-cancer vaccine that works in mice
2021-05-11
Marie-Claude Bourgeois-Daigneault and her team at the CRCHUM are using mice to show how a combination of peptides and oncolytic viruses, used as an adjuvant, can provide effective immunization against cancer.
In her laboratoryat the University of Montreal Hospital Research Centre (CRCHUM), Marie-Claude Bourgeois-Daigneault and a team of scientists usually modify viruses to make them specific to the cells of a tumour.
Once in the patient's body, these viruses, called oncolytic viruses, infect and specifically destroy the cancer cells without touching healthy cells. These viruses can even stimulate the immune system so that it is better armed to recognize and kill malignant cells. This is immunotherapy.
In a study published in Nature Communications, the scientific team at the University ...
Now is the time to think about reintroducing jaguars into the US
2021-05-11
NEW YORK (May 11, 2021) - A group of scientists say now is the time to talk about reintroducing jaguars (Panthera onca) into the U.S.
In a study published today in the journal Conservation Science and Practice, the authors provide a prospective framework for this effort and describe "righting a wrong" done to "America's Great Cat" in the Southwest more than 50 years ago. The big cats lived for hundreds of years in the central mountains of Arizona and New Mexico but were driven to local extinction by the mid-20th century, in part because of killing by government hunters.
Authors of the study include a diverse set ...
Meditative practice and spiritual wellbeing may preserve cognitive function in aging
2021-05-11
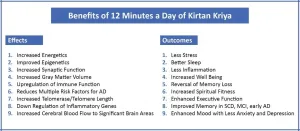
Amsterdam, May 11, 2021 - It is projected that up to 152 million people worldwide will be living with Alzheimer's disease (AD) by 2050. To date there are no drugs that have a substantial positive impact on either the prevention or reversal of cognitive decline. A growing body of evidence finds that targeting lifestyle and vascular risk factors have a beneficial effect on overall cognitive performance. A new review in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, published by IOS Press, examines research that finds spiritual fitness, a new concept in medicine that centers on psychological and spiritual wellbeing, and Kirtan Kriya, a simple 12-minute meditative practice, may reduce multiple risk factors for AD.
"The key point of this review is that making a commitment ...
Genetics: Biosynthesis pathway of a new DNA nucleobase elucidated
2021-05-11
DNA is composed of nucleobases represented by the letters A, T, G and C. They form the basis of the genetic code and are present in all living beings. But in a bacteriophage, another base, represented by the letter Z, exists. This exception, the only one observed to date, has long remained a mystery. Scientists from the Institut Pasteur and the CNRS, in collaboration with the CEA, have now elucidated the biosynthesis pathway of this base. This work has been published in the April 30th, 2021 issue of Science.
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule ...
NSU researcher part of team to sequence the genome of the leopard
2021-05-11
Study Take-Aways:
Different African populations were genetically interrelated suggesting abundant gene flow across Africa such that all African population should be considered together as single subspecies.
There appeared a striking genomic distance between leopards living in Asia vs. leopards in Africa.
Asian leopards are more genetically separated from African leopards than brown bear species are from polar bear species, the researchers found.
The two leopard groups actually diverged around the same time as Neanderthals split apart from modern humans.
The genetic differences between African and Asian leopards have been maintained ...
Heme is not just for Impossible Burgers
2021-05-11
It took an unlikely food innovation -- earth-friendly vegetarian patties, made to taste and "bleed" like the familiar meaty ones -- to make people aware of heme.
But heme is an essential part of proteins found in most life forms, from tiny bacteria to soy plants to the human body. Heme plays a crucial role in supplying cells with the energy needed to carry out chemical reactions.
In human cells, iron-containing heme is the essential cofactor of two types of molecules. One is the hemoglobin molecules that bind oxygen in the lungs and ferry it around the body. More than half ...
Simulating sneezes and coughs to show how COVID-19 spreads
2021-05-11
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- Two groups of researchers at Sandia National Laboratories have published papers on the droplets of liquid sprayed by coughs or sneezes and how far they can travel under different conditions.
Both teams used Sandia's decades of experience with advanced computer simulations studying how liquids and gases move for its nuclear stockpile stewardship mission.
Their findings reinforce the importance of wearing masks, maintaining social distancing, avoiding poorly ventilated indoor spaces and washing your hands frequently, especially with ...
Markedly poor physical functioning status of people experiencing homelessness
2021-05-11
Trinity study finds people homeless in their 20s, 30s and 40s are physically comparable to those housed in their 70s and 80s
A Trinity College study published today (Monday, 10th May 2021) demonstrates an extremely high burden of physical and mobility problems experienced by people who are homeless and were admitted for inpatient care to an acute hospital in Dublin. The study found that only one third of participants could climb a hospital stairs and there was a very common presentation of geriatric conditions such as frailty, falls and needing a mobility aid on a long term basis, despite a low median participant age of 45 years.
The study is published in the journal Scientific Reports here: http://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-88590-0
Overall ...