Physicists extract proton mass radius from experimental data
2021-05-12
(Press-News.org) Researchers have recently extracted the proton mass radius from the experimental data.
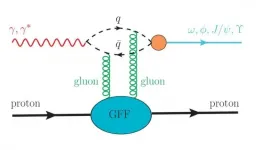
A research group at the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) presented an analysis of the proton mass radius in Physical Review D on May 11. The proton mass radius is determined to be 0.67 ± 0.03 femtometers, which is obviously smaller than the charge radius of the proton.
In the Standard Model, the proton is a composite particle made of quarks and gluons and it has a non-zero size. The radius of the proton is a global and fundamental property of the proton. It is related to the color confinement radius -- a property governed by quantum chromodynamics (QCD).
The radius of the proton is approximately 100,000 times smaller than that of the atom, and the sizes of the quark and gluon are several orders smaller than the proton radius. Scientists use various distributions to describe the shape of the proton, such as charge distribution and mass distribution.
The charge radius of the proton has been precisely measured by scientists via Lamb shift of the muonic hydrogen or the high energy electron-proton elastic scattering, with the average value of 0.8409± 0.0004 femtometers provided by the Particle Data Group. Nevertheless, knowledge of proton gravitational properties such as proton mass radius has still been very limited.
"According to recent theoretical studies by Dmitri Kharzeev, the proton mass radius is related to the scalar gravitational form factor of the proton," said Dr. WANG Rong, first author of the paper. By investigating the vector meson photoproduction data for omega, phi and J/psi from the SAPHIR (Spectrometer Arrangement for PHoton Induced Reactions) experiment at Bonn University, the LEPS (Laser Electron Photons) experiment at SPring-8 facility, and the GlueX experiment at Jefferson Lab, the researchers determined the scalar gravitational form factor and the proton mass radius.
Meanwhile, Prof. Dmitri Kharzeev, a theoretical physicist at Stony Brook University, obtained a similar result by using GlueX J/psi data. The proton mass radius was estimated to be 0.55 ± 0.03 femtometers.
"Both results might be the first-ever values of the proton mass radius with experimental evidence," said WANG. "The determination of the proton mass radius will improve our understanding of the origins of proton mass and the color confinement mechanism of strong interaction."
A lot of questions still remain. "The smaller mass radius implies that the mass distribution is significantly different from the charge distribution of the proton," said Prof. CHEN Xurong, a researcher at IMP.
Scientists are now trying to get a clearer picture of the proton mass radius and the proton structure. The GlueX experiment at Jefferson Lab will provide more data in the near future. Even more exciting, future electron-ion colliders both in the United States and in China will provide Upsilon vector meson electroproduction data for researchers to better understand these questions.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-12
Atoms are the basic building blocks for all materials. To tailor functional properties, it is essential to accurately determine their atomic structures. KAIST researchers observed the 3D atomic structure of a nanoparticle at the atom level via neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography.
Using a platinum nanoparticle as a model system, a research team led by Professor Yongsoo Yang demonstrated that an atomicity-based deep learning approach can reliably identify the 3D surface atomic structure with a precision of 15 picometers (only about 1/3 of a hydrogen atom's radius). The atomic displacement, strain, and facet analysis revealed that the surface atomic structure and strain are ...
2021-05-12
The study conducted by the University of Turku and the Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare together with an international research team is so far the largest population-level study in the world examining the connection between human gut microbiota and health and mortality in the following decades.
The composition of the research subjects' gut microbiota was analysed from stool samples collected in 2002. The researchers had access to follow-up data on the subjects' mortality until 2017, i.e., close to the present day.
"Many bacterial strains that are known ...
2021-05-12
Acetone, a volatile solvent used for everything from removing nail polish and cleaning textiles to manufacturing plastics, could get a sustainability boost from a new strain of bacteria engineered by a research team based in Japan.
They published the details of the heat-loving, acetone-producing bacteria called Moorella thermoacetica on April 23 in AMB Express.
Acetone is typically produced through the widely used cumene method, which is cost-effective but not sustainable. The process, developed in 1942, involves converting two non-renewable resources into acetone and phenol, another chemical ...
2021-05-12
The human brain is a vast network of billions of biological cells called Neurons which fires electrical signals that process information, resulting in our sense and thoughts. The ion channels of atomic scale in each neuron cell membrane plays a key role in such firings that opens and closes the ion flow in an individual cell by the electrical voltage applied across the cell membrane, acting as a "biological transistor" similar to electronic transistors in computers. For decades, scientists have learned that biological ion channels are life's transistors capable to gate extremely fast and precisely selective permeation of ions through the atomic-scale selectivity filters to maintain vital living functions. However, ...
2021-05-12
Researchers from the £12 million Developing Human Connectome Project have used the dramatic advances in medical imaging the project has provided to visualise and study white matter pathways, the wiring that connects developing brain networks, in the human brain as it develops in the womb.
Published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America, the study used magnetic resonance images (MRI) with unprecedented resolution from more than 120 healthy fetuses across the second and third trimesters of pregnancy to define how the structural connections in their ...
2021-05-12
Strawberry production is one of the driving forces in the Spanish agriculture sector, as strawberries are highly valued for their organoleptic characteristics and health benefits. These two factors, their economic relevance, and the value that consumers assign them, make this fruit an object of scientific research from multiple perspectives, including that of food safety. A research project headed by Liliana Pérez-Lavalle, Elena Carrasco, Pedro Vallesquino-Laguna, Manuel Cejudo, Guiomar Denisse Posada and Antonio Valero has aimed to evaluate whether the Salmonella Thompson bacteria, one of the pathogens that can contaminate the fruit through sewage and/or the soil, could penetrate through the roots ...
2021-05-12
Gold leaf -- gold metal hammered into thin sheets -- is used by artists and crafters to gild picture frames, artwork and clothing. Despite its luxurious appearance, the material is affordable and available at most craft stores. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed gold leaf electrodes that, in combination with a CRISPR-based assay, could sensitively detect human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA in human samples. The method also could be modified to diagnose other viral infections.
Previous research indicates that about 80% of new cases of sexually transmitted infections, such as HPV and human immunodeficiency virus (known ...
2021-05-12
Earthworms improve the soil by aerating it, breaking down organic matter and mineralizing nutrients. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology have dug up another possible role: reducing the number and relative abundance of antibiotic-resistance genes (ARGs) in soils from diverse ecosystems. These results imply that earthworms could be a natural, sustainable solution to addressing the global issue of antibiotic resistance, the researchers say.
The overuse of antibiotics in humans and animals has caused ARGs to accumulate in soils, which could contribute to the rise in antibiotic-resistant infections. Earthworms consume tons of soil per year worldwide, and their guts have a unique combination of low-oxygen conditions, neutral pH and native microbial ...
2021-05-12
Coal combustion by power plants and industry pollutes the air, causing many governments to implement mitigation actions and encourage cleaner forms of energy. Now, a new study in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology indicates that in China, indoor air pollution from residential coal burning causes a disproportionate number of premature deaths from exposure to tiny, inhalable pollutants known as PM2.5.
In China, coal is still the largest source of energy, although recent mitigation actions have replaced some coal-fired power plants with petroleum- or natural gas-powered plants. Also, many coal-fired power plants and industrial boilers have installed equipment that reduces ...
2021-05-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Kindergartners from low-income families spent more than six hours a day in front of screens during two early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, a small Ohio study suggests.
That is nearly double the screen time found before the pandemic in similar children, according to other research.
Caregivers from low-income households may have faced more difficulties than those from more advantaged families in managing the time their children spent watching TV and using computers, phones and tablets when child care was shut down, according to the researchers.
Still, the results are concerning, said Rebecca Dore, lead author of the study and senior research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Physicists extract proton mass radius from experimental data