(Press-News.org) Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) are highly localized surface waves on the interface between metal and dielectric in the optical frequency band. SSPs do not naturally exist in the microwave and terahertz frequencies, so "spoof" surface plasmon polaritons (SSPPs) are necessary for operations in those lower frequency bands.
Like optical SPPs, microwave SSPPs exhibit highly localized electromagnetic fields, subwavelength resolution, and extraordinary field confinement. Therefore, SSPP transmission lines (TLs) have been proposed as novel types of microwaveguides that offer new solutions for miniaturization, signal integrity, and low crosstalk in compact circuits for use in wireless communications and wearable electronics.
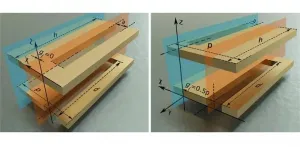
Recently, a research team from Southeast University in China applied a typical form of higher symmetry called "glide symmetry" in dual-strip SSPP TLs to achieve flexible control of modal fields, dispersion characteristics, and mutual coupling between TLs. As reported in Advanced Photonics, they constructed a hybrid TL array with a nonglide symmetric TL and a glide symmetric TL, in which a misalignment of half period is observed between the upper and lower strips. A broadened working bandwidth resulted from the glide symmetric TL, and the team demonstrated that the glide symmetry helps suppress channel crosstalk significantly without requiring extra space or feeding networks.
In their experimental demonstration, the cutoff frequency of the fundamental mode increases from 5 GHz (for a nonglide symmetric TL) to 9.5 GHz (for a glide symmetric TL). Because the fundamental mode of the glide symmetric TL is totally different from that of the nonglide one, the coupling coefficient between them is significantly lower than that between two uniform SSPP TLs. The team noted that, due to the mode mismatch in the hybrid array, a very limited portion of energy could be coupled to the neighboring TL.
Four-port model composed of two channels: one is the nonglide symmetric transmission line channel, and the other is the glide symmetric one. Credit: Xiao Tian Yan et al., doi 10.1117/1.AP.3.2.025001
Tie Jun Cui, professor at Southeast University's Institute of Electromagnetic Space, remarks, "Glide symmetry offers powerful and flexible control of SSPPs and may bring about new solutions in future integrated circuits." Cui envisions that when serious line-to-line interference damages the performance of circuits, an alternating arrangement of glide and nonglide symmetric TLs can restore and guarantee signal accuracy. Cui notes, "No extra space or design of circuits is needed when the nonglide symmetric TL is replaced with a glide one." This space-saving solution may supply significant improvements to future integrated circuits and systems.
Read the open access article: Xiao Tian Yan et al., "Glide symmetry for mode control and significant suppression of coupling in dual-strip SSPP transmission lines," Adv. Photon. 3(2), 026001 (2021), doi 10.1117/1.AP.3.2.025001.
Better integrated circuits with glide symmetry
Glide symmetry offers a compact, flexible solution for suppression of channel crosstalk in SSPP transmission lines
2021-05-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Anesthetic may affect tau spread in the brain to promote Alzheimer's disease pathology
2021-05-12
BOSTON - During the development and progression of Alzheimer's disease, a protein called tau accumulates and spreads in the brain. Understanding the mechanisms behind tau spread--and its consequences--may point to new prevention and treatment strategies for Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia. New insights now come from research that was led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and involves an anesthetic known to affect cognitive function. The findings are published in Communications Biology.
The scientists note that inflammation plays an important role in Alzheimer's disease, and microglia--immune cells that reside in the brain--are thought to be involved in this process by producing an ...
Untangling the brain: new research offers hope for Alzheimer's disease
2021-05-12
Since the discovery of Alzheimer's disease over a century ago, two hallmarks of the devastating illness have taken center stage.
The first, known as amyloid plaques, are dense accumulations of misfolded amyloid protein, occurring in the spaces between nerve cells. Most efforts to halt the advance of Alzheimer's disease have targeted amyloid protein plaques. To date, all have met dispiriting failure.
The second classic trait has, until recently, received less scrutiny. It consists of string-like formations within the bodies of neurons, produced by another crucial protein-- tau. These are known as neurofibrillary tangles.
In a new study, researchers with the ASU-Banner Neurodegenerative Disease Center at the Biodesign ...
Rapid COVID-19 diagnostic test delivers results within 4 minutes with 90 percent accuracy
2021-05-12
PHILADELPHIA--A low-cost, rapid diagnostic test for COVID-19 developed by Penn Medicine provides COVID-19 results within four minutes with 90 percent accuracy. A paper published this week in Matter details the fast and inexpensive diagnostic test, called RAPID 1.0 (Real-time Accurate Portable Impedimetric Detection prototype 1.0). Compared to existing methods for COVID-19 detection, RAPID is inexpensive and highly scalable, allowing the production of millions of units per week.
Despite the urgency of the pandemic, most available methods for COVID-19 testing use RT-PCR--reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction--to detect ...
On the road to smart cities: Where smart vehicles stand and where they're going
2021-05-12
Central to any technological progress is the enrichment of human life. The internet and wireless connectivity have done that by allowing not only virtually anyone anywhere to connect real time, but by making possible connections between humans and a range of intelligent devices both indoors and outdoors, putting smart cities on the horizon.
One key aspect of realizing smart cities is "smart vehicles", the latest development in intelligent transportation systems (ITS), which involve the integration of communication, mapping, positioning, network, and sensor technologies to ensure cooperative, efficient, intelligent, safe, and economical transportation.
For decades, research on bringing to the streets smart vehicles that operate ...
Computer designs magnonic devices
2021-05-12
The field of magnonics offers a new type of low-power information processing, in which magnons, the quanta of spin waves, carry and process data instead of electrons. The end goal of this field is to create magnonic circuits, which would be smaller and more energy-efficient than current electronic ones.
Until recently, the development of a functional magnonic device could take years of trial-and-error. Researchers from the University of Vienna and the TU Kaiserslautern have developed a new computational method to design new devices in a considerably shorter time. Moreover, the efficiency added through this novel inverse design method helps overcome a traditional problem with such devices: they were just suitable for one function only. Now, thanks to the proposed ...
A hairpin to fight cancer
2021-05-12
The inhibition of pathological protein-protein interactions is a promising approach for treating a large number of diseases, including many forms of cancer. A team of researchers has now developed a bicyclic peptide that binds to beta-catenin--a protein associated with certain types of tumor. The secret of their success is the cyclic nature and the hairpin shape of the peptide, which mimics a natural protein structure, they report in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Because of the extensive protein regions involved in protein-protein interactions, therapeutic approaches involving small molecules are often unsuccessful. Protein mimetics are alternatives that imitate the spatial structure of binding segments of natural protein binding partners. ...
10 years after obesity surgery: How did life turn out?
2021-05-12
In a new study from Lund University and the University of Gothenburg, patients were interviewed about their experiences ten years after undergoing obesity surgery. The results show that the effect on eating and weight regulation persisted, whereas other problems, such as feelings of guilt about still not being healthy enough, remained.
"This is one of few follow-ups from a patients perspective so long after surgery", says My Engström, researcher in nursing at the University of Gothenburg.
18 patients were interviewed in the study. All of them experienced that their eating habits and appetite were still affected after the operation: their bodies still objected, preventing ...
Researchers develop methods to understand how tb consumes its favourite foods
2021-05-12
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is incredible in that it can survive for decades within its human host. It does this by varying its diet to successfully steal nutrients from the human host including immune cells; it is known to acquire and absorb multiple carbon sources from the body during infection.
In a paper published in the journal Molecular Systems Biology, Surrey scientists detail how they measure the flow of metabolites or "fluxes" through metabolic pathways when Mycobacterium tuberculosis is consuming some of its favourite nutrients. Measuring these 'fluxes' could help scientists advance new tuberculosis drugs as well as understand why the bacterium survives so long in humans and why current antibiotics are often ineffective.
By growing Mycobacterium ...
Excitation spectral microscopy integrates multi-target imaging and quantitative biosensing
2021-05-12
The multiplexing capability of fluorescence microscopy is severely limited by the broad fluorescence spectral width. Spectral imaging offers potential solutions, yet typical approaches to disperse the local emission spectra notably impede the attainable throughput and place substantial constraints on temporal resolution. Tunable bandpass filters provide a possibility to scan through the emission wavelength in the wide field. However, applying narrow bandpasses to the fluorescence emission results in inefficient use of the scarce signal.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Ke Xu ...
New method for producing synthetic DNA
2021-05-12
The DNA sequences produced are also called oligonucleotides. These are widely used for disease identification, for the manufacture of oligonucleotide-based drugs, and for several other medical and biotechnological applications.
The high demand for oligonucleotides therefore requires an efficient automated method for their chemical production.This process relies on phosphoramidites, which are chemical compounds that have the disadvantage of being unstable unless stored at the ideal -20 degrees Celsius.
Instruments used for DNA synthesis are not able to cool down the phosphoramidites, and consequently it is unavoidable that some of them degrade after being added ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Better integrated circuits with glide symmetryGlide symmetry offers a compact, flexible solution for suppression of channel crosstalk in SSPP transmission lines