Freeform imaging systems: Fermat's principle unlocks 'first time right' design
2021-05-13
(Press-News.org) Optical imaging systems have been playing an essential role in scientific discovery and societal progress for several centuries. For more than 150 years scientists and engineers have used aberration theory to describe and quantify the deviation of light rays from ideal focusing in an imaging system. Until recently most of these imaging systems included spherical and aspherical refractive lenses or reflective mirrors or a combination of both. With the introduction of new ultra-precision manufacturing methods, it has become possible to fabricate lenses and mirrors that lack the common translational or rotational symmetry about a plane or an axis. Such optical components are called freeform optical elements and they can be used to greatly extend the functionalities, improve performance, and reduce volume and weight of optical imaging systems. Today, the design of optical systems largely relies on efficient raytracing and optimization algorithms. A successful and widely used optimization-based optical design strategy therefore consists of choosing a well-known optical system as a starting point and steadily achieving incremental improvements. Such a "step-and-repeat" approach to optical design, however, requires considerable experience, intuition, and guesswork, which is why it is sometimes referred to as "art and science". This applies especially to freeform optical systems.
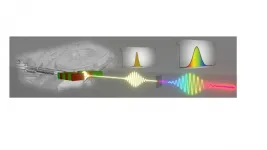
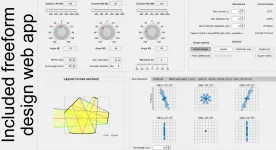
In a newly published paper in Light Science & Applications - Nature, researchers at Brussels Photonics (B-PHOT), Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Belgium have developed a deterministic direct optical design method for freeform imaging systems based on differential equations derived from Fermat's principle and solved using power series. The method allows calculating the optical surface coefficients that ensure minimal image blurring for each individual order of aberrations. They demonstrate the systematic, deterministic, scalable, and holistic character of their method for mirror- and lens-based design examples. The reported approach provides a disruptive methodology to design optical imaging systems from scratch, while largely reducing the 'trial and error' approach in present-day optical design.
The scientists summarize the operational principle of their method:
"We only need to specify the layout, the number and types of surfaces to be designed and the location of the stop. The established differential equations and solution scheme requires only two further steps: (1) solve the non-linear first order case using a standard non-linear solver; (2) solve the linear systems of equations in ascending order by setting unwanted aberrations to zero or by minimizing a combination thereof as required by the targeted specifications of the imaging freeform system. Most importantly, these two steps are identical for all (freeform) optical designs"
"The presented method allows a highly systematic generation and evaluation of directly calculated freeform design solutions that can be readily used as an excellent starting point for further and final optimization. As such, it allows the straightforward generation of 'first time right' initial designs that enable a rigorous, extensive and real-time evaluation in solution space when combined with available local or global optimization algorithms."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-13
The relevance for radiology applications is probably the most known advantage of X-ray beams (keV energies) with respect to visible radiation (eV energies) and can be traced back to their superior penetration depth. On a more fundamental ground, however, the relevance of this photon energy range relies on the capability of probing inner shell electrons (as they have comparable binding energies) and mapping molecular structures on the atomic-scale (as typical interatomic spacings are comparable to X-ray wavelengths). Building on such capabilities, large efforts have been devoted by the scientific community to develop X-ray sub-picosecond sources able to access matter properties with a time resolution sufficient to access elemental molecular motions. Free electron lasers (FEL), nowadays available ...
2021-05-13
UNSW medical researchers have found a way to starve pancreatic cancer cells and 'disable' the cells that block treatment from working effectively. Their findings in mice and human lab models - which have been 10 years in the making and are about to be put to the test in a human clinical trial - are published today in Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Pancreatic cancer has seen minimal improvement in survival for the last four decades - and without immediate action, it is predicted to be the world's second biggest ...
2021-05-13
The Indian public blamed foreigners, minority groups and doctors for the rapid spread of COVID-19 across the country during the first wave, due to misinformation, rumour and long-held discriminatory beliefs, according to an international study led by Monash University.
This resulted in people refusing to get tested for fear of humiliation or public reprisals, which included attacks on Muslims and health care workers.
However, when presented with accurate and reliable information about the virus spread, the Indian public back-pedalled on those negative sentiments and were more likely to get tested and seek medical help, highlighting the importance of health advice from credible sources.
A ...
2021-05-13
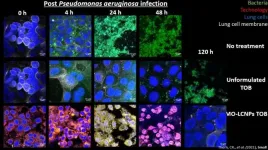
World-first nanotechnology developed by the University of South Australia could change the lives of thousands of people living with cystic fibrosis (CF) as groundbreaking research shows it can improve the effectiveness of the CF antibiotic Tobramycin, increasing its efficacy by up to 100,000-fold.
The new technology uses a biomimetic nanostructured material to augment Tobramycin - the antibiotic prescribed to treat chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections in severe cases of CF - eradicating the infection in as little as two doses.
In Australia, cystic fibrosis (CF) affects one in 2500 babies - or one baby born every four days - causing severe impairments to a person's ...
2021-05-13
Cancer death rates have fallen dramatically in the United States, but factor in obesity, as researchers did at the University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, and the picture changes.
In a study published May 10 in JAMA Network Open, researchers showed that obesity-related cancer deaths are improving, but at a slowing pace.
Based on mortality data for 50 million people, deaths from cancers not associated with obesity -- that's lung cancer and skin cancer, among others - are declining at a rate almost three times faster than cancers linked to obesity, such as stomach, colorectal, uterine, thyroid and postmenopausal breast cancer.
"These are cancers where we could see even larger mortality improvements with creative and practical tools to combat ...
2021-05-13
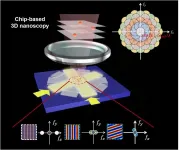
Compared with the superresolution microscopy that bases on squeezing the point spread function in the spatial domain, the superresolution microscopy that broadens the detection range in the spatial frequency domain through the spatial-frequency-shift (SFS) effect shows intriguing advantages including large field of view, high speed, and good modularity, owing to its wide-field picture acquisition process and universal implementation without using special fluorophores labeling.
To enable spatial-frequency-shift microscopy with a superresolution at the subwavelength scale, it is essential to use the near-field evanescent wave with a larger wave vector than the far-field propagation wave for illumination, which can be built on the integrated photonics, paving the way for compact ...
2021-05-13
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU), collaborating with scientists from the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) and RIKEN, develop a novel technique for live-cell fluorescent imaging which leads them to discover a new actin structure in starfish early embryos.
Tokyo, Japan - Monitoring alignments of the building blocks of cells is important to understand how the cells are built. By collaborating with imaging scientists at the MBL, researchers from Japan have developed a new probe which they call POLArIS, allowing real-time imaging of molecular orientations in live cells.
A fluorophore emits polarized light as it glows. The orientation of polarized fluorescence ...
2021-05-13
It is difficult for us to succeed in whatever we set out to do if we lack motivation. We usually need it as a driving force to achieve both short- and long-term goals, from household chores to getting a degree. However, because of the ongoing pandemic, our lifestyles have been subjected to drastic and dynamic changes, and many work- and study-related activities are now carried out online exclusively. This, among other complex factors, have made it difficult for some people to stay focused and motivated, and psychology researchers are trying to find effective and widely applicable solutions to address such problems.
In a END ...
2021-05-13
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new study's findings dispel the misconception that patients and providers are at high risk of catching COVID-19 at the dentist's office.
SARS-CoV-2 spreads mainly through respiratory droplets, and dental procedures are known to produce an abundance of aerosols - leading to fears that flying saliva during a cleaning or a restorative procedure could make the dentist's chair a high-transmission location.
Ohio State University researchers set out to determine whether saliva is the main source of the spray, collecting samples from personnel, equipment and other surfaces reached by aerosols during a range ...
2021-05-13
Twenty-seven years ago, more than 1 million Rwandans were killed during the genocide against the Tutsi in Rwanda from April 7 to July 4, 1994. It is estimated that 100,000 to 250,000 women were raped during the 100-day genocide, and that 10,000 children were born as a result. A new study finds that Rwandans who were conceived by mothers who survived the 1994 genocide against the Tutsi have poorer adult health outcomes than those who were conceived by Rwandan mothers living outside the country at that time. In addition, those who were conceived through genocidal rape have poorer adult health ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Freeform imaging systems: Fermat's principle unlocks 'first time right' design