Prehistoric footprints suggest mammals did like to be beside the seaside
2021-05-13
(Press-News.org) Fossilised footprint tracks, recently discovered within the Hanna Formation in Wyoming, USA, which have been dated to 58 million years ago, may represent the earliest evidence of mammals gathering by the sea, according to a study published in Scientific Reports. The findings suggest that mammals may have first used marine habitats at least 9.4 million years earlier than previously thought, in the late Paleocene (66-56 million years ago), rather than the Eocene (56-33.9 million years ago).
Drs. Anton Wroblewski and Bonnie Gulas-Wroblewski examined and photographed over 1,000 metres of fossilised footprints in an area dated back to 58 million years ago by plant and pollen fossils. The authors identified various different tracks. One set showed relatively large, five-toed footprints, comparable to the foot size of a modern-day brown bear, another showed medium-sized, four-toed footprints. The authors suggest that the five-toed prints were made by Coryphodon, a type of semiaquatic Pantodont, similar to a hippopotamus. The four-toed prints did not match skeletal evidence of mammals known from the late Paleocene, but show similarities with artiodactyls and tapiroids (types of hoofed mammals) which have yet to be shown to have existed in the Paleocene.
The tracks led to and crossed an area which also held traces of prehistoric marine molluscs and worms, as well as sea anemones, indicating the area was once a shallow tidal lagoon or bay. The authors speculate that prehistoric mammals gathered by the sea for similar reasons as modern-day mammals, such as crossing to migrate, protection from predators and biting insects, and to access sodium minerals, which would have been limited in prehistoric North American tropical forests.
INFORMATION:
Article details
Earliest evidence of marine habitat use by mammals
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-88412-3
Corresponding Author:
Anton Wroblewski
University of Utah, Utah, USA
Email: anton.wroblewski@utah.edu
Ph: 1-281-658-7138
Please link to the article in online versions of your report (the URL will go live after the embargo ends):
https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-88412-3
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-13
Climate change may be accelerating the degradation of ancient rock paintings in Indonesia, including the oldest known hand stencil in the world which dates back to 39,900 years ago, according to a study published in Scientific Reports.
Rock paintings made using red and mulberry-coloured pigments in the limestone caves and rock shelters of Maros-Pangkep, Indonesia have been dated to between 20,000 and 45,000 years old. Anecdotal evidence suggests that the paintings have been deteriorating at an accelerated rate in recent decades, but the reasons for this have been unclear.
Jillian Huntley and colleagues investigated the potential causes of accelerated rock art degradation at 11 cave art sites in Maros-Pangkep, by analysing ...
2021-05-13
Radical changes to the food system are needed to safeguard our food supply and combat malnutrition in the face of climate change, environmental degradation and epidemics, says new report.
Researchers at the University of Cambridge say our future global food supply cannot be safeguarded by traditional approaches to improving food production. They suggest state-of-the-art, controlled-environment systems, producing novel foods, should be integrated into the food system to reduce vulnerability to environmental changes, pests and diseases. Their report is published today in the journal Nature Food.
The researchers say that global malnutrition could be eradicated by farming foods including spirulina, chlorella, larvae of insects such as the house fly, mycoprotein (protein derived ...
2021-05-13
A new study with zebrafish shows that a deadly form of skin cancer -- melanoma -- alters the metabolism of healthy tissues elsewhere in the body. The research from Washington University in St. Louis suggests that these other tissues could potentially be targeted to help treat cancer.
"Tumors rely on a constant supply of nutrients to grow. Instead of competing with tumors for nutrients, other tissues can reprogram their metabolism to be complementary. In some instances, this may even allow healthy tissues to feed the tumor," said Gary Patti, the Michael and Tana Powell Professor of Chemistry in Arts & Sciences at Washington University and a professor of chemistry and medicine at the School of Medicine.
Patti is the corresponding author of the study published May 13 in Cell Metabolism.
Cancer ...
2021-05-13
Scientists exploring the drivers of Antarctic climate change have discovered a new and more efficient pathway for the creation of natural aerosols and clouds which contribute significantly to temperature increases.
The Antarctic Peninsula has shown some of the largest global increases in near-surface air temperature over the last 50 years, but experts have struggled to predict temperatures because little was known about how natural aerosols and clouds affect the amount of sunlight absorbed by the Earth and energy radiated back into space.
Studying data from seas around the Peninsula, experts have discovered that most new particles are formed in air masses arriving from the partially ice-covered Weddell Sea - a significant source ...
2021-05-13
Today, the rocks of the Hanna Formation in south-central Wyoming are hundreds of miles away from the nearest ocean. But around 58 million years ago, Wyoming was oceanfront property, with large hippo-like mammals traipsing through nearshore lagoons.
In a study published in Scientific Reports, geologist Anton Wroblewski, an adjunct associate professor in the Department of Geology and Geophysics, and applied biodiversity scientist Bonnie Gulas-Wroblewski of the Texas A&M Natural Resources Institute, report the discovery of several sets of ...
2021-05-13
What The Viewpoint Says: Questions regarding the safety of COVID-19 vaccination for patients with cancer are explored in this article.
Authors: Dimitrios P. Kontoyiannis, M.D., Sc.D.,Ph.D., of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.1218)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
2021-05-13
What The Study Did: This survey study examined differences between male and female physicians in the use of social media and reported career and professional benefits.
Authors: Shikha Jain, M.D., of the University of Illinois at Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.9834)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
2021-05-13
What The Study Did: Advertisements on videos on made-for-kids channels on YouTube, as well as the frequency of age-inappropriate ads, were analyzed in this study.
Authors: Jenny S. Radesky, M.D., of the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.9890)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
2021-05-13
Among other things, dams serve as reservoirs for drinking water, agricultural irrigation, or the operation of hydropower plants. Until now, it had been assumed that dams act as net carbon stores. Researchers from the Helmholtz Centre of Environmental Research (UFZ) together with Spanish scientists from the Catalan Institute for Water Research (ICRA) in Girona and the University of Barcelona showed that dams release twice as much carbon as they store. The study has been published in Nature Geosciences.
Whether leaves, branches, or algae - streams transport large amounts of carbon-containing material. If the water is dammed, the material gradually settles and accumulates at the bottom ...
2021-05-13
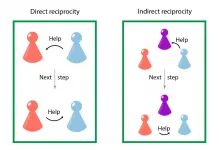
Cooperation as a successful strategy has evolved in both nature and human society, but understanding its emergence can be a difficult task. Researchers have to abstract interactions between individuals into mathematical formulas to be able to create a model that can be used for predictions and simulations.
In the field of evolutionary game theory, they often investigate strategies of players in a simple game of giving and receiving benefits. Such strategies tell players how to behave in a given interaction. The scientists' findings counter the narrative that only the strongest and most selfish flourish and survive. Instead, they show how cooperation can be a successful and stable strategy.
Researchers, spearheaded by Laura Schmid ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Prehistoric footprints suggest mammals did like to be beside the seaside