(Press-News.org) The COVID-19 pandemic has been shown to have caused a significant strain on the healthcare system and resources in the United States. However, data regarding the impact of the virus on hip fractures, primarily seen in elderly patients, is lacking.
Researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) sought to compare characteristics and outcomes of hip fracture patients admitted during the COVID-19 outbreak to patients admitted before the outbreak. They also examined characteristics and outcomes of hip fracture patients with and without the virus. Their findings were presented at the 2021 Spring American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine (ASRA) Annual Meeting.1
"Studying this topic is important because events that stress the healthcare system, like this pandemic, allow us to gain rare insights into what happens to medical care when resources become scarce," said principal investigator Stavros Memtsoudis, MD, PhD, MBA, an anesthesiologist at HSS.
Dr. Memtsoudis and colleagues compared patient and healthcare characteristics, COVID-19 diagnoses and outcomes for hip-fracture patients from March to April 2019 and March to April 2020. Observed outcomes included length of hospital stay, admission to an intensive care unit (ICU), use of mechanical ventilation, 30-day readmission, discharge disposition and postoperative complications.
The number of hip fracture cases during the COVID-19 surge decreased by 50% compared with the same time period during the previous year. "One of the major takeaways from this study was we saw that fractures were more commonly treated nonoperatively, and how outcomes differed," Dr. Memtsoudis noted. During the pandemic, hip fracture patients were discharged earlier and were less likely to be admitted to the ICU.
Other factors did not differ before and after COVID-19, including in-hospital mortality rate, 30-day readmission rate, use of mechanical ventilation, and complication rate.
Hip-fracture patients with COVID-19 stayed in the hospital longer, had higher rates of complications during surgery, increased rates of mortality, and more frequently received nonsurgical treatment.
These results show two main considerations for hospitals. As society begins to return to more normal activities, rates of hip fracture are likely to increase back to pre-COVID-19 levels. Hospitals should be prepared and have plans for treating hip fracture patients with COVID-19, as well as protecting non-COVID-19 patients from exposure.
Additionally, findings that demonstrate shorter length of stay in the hospital, less use of the ICU, and earlier home discharge did not compromise outcomes and deserve further study. This raises the question of whether the strategies of care for hip fracture patients used before the pandemic should be adjusted.
"These results should make us reevaluate our practice going forward to make sure we do not waste resources but also affirm interventions that truly are beneficial," Dr. Memtsoudis concluded.
INFORMATION:
Reference
1. Haoyan Zhong MPA, Jashvant Poeran MD PhD, Jiabin Liu MD PhD, Lauren A. Wilson MPH, Stavros G. Memtsoudis MD PhD MBA FCCP. "Hip Fracture Characteristics and Outcomes During COVID 19: A Large Retrospective National Database Review." Presented at: 46th Annual Regional Anesthesiology and Acute Pain Medicine Meeting of the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine (ASRA), May 13-15, 2021; Orlando, FL.
About HSS
HSS is the world's leading academic medical center focused on musculoskeletal health. At its core is Hospital for Special Surgery, nationally ranked No. 1 in orthopedics (for the 11th consecutive year), No. 4 in rheumatology by U.S. News & World Report (2020-2021), and named a leader in pediatric orthopedics by U.S. News & World Report "Best Children's Hospitals" list (2020-2021). HSS is ranked world #1 in orthopedics by Newsweek (2020-2021). Founded in 1863, the Hospital has the lowest complication and readmission rates in the nation for orthopedics, and among the lowest infection rates. HSS was the first in New York State to receive Magnet Recognition for Excellence in Nursing Service from the American Nurses Credentialing Center five consecutive times. The global standard total knee replacement was developed at HSS in 1969. An affiliate of Weill Cornell Medical College, HSS has a main campus in New York City and facilities in New Jersey, Connecticut and in the Long Island and Westchester County regions of New York State, as well as in Florida. In addition to patient care, HSS leads the field in research, innovation and education. The HSS Research Institute comprises 20 laboratories and 300 staff members focused on leading the advancement of musculoskeletal health through prevention of degeneration, tissue repair and tissue regeneration. The HSS Global Innovation Institute was formed in 2016 to realize the potential of new drugs, therapeutics and devices. The HSS Education Institute is a trusted leader in advancing musculoskeletal knowledge and research for physicians, nurses, allied health professionals, academic trainees, and consumers in more than 130 countries. The institution is collaborating with medical centers and other organizations to advance the quality and value of musculoskeletal care and to make world-class HSS care more widely accessible nationally and internationally. http://www.hss.edu.
Interim results of a study conducted by researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) suggest that oral tranexamic acid (TXA) is non-inferior to intravenous (IV) TXA in preventing blood loss in total knee and total hip replacement surgery. These findings were presented at the 2021 Spring American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine (ASRA) Annual Meeting.1
Previously available information suggests that oral, IV and topical TXA are all effective at reducing blood loss and drastically reducing blood transfusion rates during and after surgery, but research with direct comparisons for each method is limited.
"TXA in orthopedic surgery has become the standard ...
While it has been said that the eyes are a window to the soul, a new study shows they could be a means for understanding diseases of the brain. According to new research by scientists at the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, retinal scans can detect key changes in blood vessels that may provide an early sign of Alzheimer's, while offering important insights into how one of the most common Alzheimer's risk genes contributes to the disease.
"The most prevalent genetic risk for Alzheimer's disease is a variant of the APOE gene, known as APOE4," said lead author Fanny Elahi, MD, PhD. "We still don't fully understand how this variant increases risk of brain degeneration, we just know that it does, and that this risk is modified by sex, race, and lifestyle. "Our ...
Climate change is exacerbating problems like habitat loss and temperatures swings that have already pushed many animal species to the brink. But can scientists predict which animals will be able to adapt and survive? Using genome sequencing, researchers from McGill University show that some fish, like the threespine stickleback, can adapt very rapidly to extreme seasonal changes. Their findings could help scientists forecast the evolutionary future of these populations.
A popular subject of study among evolutionary ecologists, stickleback are known for their different shapes, sizes, and behaviours - they can even live in both seawater and freshwater, and under a wide range of temperatures. But what ...
Plants have evolved unique immunity mechanisms that they can activate upon detecting the presence of a pathogen. Interestingly, the presence of some nonpathogenic microorganisms can also prompt a plant to activate its systemic immunity mechanisms, and some studies have shown that pretreating agricultural crops with such "immunity-activating" nonpathogenic microorganisms can leave the crops better prepared to fight off infections from pathogenic microorganisms. In effect, this means that immunity-activating nonpathogenic microorganisms can function like vaccines for plants, providing a low-risk stimulus for the plant's immune system that prepares it for dealing with genuine threats. These are exciting findings for crop scientists because they suggest the ...
Researchers at UC San Francisco have observed a new feature of neural activity in the hippocampus - the brain's memory hub - that may explain how this vital brain region combines a diverse range of inputs into a multi-layered memories that can later be recalled.
Using a special "micro-grid" recording device developed by colleagues at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), the UCSF researchers were able to measure hippocampus activity in study participants undergoing surgery to treat severe epilepsy. They discovered that brain waves travel back and forth across this structure, integrating messages ...
The international scientific community agrees that the latest findings of an FAU research team will revolutionise the entire chemistry of magnesium. The research team have discovered magnesium, which usually has a double positive charge in chemical compounds, in the elemental zero-oxidation state. They have published their ground-breaking findings in the journal Nature.
In the periodic table of elements, magnesium (Mg) is a metal with low electronegativity, which means it does not easily attract electrons but easily loses both the electrons in its outer shell during chemical reactions. It therefore only exists in nature as a compound ...
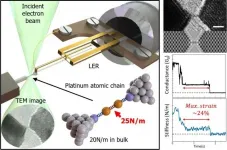
Ishikawa, Japan - Today, many well-studied materials in various fields, such as electronics and catalysis, are close to reaching their practical limits. To further improve upon modern technology and outperform state-of-the-art devices, researchers looking for new functional materials have to push the boundaries and explore more extreme cases. A clear example of this is the study of low-dimensional materials, such as monoatomic layers (2D materials) and monoatomic chains (1D materials).
It has been proved time and time again that low-dimensional materials exhibit exotic properties that are absent in their 3D bulk counterparts. For example, monoatomic chains of metals like gold ...
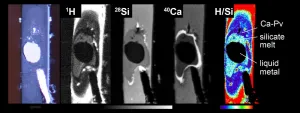
High-temperature and high-pressure experiments involving a diamond anvil and chemicals to simulate the core of the young Earth demonstrate for the first time that hydrogen can bond strongly with iron in extreme conditions. This explains the presence of significant amounts of hydrogen in the Earth's core that arrived as water from bombardments billions of years ago.
Given the extreme depths, temperatures and pressures involved, we are not physically able to probe very far into the earth directly. So, in order to peer deep inside the Earth, researchers use techniques involving seismic data to ascertain things like composition and density of subterranean material. Something that has stood out for as long as these kinds of measurements have been taking place is that the core is primarily ...
The ease with which anyone can create online content for free, especially on social media, has led to superabundance of information being one of the defining characteristics of today's communication systems. This situation has resulted in increasingly intense competition for attention, which has become a scarce good. The researchers from the Complex Systems group (CoSIN3) at the UOC's Internet Interdisciplinary Institute (IN3) María José Palazzi and Albert Solé --professor at the Faculty of Computer Science, Multimedia and Telecommunications?--, led by Javier Borge, have participated in the design of ...
When it comes to ancient Roman imperial architecture, most people usually have a mental image of white marble statues, columns, or slabs. While it is true that many buildings and squares at that time were decorated with marble, it was frequently not white but colored marble that was employed, such as the green-veined Cipollino Verde, which was extracted on the Greek island of Euboea. Because marble was very expensive, it was often placed in thin slabs as a cladding over other, cheaper stones. "To date, however, no actual remains of marble workshops from the Roman imperial era have been found, so little is known about marble processing during this period," said Professor Cees Passchier ...