Toward overcoming solubility issues in organic chemistry
2021-05-18
(Press-News.org) Scientists from Hokkaido University have developed a rapid, efficient protocol for cross-coupling reactions, vastly expanding the pool of chemicals that can be used for the synthesis of useful organic compounds.
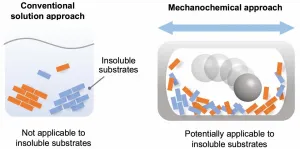
Chemical reactions are a vital process in the synthesis of products for a diversity of purposes. For the most part, these reactions are carried out in the liquid phase, by dissolving the reactants in a solvent. However, there are a significant number of chemicals that are partially or completely insoluble, and thus have not been used for synthesis. The starting materials required for the synthesis of many cutting-edge organic materials--such as organic semiconductors and luminescent materials--are often poorly soluble, leading to problems in solution-based synthesis. Therefore, the development of a solvent-independent synthetic approach to overcome these long-standing solubility issues in organic synthesis is highly desired to synthesize new valuable organic molecules.
In recent years, synthetic techniques using ball milling have been used to carry out solvent-free reactions in the solid phase. It has been proposed that the use of ball milling would potentially overcome the aforementioned solubility issues in synthetic chemistry, but a systematic study for such purpose has never been carried out.
A team of four scientists from Hokkaido University's Institute for Chemical Reaction Design and Discovery (WPI-ICReDD), led by Associate Professor Koji Kubota and Professor Hajime Ito, have developed a rapid, efficient, solvent-free protocol for Suzuki?Miyaura cross-coupling reaction of insoluble aryl halides. The protocol was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Aryl halides are popular starting materials for the synthesis of organic functional molecules, primarily by the palladium-catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction -- for which Hokkaido University's Professor Emeritus Akira Suzuki shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Although the cross-coupling reactions have been employed for the synthesis of a wide range of valuable molecules, insoluble aryl halides are not suitable substrates because Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions have primarily been carried out in solution.
Given this limitation, the scientists focused on the development of an efficient solid-state Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling of a number of extremely unreactive insoluble aryl halides. The key equipment consisted of a ball mill, for mixing the reactants; a heat gun, to increase the temperature at which the reactions took place; and the use of a catalytic system composed of palladium acetate (the catalyst), SPhos (a high-performance ligand for Suzuki?Miyaura cross-coupling reactions) and 1,5-cyclooctadiene (dispersant and stabilizer).
The capstone of this study was the application of the solvent-free solid-state reaction to mostly-insoluble aryl halides. These reactants did not yield any products in conventional solution-based reactions. The solid-state reactions using the high-temperature ball milling, however, gave the desired products. Importantly, the team discovered a new strong photoluminescence material prepared from insoluble pigment violet 23.
"The high-temperature ball-milling technique and our catalytic system are essential for these cross-coupling reactions of insoluble aryl halides, and the protocol we have developed expands the diversity of organic molecules derived from insoluble starting materials," says Koji Kubota.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-18
Vaccines are turning the tide of the pandemic, but the risk of infection is still present in some situations. If you want to visit a friend, get on a plane, or go see a movie, there is no highly accurate, instant test that can tell you right then and there whether or not you have a SARS-CoV-2 infection. But new research from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) could help get reliable instant tests on the market.
A study led by Michal Hammel and Curtis D. Hodge suggests that a highly sensitive lateral flow assay - the same type of device used in home pregnancy tests - could be developed using pairs of rigid antibodies that bind to the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Such a test would only require a small drop of mucus or saliva, could give results ...
2021-05-18
The first-ever discovery of an extraterrestrial radioactive isotope on Earth has scientists rethinking the origins of the elements on our planet.
The tiny traces of plutonium-244 were found in ocean crust alongside radioactive iron-60. The two isotopes are evidence of violent cosmic events in the vicinity of Earth millions of years ago.
Star explosions, or supernovae create many of the heavy elements in the periodic table, including those vital for human life, such as iron, potassium and iodine.
To form even heavier elements, such as gold, uranium and plutonium it was thought that a more violent event may be needed, such as two neutron stars merging.
However, a study led by Professor Anton Wallner from The Australian National University (ANU) suggests ...
2021-05-18
A rigorous meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that compared the effects of medical therapies alone with medical therapies plus revascularization in patients with stable ischemic heart disease (SIHD) was presented at EuroPCR on May 18, 2021. The study concluded that adding revascularization was associated with a statistically important reduction in cardiovascular death associated with a statistically important reduction in spontaneous myocardial infarction (MI), providing a biologically plausible explanation for the observed benefit.
An international group of investigators performed a meta-analysis of RCTs conducted between 1979 and 2020. Strict entry criteria were established to assure the analysis was restricted to studies involving elective, ...
2021-05-18
When it comes sharing recipes on social media, what users post, and what they cook may be two entirely different things. That's the conclusion of a END ...
2021-05-18
An international team of scientists from the Menzies Health Institute Queensland (MHIQ) at Griffith University and from City of Hope, a research and treatment center for cancer, diabetes and other life-threatening diseases in the U.S., have developed an experimental direct-acting antiviral therapy to treat COVID-19.
Traditional antivirals reduce symptoms and help people recover earlier. Examples include Tamiflu®, zanamivir and remdesivir.
This next-generation antiviral approach used gene-silencing RNA technology called siRNA (small-interfering RNA) to attack the virus' genome directly, which stops ...
2021-05-18
ATLANTA - MAY 18, 2021 - A new study finds breast cancer survivors in general have higher risk of new cancer diagnosis compared to healthy individuals. The article, which appears in CANCER, states that compared to the general population in the United States, the risk of new cancer diagnoses among survivors was 20% higher for those with hormone receptor (HR) positive cancers and 44% higher for those with HR-negative cancers.
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed and prevalent cancer among women in the U.S., with over 3.9 million living breast cancer survivors as of 2019. The number of survivors is expected to increase with the aging population and advances in breast cancer treatment.
Subsequent primary cancer (SPC) after breast cancer is a well-known late effect, but the ...
2021-05-18
PULLMAN, Wash. - Alterations in the epigenetic programming of hatchery-raised steelhead trout could account for their reduced fertility, abnormal health and lower survival rates compared to wild fish, according to a new Washington State University study.
The study, published May 18 in Environmental Epigenetics, establishes a link between feeding practices that promote faster growth, as well as other environmental factors in fish hatcheries, and epigenetic changes found in the sperm and red blood cells of of steelhead trout.
The research was done at a national fish hatchery on the Methow River in Winthrop, Washington and at another hatchery ...
2021-05-18
An international research team headed by Michal Hocek of the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences (IOCB Prague) and Charles University and Ciara K. O'Sullivan of Universitat Rovira i Virgili (URV) in Spain have developed a novel method for labeling DNA, which in the future can be used for sequencing DNA by means of electrochemical detection. The researchers presented their results in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
A DNA molecule comprises four basic building blocks, nucleotides. The genetic information carried within the molecule is determined by the order of the nucleotides. Knowledge of the order of these building blocks, which is known ...
2021-05-18
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- A new coronavirus test can get accurate results from a saliva sample in less than 30 minutes, researchers report in the journal Nature Communications. Many of the components of the hand-held device used in this technology can be 3D-printed, and the test can detect as little as one viral particle per 1-microliter drop of fluid.
"We developed a rapid, highly sensitive and accurate assay, and a portable, battery-powered device for COVID-19 testing that can be used anywhere at any time," said University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign chemical and biomolecular engineering professor Huimin Zhao, who led the research. Though it is still in the ...
2021-05-18
A new study published in Nature Communications provides an important new basis for comparing the effectiveness of different tuberculosis treatments.
Tuberculosis, a disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), is typically the leading infectious cause of death globally, killing 1.2 million people each year. The availability of a new way to evaluate treatments can save lives.
In the study, faculty at the University of Colorado School of Medicine at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus partnered with the University of California ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Toward overcoming solubility issues in organic chemistry