Tree species diversity is no protection against bark beetle infestation
2021-05-19
(Press-News.org) In recent years, foresters have been able to observe it up close: First, prolonged drought weakens the trees, then bark beetles and other pests attack. While healthy trees keep the invaders away with resin, stressed ones are virtually defenseless. Freiburg scientist Sylvie Berthelot and her team of researchers from the Faculty of Environment and Natural Resources and the Faculty of Biology are studying the importance of tree diversity on bark beetle infestation. They are investigating whether the composition of tree species affects bark beetle feeding behavior. The team recently published their findings in the Journal of Ecology.
In a 1.1 hectare experimental set-up in Freiburg, six native deciduous and coniferous tree species from Europe and six deciduous and coniferous tree species from North America were each planted in different mono- and mixed plots. After the severe drought in the summer of 2018, the Sixtoothed spruce bark beetle mainly attacked the native species: the European spruce and the European larch. "We were surprised that the beetles exhibited only a slight interest in the exotic conifer species, such as the American spruce," Berthelot says.
While measuring the infestation, the researchers found that the position within the experimental site was also crucial. The trees at the edge were attacked the most. Therefore, Berthelot suspects that the bark beetle entered the testing plot from outside. "In addition, environmental influences weaken the unprotected outer trees more, so they are more susceptible."
At the same time, the likelihood of which trees the bark beetles will attack changes the more tree species there are. Until now, the researchers assumed that tree diversity reduces the infestation of insect pests such as the bark beetle. But their experiment shows that "increasing tree diversity can reduce the risk of bark beetle infestation for species that are susceptible to high infestation rates, such as larch and spruce. But the risk for less preferred species such as pine or exotic trees may increase with tree diversity, as beetles, once attracted, also attack these trees," Berthelot says. Although the study indicates that non-native tree species are less attacked because the bark beetles are unfamiliar with these species. "However, this effect may weaken over the years," she said. As a result, the risk of infestation in mixed forests is redistributed among tree species rather than reduced for all.
The team is conducting research as part of the International Diversity Experiment Network with Trees, or IDENT. The international network is dedicated to research on tree species diversity and its influence on ecosystem functions. The same experimental setup was established in Freiburg as in Canada, the US and Italy.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-19
SAN ANTONIO (May 19, 2021) -- Four months of multi-drug therapy that included rifapentine and moxifloxacin treated active tuberculosis (TB) as effectively as the standard six-month regimen in a multinational study, cutting treatment time by a third. Coauthors including Marc Weiner, MD, of The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, reported the findings May 6 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
"Shorter treatment would be easier for people to complete without missing doses, and ultimately may be cost-effective," said Dr. Weiner, associate professor in the health science center's Joe R. and Teresa Lozano END ...
2021-05-19
A team of researchers at the Centre Spatial de Liège (CSL) of the University of Liège has just developed a method to identify the contributors and origins of stray light on space telescopes. This is a major advance in the field of space engineering that will help in the acquisition of even finer space images and the development of increasingly efficient space instruments. This study has just been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Space telescopes are becoming more and more powerful. Technological developments in recent years have made it possible, for example, to observe objects further and further into the universe or to measure the composition of the Earth's atmosphere with ever greater precision. However, there is still one factor limiting the performance ...
2021-05-19
HAMILTON, ON (May 19, 2021) - Researchers have found that the inclusion of a third drug to commonly used dual-drug inhalers can reduce asthma exacerbations and improve control over the disease in children, adolescents, and adults with moderate-to-severe asthma.
A team from McMaster University and The Research Institute of St. Joe's Hamilton announced their findings from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Data from 20 randomized controlled trials, which included a total of almost 12,000 patients, were analyzed in the study.
Dual-drug inhalers used to treat asthma typically contain an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) to reduce inflammation, as well as a long-acting beta-adrenoceptor agonist (LABA) that acts as a bronchodilator. High-certainty evidence showed that the inclusion of a third ...
2021-05-19
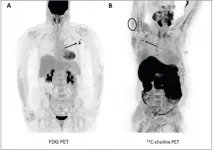
Leesburg, VA, May 19, 2021--According to an open-access article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), increased axillary lymph node or ipsilateral deltoid uptake is occasionally observed on FDG or 11C-choline PET performed after Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccination.
"Recognition of occasional abnormal axillary lymph node or deltoid uptake on PET examinations performed after COVID-19 vaccination will aid interpreting physicians and reduce unnecessary biopsies," wrote corresponding author Jason R. Young from the department of radiology at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, MN.
Young and colleagues' retrospective study included ...
2021-05-19
For the first time, geological records have been used to reconstruct the history of Larsen C Ice Shelf in Antarctica. The ice shelf is the largest remaining remnant of a much more extensive area of ice on the Antarctic Peninsula that began to break up during the 1990s (Larsen A), and saw a huge collapse in 2002 (Larsen B). This new reconstruction enables scientists to better understand if and when the remaining ice shelf could collapse in the future.
Publishing this month in the journal Geology an international team describes how the largest remaining ice shelf on the Antarctic ...
2021-05-19
By mapping its genetic underpinnings, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have identified a predictive causal role for specific cell types in type 1 diabetes, a condition that affects more than 1.6 million Americans.
The findings are published in the May 19, 2021 online issue of Nature.
Type 1 diabetes is a complex autoimmune disease characterized by the impairment and loss of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells and subsequent hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), which is damaging to the body and can cause other serious health problems, such as heart disease and vision loss. Type 1 is less common than type 2 diabetes, but its prevalence is growing. The U.S. Centers for Disease ...
2021-05-19
Boulder, Colo., USA: Deep pools below waterfalls are popular recreational swimming spots, but sometimes they can be partially or completely filled with sediment. New research showed how and why pools at the base of waterfalls, known as plunge pools, go through natural cycles of sediment fill and evacuation. Beyond impacting your favorite swimming hole, plunge pools also serve important ecologic and geologic functions. Deep pools are refuges for fish and other aquatic animals in summer months when water temperatures in shallow rivers can reach lethal levels. Waterfalls also can liquefy sediment within the pool, potentially triggering debris flows that can damage property and threaten ...
2021-05-19
Florida State University researchers have more insight into a strange sea creature found in oceans around the world and what their presence means for the health of a marine ecosystem.
Scientists have thought that salps -- small marine organisms that look like clear, gelatinous blobs -- competed for resources with krill, shrimp-like creatures that are an important food source for many marine animals. But new research published in Limnology and Oceanography suggests that salps are actually competing for food with an organism known as a protist.
An image of a salp taken during research. New research published in Limnology and Oceanography suggests that salps are actually competing for food with an organism known as a protist. (Courtesy of ...
2021-05-19
A heart surgeon doesn't need to grasp quantum mechanics to perform successful operations. Even chemists don't always need to know these fundamental principles to study chemical reactions. But for Kang-Kuen Ni, the Morris Kahn associate professor of chemistry and chemical biology and of physics, quantum spelunking is, like space exploration, a quest to discover a vast and mysterious new realm.
Today, much of quantum mechanics is explained by Schrödinger's equation, a kind of master theory that governs the properties of everything on Earth. "Even though ...
2021-05-19
The amount of nutrients people get from the crops that they eat is a type of 'postcode lottery', according to new research that has analysed thousands of cereal grains and soils as part of a project to tackle hidden hunger in Malawi and Ethiopia.
A global team led by the University of Nottingham and its Future Food Beacon including academics and researchers from Addis Ababa University (AAU) in Ethiopia and Lilongwe University of Agriculture and Natural Resources (LUANAR) in Malawi, working on the GeoNutrition project, have discovered more about the relation between soils, crops and micronutrient deficiencies among people living there. Their ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Tree species diversity is no protection against bark beetle infestation