Technique uses fluctuations in video pixels to measure energy use of developing embryos
2021-05-20
(Press-News.org) Scientists have made a major breakthrough in the study of embryonic development and how it can be impacted by external factors such as climate change.
Researchers at the University of Plymouth have developed a cutting edge technique which enables them to instantly examine the biological traits and behaviours of developing embryos as an energy signature, rather than focusing on individual characteristics.
The method, outlined in a study published in BMC Bioinformatics, is built around timelapse video captured by the researchers of aquatic animals - specifically, the embryos of a freshwater pond snail Radix balthica - during their earliest and most dynamic life stages.
With each video being composed of a series of individual pixels, whose brightness fluctuates from one frame to the next, the team developed a means of using these fluctuations to track detailed changes in energy usage.
The resulting energy proxy traits mean that rather than choosing individual aspects to measure, scientists can capture all of the traits visible in a video as a spectrum of energy values capturing a greater breadth of biological response.
Energy proxy traits respond markedly differently to traditional measurements of the phenotype (an organism's observable characteristics) such as heart rate or movement, and importantly they are highly specific to different temperatures throughout development.
The team also used the technique to demonstrate that the overall amount of energy expressed during the development of an embryo could be used to predict its growth rate, suggesting it may reflect the actual usage of energy by the embryo itself.
Dr Oli Tills, Research Fellow in the School of Biological and Marine Sciences and the new study's lead author, said: "Choosing what to measure can often be a tough choice for biologists, but it can drive the outcome of experiments. This choice can be likened to throwing darts while blindfolded, with the hope that you hit the bullseye by choosing biological traits of relevance that respond in informative ways during experiments.
"Biodiversity makes this task a significant challenge when studying the phenotype by presenting a huge range of form and function to choose from. This study has important implications for how we approach such studies in future. It presents a method that is transferrable to different species, experimental approaches and which moves away from the limitations of our previous pot luck approach."
The new research builds on existing work by the same Plymouth team applying bioimaging, robotics and computer vision to produce automated measurements of the size, shape, movement and function - including heart rate - of aquatic organisms.
INFORMATION:
In April 2020, Dr Tills was awarded a UK Research and Innovation's Future Leaders Fellowship to draw on the enabling technologies of 3D printing, Artificial Intelligence and Big Data analytics and build new approaches to understanding embryonic development.
The study is also further evidence of the University of Plymouth's world-leading approach to marine and climate science, and it was recently named the best university globally for marine research and teaching in the Times Higher Education Impact Rankings 2021.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-20
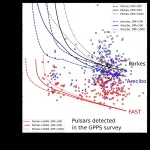
Using the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST), a research team led by Prof. HAN Jinlin from National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) has discovered 201 pulsars, including many very faint pulsars, 40 millisecond pulsars (MSPs), and 16 pulsars in binaries.
These discoveries were published in Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics.
Pulsars are compact remnants of the death of bright, massive stars. They have the strongest magnetic field, highest density and fastest rotation of any celestial body in the Universe, and show significant ...
2021-05-20
Nearly two thirds (61%) expressed concern about their worsening mood in Lockdown and associated restrictions1.
34% said they felt more anxious and 28% felt more depressed during Lockdown and associated restrictions1.
Coffee helped lift nearly half (44%) of adult's negative moods in Lockdown and associated restrictions1.
A new pan-European survey funded by the Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee exploring the impact of COVID-19 Lockdowns and associated restrictions (in those countries where there has been no Lockdown), has found that nearly two thirds of adults (61%) expressed concern about their worsening mood; two times higher than those concerned about physical inactivity (24%)1.
Understanding the effects of COVID-19 restrictions ...
2021-05-20
Scientists from Hokkaido University have shown that an antigen-based test for quantifying SARS-CoV-2 in saliva samples is simple, rapid, and more conducive for mass-screening.
More than a year into the COVID-19 pandemic, the RT-PCR test remains the gold standard for detection of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This method requires trained personnel at every step, from collection of nasopharyngeal swab (NPS) samples to interpretation of the results; in addition, the entire process ranges from 24-48 hours on average. As the virus can be transmitted by an infected person before symptoms ...
2021-05-20
Fixed-dose combination of nivolumab and relatlimab holds the cancer in check significantly longer than nivolumab alone
This is the first regimen to demonstrate a statistical benefit over anti-PD-1 monotherapy in metastatic melanoma
BOSTON - A combination of two drugs that target different proteins on immune system T cells kept advanced melanoma in check significantly longer than one of the drugs alone in a phase 3 clinical trial involving 714 patients. Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investigators co-led the study. Findings will be presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, being held ...
2021-05-20
HOUSTON -- The glutaminase (GLS1) inhibitor IACS-6274, discovered and developed by The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center's Therapeutics Discovery division, appears to be well-tolerated with successful target inhibition and early signs of anti-tumor activity in a biomarker-driven Phase I trial. Interim results of the study will be presented at the 2021 American Society for Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting on June 4.
On the trial, 17 of 20 evaluable patients achieved a best response of stable disease, with a disease control rate of 60% at 12 weeks. Six patients with biomarker-defined advanced cancers ...
2021-05-19
URBANA, Ill. - Women's ability to work as entrepreneurs can help alleviate poverty and malnutrition in developing countries. As local governments and development organizations aim to encourage business opportunities, it's important to identify projects suited for women's lives in rural households.
The soy kit, which includes common household items such as a pot, spoon, thermometer, and cheese cloth, enables entrepreneurs to create value-added products from soy in small-scale household settings. The kit has potential to improve the economic conditions of Malawi women in a sustainable way, a University of Illinois study concludes.
"The larger issue is about adding value to agricultural products in the developing world as a means ...
2021-05-19
Boulder, Colo., USA: The Paleozoic era culminated 251.9 million years ago in the most severe mass extinction recorded in the geologic record. Known as the "great dying," this event saw the loss of up to 96% of all marine species and around 70% of terrestrial species, including plants and insects.
The consensus view of scientists is that volcanic activity at the end of the Permian period, associated with the Siberian Traps Large Igneous Province, emitted massive quantities of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere over a short time interval. This caused a spike in global temperatures and a cascade of other deleterious ...
2021-05-19
Keto, gluten-free, organic: If a pet owner is on a specific diet, chances are their dog is on it, too, a new U of G study reveals.
But when it comes to a grain-free diet, owners seem to choose it more for their dogs than themselves, the study also found.
"It demonstrates that many variables, not just dietary habits, influence the selection of dog food," said study lead author Sydney Banton, a master's student in U of G's Department of Animal Biosciences.
The international Pet Food Consumer Habit Survey is the first of its kind to examine factors involved in ...
2021-05-19
NEWPORT, Ore. - The population of white sharks that call the Central California coast their primary home is holding steady at about 300 animals and shows some signs of growth, a new long-term study of the species has shown.
Between 2011 and 2018, researchers were able to identify hundreds of individual adult and subadult white sharks, which are not fully mature but are old enough to prey on marine mammals. They used that information to develop estimates of the sharks' abundance.
"The finding, a result of eight years of photographing and identifying individual ...
2021-05-19
In new research, Texas A&M University scientists have for the first time revealed a single microscopic defect called a "twin" in a soft-block copolymer using an advanced electron microscopy technique. This defect may be exploited in the future to create materials with novel acoustic and photonic properties.
"This defect is like a black swan -- something special going on that isn't typical," said Dr. Edwin Thomas, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. "Although we chose a certain polymer for our study, I think the twin defect will be fairly universal across a bunch of similar soft matter systems, like oils, surfactants, biological materials and natural polymers. Therefore, our findings will be valuable to diverse research across the soft matter field."
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Technique uses fluctuations in video pixels to measure energy use of developing embryos