Using waste heat to power an environmentally sustainable future
City, University of London's Dr Martin White, explores a novel organic Rankine system for converting waste heat into electricity.
2021-05-24
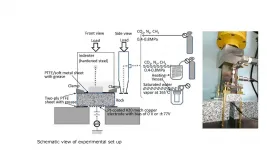
(Press-News.org) In his most recent published research, appearing in Applied Thermal Engineering, City, University of London's Dr Martin White explores a novel organic Rankine cycle system, based on a two-phase expansion through numerical simulations of the system.
His paper, Cycle and turbine optimisation for an ORC operating with two-phase expansion, considers the use of modern fluids whose properties could help to mitigate concerns around turbine damage, whilst allowing the benefits of two-phase expansion to be realised.
Waste heat from a range of industries, ranging from iron and steel to food and drink, is currently ejected into the environment. Thus, the recovery of this wasted energy could have a significant role in reducing the environmental footprint of the manufacturing sector and help to ensure future manufacturing practices are sustainable.
Dr White, a Lecturer in Thermal Power in the School of Mathematics, Computer Science and Engineering, says:
"One of the most promising groups of waste-heat recovery technologies are those that are able to convert this waste heat into electricity. However, current technologies, typically based on the organic Rankine cycle (ORC) - which is similar to a steam cycle but operates with a different fluid rather than water - typically have relatively poor thermodynamic performance and are associated with high costs."
In a conventional ORC system, power is produced by the turbine which is designed to operate completely with a fluid that is in a gaseous state. This is done to avoid the presence of liquid droplets within the turbine that could damage or erode the machine. However, previous investigations have suggested that the admission of a two-phase fluid, which is a combination of liquid and vapour, could enhance the power output from these systems.
Dr White believes that if a suitable turbine design intended for two-phase operation can be designed, the performance of ORC systems could be enhanced.
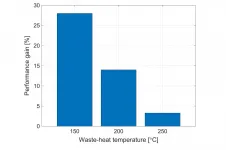
The simulations he has carried out indicate that for waste heat temperatures up to 250 degrees centigrade, the introduction of two-phase expansion could generate up to 28% more power than conventional single-phase systems. Moreover, candidate designs for the turbine are proposed which require further investigation in later studies.
The work was conducted by Dr White as part of his Research Fellowship, funded by the Royal Academy of Engineering.
Through his Fellowship, Dr White is investigating next-generation waste-heat recovery technologies based on two-phase expansion.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-24
It has been documented over hundreds of years that various electromagnetic anomalies occur during a few weeks before the occurrence of a large earthquake. These electromagnetic anomalies are variations that appear in telluric current, geomagnetism, electromagnetic waves etc. before the earthquake.
Although there are various models to explain the mechanism, the large current generated at the source was not fully explained. For example, many researchers thought that the stress applied to the fault produced an electric current, but the stress applied to the fault takes place over hundreds or thousands of years before the occurrence of the earthquake. It is a common belief among seismologists ...
2021-05-24
Telomeres are protective caps on DNA that shorten as we grow older. Now, one of the first studies to examine telomere length (TL) in childhood finds that the initial setting of TL during prenatal development and in the first years of life may determine one's TL throughout childhood and potentially even into adulthood or older age. The study also finds that TL decreases most rapidly from birth to age 3, followed by a period of maintenance into the pre-puberty period, although it was sometimes seen to lengthen.
The study, which followed children from birth to age 9, was led by researchers ...
2021-05-24
AMHERST, Mass. - New developments in recreational fishing technology--from the use of aerial drones and social media scouting reports to advances in hook design--are creating challenges for fisheries management and effective policy making, according to a new study co-authored by University of Massachusetts Amherst researcher Andy Danylchuk.
With the opening of the spring fishing season, millions of recreational fishing aficionados across North America are dusting off their tackleboxes, fitting together their rods, and heading to the bait and tackle shop to purchase the latest ...
2021-05-24
(Boston)--Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is caused by diabetes and hypertension. In 2017, the global prevalence of CKD was 9.1 percent, which is approximately 700 million cases. Chronic kidney damage is assessed by scoring the amount of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IFTA) in a renal biopsy sample. Although image digitization and morphometric (measuring external shapes and dimensions) techniques can better quantify the extent of histologic damage, a more widely applicable way to stratify kidney disease severity is needed.
Now, researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have developed a novel Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool to predict the grade of IFTA, a known structural ...
2021-05-24
(Boston)--Since 2008, researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) and VA Boston Healthcare System have studied Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE), a progressive brain disease associated with repetitive head impacts that has been diagnosed after death in the brains of American football players and other contact sport athletes as well as members of the armed services. Clinically, impulsivity, explosivity, depression, memory impairment and executive dysfunction have been reported to occur in the disease.
While many of the scientific studies to date ...
2021-05-24
New study fills an important knowledge gap about the potential health effects of hair relaxers commonly used by Black women.
(Boston)--The lifetime risk of breast cancer is similar among Black and white women in the U.S., but Black women are disproportionately affected by aggressive breast cancer subtypes such as estrogen receptor (ER) negative tumors, which are diagnosed at a younger age and have a higher mortality rate. While certain hair care products, including relaxers (straighteners) and leave-in conditioners, used more commonly by Black than white women may contain compounds with estrogens or endocrine-disrupting chemicals, few epidemiologic studies have assessed the relationship of hair relaxer use to breast cancer risk.
Researchers have now found no association ...
2021-05-24
CLEVELAND -- A new paper in the June issue of New England Journal of Medicine Catalyst Innovations in Care Delivery describes how the University Hospitals (UH) system applied design-based thinking in a re-imagined process for referrals of patients from primary care physicians to psychiatrists in a value-based, high-reliability model.
"Referrals from primary care to specialty care represent a critical pathway in the patient journey to wellness. As we move toward value-based payment models, high-reliability referral pathways will be of increasing importance in achieving better outcomes at lower cost," said Patrick Runnels, MD, Chief Medical Officer of Population Health and Behavioral Health at UH, Vice Chair of Psychiatry at Case Western ...
2021-05-24
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Schools in the U.S. are set to receive $123 billion in federal pandemic relief funding. Across the country, parents and school administrators are engaging in spirited debates about whether to teach critical race theory. And Americans are bitterly divided in their opinions about how and when to resume in-person instruction following rising rates of vaccination against COVID-19.
One might expect that given all that's at stake, school board meetings across the U.S. would be hotbeds of discussion. But in many cases, they're the same staid, sparsely attended affairs that they can often be.
"We have more ...
2021-05-24
ATLANTA--Absentee property ownership in many small college football towns has a negative impact on permanent residents of those communities, according to a study by a Georgia State University geosciences researcher.
The research is the first known attempt to quantify and map local geographies of gameday home investments.
Each weekend in the fall tens of thousands of football fans flood into college towns to watch their favorite teams kick off against rival schools. Many of them stay in gameday homes, investment properties that sit vacant for much of the year. Taylor Shelton, assistant professor of geosciences and the study's author, examined data from more than a dozen college towns in the South where schools in the Southeastern Conference attract large ...
2021-05-24
BOSTON - A clinical trial pairing community health workers (CHWs) with patients admitted to Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has found that fewer intervention group participants were readmitted within 30 days than were control group participants. The effect was significant for those discharged to short-term rehabilitation but not for those discharged home. The study, one of few of its kind, has been published in JAMA Network Open.
"These results indicate that CHW interventions may help reduce hospital readmissions and improve preventive care among some clinically complex patients ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Using waste heat to power an environmentally sustainable future
City, University of London's Dr Martin White, explores a novel organic Rankine system for converting waste heat into electricity.