Real-world flight data shows continued need for social distancing
2021-05-26
(Press-News.org) REYKJAVIK, Iceland 26 May 2021 - Current vaccination programmes alone will have a limited effect in stopping the second wave of COVID infections in the US, according to a study conducted by scientists from Reykjavik University, University of Lyon, University of Southern Denmark and University of Naples Federico II, and published in the Nature Group journal Scientific Reports today. The findings suggest that strict social distancing and other non-pharmaceutical methods are still necessary to end the ongoing second wave in the US and prevent a new one from rising.
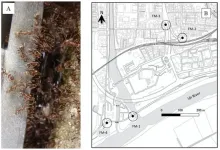
The study fed real-world data on human mobility into a mathematical model previously used to predict the second wave of COVID in the US. As a proxy for general human mobility between regions in the US, the authors use data from the OpenSky Network, a non-profit association that provides open access to real-world air traffic control data for research purposes. The mathematical model, previously developed by the authors, was first tested and calibrated using data on the pandemic's progression in the first wave. Here, deploying the model on flight-control data, they show that given current rates of mobility in the US and the rate of vaccination, the vaccination campaign alone will not stop the ongoing wave of infections.
Dr Anna Sigridur Islind and Dr Maria Oskarsdottir, assistant professors in the Department of Computer Science at Reykjavik University, led the work with the OpenSky Data. "Our analysis clearly demonstrates that continued vigilance is needed regarding social distancing and other non-pharmaceutical methods in the US, since not everyone can be vaccinated at once and because there is a considerable time lag from vaccination to immunity," Dr Islind said.
"Our results underscore the importance of using real-world data on human mobility relating to the pandemic and to inform public health strategies. This is especially important in a pandemic as complex as COVID and that has had such an uneven public health response, with huge variability in vaccination rates, social distancing regulations, and other measures. The flight-control data is very useful, as it comprises real-world information about rates of interstate travel and so provides a valuable broader view of human mobility on a large scale," Dr Oskarsdottir added.
INFORMATION:
For further information, please contact
Eirikur Sigurdsson, Director of Communications at Reykjavik University,
+354 859 5117, eirikursig@ru.is
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-26
Researchers have successfully detected the environmental DNA (eDNA *1) of the Argentine ant (*2) in surface soil samples from sites on Kobe's Port Island and in Kyoto's Fushimi District, two areas that have a long history of destruction caused by this invasive species. The research group included then graduate student YASASHIMOTO Tetsu and Associate Professor MINAMOTO Toshifumi of Kobe University's Graduate School of Human Development and Environment, Visiting Professor OZAKI Mamiko of the Graduate School of Engineering, and NAKAJIMA Satoko, formally of the Kyoto Prefectural Institute of Public Health and Environment.
This method can be used to enable scientists ...
2021-05-26
A newly released scientific paper in Nature Publishing's Scientific Reports Journal has revealed unprecedented amounts of highly toxic mercury are deposited in the deepest trenches of the Pacific Ocean.
The study, a multi-national effort involving scientists from Denmark, Canada, Germany and Japan, reports the first-ever direct measurements of mercury deposition into one of the logistically most challenging environments to sample on Earth, and the deepest at eight to 10 kilometers under the sea.
Lead author Professor Hamed Sanei, Director of the Lithospheric Organic Carbon Laboratory (LOC) at the Department of Geoscience, ...
2021-05-26
What information is retained in a memory over time, and which parts get lost? These questions have led to many scientific theories over the years, and now a team of researchers at the Universities of Glasgow and Birmingham have been able to provide some answers.
Their new study, which is published today in Nature Communications, demonstrates that our memories become less vibrant and detailed over time, with only the central gist eventually preserved. Moreover, this 'gistification' of our memories is boosted when we frequently recall our recent experiences.
The work could have implications in a number of areas, including the nature of memories in post-traumatic stress disorder, the repeated questioning ...
2021-05-26
The biological clock is present in almost all cells of an organism. As more and more evidence emerges that clocks in certain organs could be out of sync, there is a need to investigate and reset these clocks locally. Scientists from the Netherlands and Japan introduced a light-controlled on/off switch to a kinase inhibitor, which affects clock function. This gives them control of the biological clock in cultured cells and explanted tissue. They published their results on 26 May in Nature Communications.
Life on Earth has evolved under a 24-hour cycle; of light and dark, hot and cold. 'As a result, our cells are synchronized to these 24-hour oscillations,' says Wiktor Szymanski, Professor of Radiological Chemistry at the University ...
2021-05-26
CLEVELAND, Ohio (May 26, 2021)--Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), which causes tingling and numbness in the hand, more commonly affects women than men and tends to peak around the age of menopause. A new study suggests the risk of severe CTS increases in women who underwent bilateral oophorectomy before menopause, and estrogen therapy didn't provide a protective effect. Study results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common nerve disorder in the upper body. Although predominately idiopathic in nature, an association with sex hormones has been suggested because of a higher incidence in women ...
2021-05-26
Oncotarget published "Creation of a new class of radiosensitizers for glioblastoma based on the mibefradil pharmacophore" which reported that this group previously identified a calcium channel blocker, mibefradil, as a potential GBM radiosensitizer. They discovered that mibefradil selectively inhibits a key DNA repair pathway, alternative non-homologous end joining.
Then, they initiated a phase I clinical trial that revealed promising initial efficacy of mibefradil, but further development was hampered by dose-limiting toxicities, including CCB-related cardiotoxicity, off-target hERG channel and cytochrome P450 enzymes interactions.
Here, the authors show that mibefradil inhibits ...
2021-05-26
Even among a large group of cancer survivors who were mostly insured, college educated and had annual incomes above the national average, up to 10% delayed care in the previous 12 months because they simply could not afford out of pocket expenses like copays and deductibles, investigators report.
Being unable to get time off from work and being "nervous" about seeing a health care provider, were among the other frequently cited reasons for not always getting timely survivorship care, investigators at the Medical College of Georgia and Georgia Cancer Center report in the journal Cancer Medicine.
Investigators analyzed data from 5,426 cancer survivors who volunteered to share their information with the National Institutes of Health's All of Us Research Program, a historic effort ...
2021-05-26
The pandemic has increased older adults' willingness to receive the flu shot, new research shows.
The study analyzed survey results of 4,501 Canadians over the age of 50 from ten provinces.
Twenty per cent of 1,001 research participants aged 50 to 64 indicated they had not considered getting a flu shot, but were now more likely to given the impact of COVID-19. Of these respondents, 92 per cent inducated that they had not been vaccinated against influenza the year before.
Of the 3,500 participants aged 65 and older, eight per cent reported that they had not originally planned to get a flu shot but were now more likely to receive it.
"The pandemic has been ...
2021-05-26
A hidden planetary crisis has long been neglected that is as serious as the disappearance of species and degradation of habitats. Genetic diversity, which reflects the variation in DNA within species and populations and is the key to their capacity to adapt in times of change, is being lost at an alarming rate. According to an article by 28 authors representing 16 countries, the loss of genetic diversity can affect resiliency in the face of environmental change and result in the loss of important services provided to society. Once gone, genetic diversity can take millennia to return. ...
2021-05-26
A new study by Cardiff University in collaboration with the University of Hertfordshire has revealed the huge "secondary burden" placed on those closest to people living with Long Covid.
The researchers surveyed more than 700 Covid-19 survivors along with their partners and close relatives to understand for the first time the impact of the disease on families as a whole.
The findings, published today in BMJ Open, suggest family quality of life is being "severely affected" and a major system of support is needed for both survivors - and those closest to them.
Survivors and their families spoke ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Real-world flight data shows continued need for social distancing