INFORMATION:
Ionophobic electrode boosts energy storage performance
2021-05-27
(Press-News.org) Using renewable energy to replace fossil energy is now considered the best solution for greenhouse gas emission and air pollution problems. As a result, the demand for new and better energy storage technology is strong.
As part of the effort to improve this technology, a group led by Prof. ZHANG Suojiang from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) recently found that ionophobic electrodes can boost energy storage performance.
Their study was published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A on May 8.
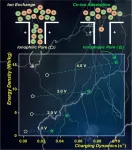
Electric Double-Layer Capacitors (EDLCs) with ionic liquids (ILs)--as a new type of energy storage device--can fill the gap between the power density of batteries and the energy density of conventional capacitors. However, ILs in nanopores often exhibit sluggish diffusion dynamics, which hinder high power density.
In this study, the researchers proposed a new strategy to synergistically improve the energy density and power density of EDLCs with ILs based on massive molecular dynamics simulations.
They constructed a series of EDLCs with different wettability (from ionophilic to ionophobic), using the electrolyte 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate.
When comparing EDLCs with an ionophilic electrode to EDLCs with an extremely ionophobic electrode, the researchers found that the charging time for the latter decreased by ~80% while the capacitance increased by nearly 100% (at U = 4V).
For EDLCs with an ionophobic electrode, ILs cannot spontaneously enter into the porous electrode without charging. With the increase in charging voltage, both the counter ion and co-ion will start to enter the nanopore when the voltage is beyond one critical value (~2 V). At the same time, the diffusion dynamics of ions are faster than the bulk ILs due to the sparsity of ions in the pore.
"Charging the ionophobic pore is like compressing a spring. Once the spring is released, much energy will be generated," said Prof. HE Hongyan from IPE.
This study also identified the quantitative relationship between charging time/capacitance and ionophobic property/pore geometry/electric potential. It revealed how abnormal co-ion adsorption, which does not exist in the common ionophilic electrode, enhances the overall performance of EDLCs with ILs.
The idea of introducing ionophobicity may help the rational design of IL-based high-performance supercapacitors or other energy storage applications in the future.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fish adapt to ocean acidification by modifying gene expression
2021-05-27
Human-driven global change is challenging the scientific community to understand how marine species might adapt to predicted environmental conditions in the near-future (e.g. hypoxia, ocean warming, and ocean acidification). The effects of the uptake of anthropogenic atmospheric CO2 by oceans affects (i.e. ocean acidification) propagate across the biological hierarchy, from changes in the building blocks of life at nano-scales to organism, physiology and behaviour through ecosystem processes and their properties.
To survive in a reduced pH environment, marine organisms have to adjust their physiology which, at the molecular level, is achieved by modifying the expression ...
Quantification of the internal OH- effects in upconversion nanocrystals
2021-05-27
The great application prospect in biology, medicine, optogenetics, photovoltaics and sustainability has enabled lanthanide ions-doped upconversion nanoparticles to attract widespread attention which derives mainly from their superior anti-Stokes spectroscopic property. However, the relatively low upconversion efficiency remains a major bottleneck on their way of actual applications. Internal OH- impurity is known as one of the main detrimental factors affecting the upconversion efficiency of nanomaterials. Different from surface/ligand related emission quenching which can be effectively diminished by, e.g., core/shell structure, internal OH- is easy to be introduced during synthesis but difficult to be quantified and controlled.
In a new paper published in Light Science ...
Low on antibodies, blood cancer patients can fight off COVID-19 with T cells
2021-05-27
PHILADELPHIA--Antibodies aren't the only immune cells needed to fight off COVID-19 -- T cells are equally important and can step up to do the job when antibodies are depleted, suggests a new Penn Medicine study of blood cancer patients with COVID-19 published in Nature Medicine. The researchers found that blood cancer patients with COVID-19 who had higher CD8 T cells, many of whom had depleted antibodies from cancer treatments, were more than three times likelier to survive than patients with lower levels of CD8 T cells.
"It's clear T cells are critical in terms of the early infection and to help control the virus, but we also showed that they can compensate for B cell and antibody responses, which blood cancer patients are likely missing because of the drugs," said co-senior author Alexander ...
Fungus fights mites that harm honey bees
2021-05-27
PULLMAN, Wash. -- A new fungus strain could provide a chemical-free method for eradicating mites that kill honey bees, according to a study published this month in Scientific Reports.
A team led by Washington State University entomologists bred a strain of Metarhizium, a common fungus found in soils around the world, to work as a control agent against varroa mites. Unlike other strains of Metarhizium, the one created by the WSU research team can survive in the warm environments common in honey bee hives, which typically have a temperature of around 35 Celsius (or 95 F).
"We've known that metarhizium could kill mites, but it was expensive and didn't last long because the fungi died in the hive heat," said Steve Sheppard, professor in WSU's Department of Entomology and corresponding ...
Mixtures of two herbicides have less environmental impact when mixed in laboratories
2021-05-27
A research group at the University of Córdoba evaluated the commercial mixture formulated in a laboratory and the tank-based mixture of two herbicides to determine which method is more effective in terms of weed control and environmental impact.
In 2017 the company Nufarm Europe proposed to the Higher Technical School of Agricultural and Forestry Engineering (ETSIAM) at the UCO a study of the results of two products having a significant agronomic impact: the herbicides glyphosate and 2,4-D (synthetic auxin). After three years of research, they concluded that the commercial mix produced in the company's laboratories is more effective than manual mixes produced in tanks.
To do this, they used in vivo techniques (tests with greenhouse ...
UTSA researchers among collaborative improving computer vision for AI
2021-05-27
MAY 26, 2021 -- Researchers from UTSA, the University of Central Florida (UCF), the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) and SRI International have developed a new method that improves how artificial intelligence learns to see.
Led by Sumit Jha, professor in the Department of Computer Science at UTSA, the team has changed the conventional approach employed in explaining machine learning decisions that relies on a single injection of noise into the input layer of a neural network.
The team shows that adding noise--also known as pixilation--along multiple layers of a network provides a more robust representation of an image that's recognized by the AI ...
Development anomalies recorded for the first time in a rare tiger moth
2021-05-27
The Menetries' tiger moth (Arctia menetriesii) is one of the rarest and most poorly studied Palaearctic moth species. Even though its adult individuals are large and brightly coloured, they are difficult to spot, because they aren't attracted to light, they're not active at night, and they fly reluctantly. Currently, the species only inhabits two countries - Finland and the Russian Federation, and is included in the Red Lists of both, as Data Deficient in the former and Vulnerable in the latter.
For 13 years, researcher Evgeny Koshkin of the Institute of Water and Ecology Problems of the Far ...
Sleep warning for older men
2021-05-27
Men aged 65 and over should monitor their sleep patterns and seek medical advice after a warning from Flinders University experts that disrupted slumber can be linked to cognitive dysfunction.
In a new article published in the Journal of Sleep Research, the Adelaide Institute for Sleep Health research group studied a group of 477 middle-aged and older men's attention and processing speed in relation to their sleep.
The participants from the Florey Adelaide Male Ageing Study undertook cognitive testing and a successful sleep study.
"Less deep sleep and more light sleep is related to slower responses on cognitive function tests," says lead author Jesse Parker. ...
Shiny mega-crystals that build themselves
2021-05-27
To really appreciate what a team of researchers led by Maksym Kovalenko and Maryna Bodnarchuk has achieved, it is best to start with something mundane: Crystals of table salt (also known as rock salt) are familiar to anyone who has ever had to spice up an overtly bland lunch. Sodium chloride - NaCl in chemical terms - is the name of the helpful chemical; it consists of positively charged sodium ions (Na+) and negatively charged chloride ions (Cl-). You can imagine the ions as beads that strongly attract each other forming densely packed and rigid crystals like the ...
NTU Singapore scientists turn aquaculture waste into new biomaterial for tissue repair
2021-05-27
Scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have developed a new biomaterial made entirely from discarded bullfrog skin and fish scales that could help in bone repair.
The porous biomaterial, which contains the same compounds that are predominant in bones, acts as a scaffold for bone-forming cells to adhere to and multiply, leading to the formation of new bone.
Through laboratory experiments, the NTU Singapore team found that human bone-forming cells seeded onto the biomaterial scaffold successfully attached themselves and started multiplying - a sign of growth. They also found that the risk of the biomaterial triggering an inflammatory response is low.
Such a scaffold could be used to help with the regeneration of ...