INFORMATION:
Co-authors include Dr. Augusto Ochoa, Director of the LSU Health New Orleans Stanley S. Scott Cancer Center, Dr. Justin Brown of the Pennington Biomedical Research Center and member of the LSU Health New Orleans Stanley S. Scott Cancer Center, and Dr. Linda Anne Gilmore of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health -- National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institute of General Medicine Sciences, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Cancer Institute -- Nutrition Obesity Research Center at Pennington Biomedical Research Center, LSU Health New Orleans, and Susan G. Komen Foundation.
LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans educates Louisiana's health care professionals. The state's flagship health sciences university, LSU Health New Orleans includes a School of Medicine with branch campuses in Baton Rouge and Lafayette, the state's only School of Dentistry, Louisiana's only public School of Public Health, and Schools of Allied Health Professions, Nursing, and Graduate Studies. LSU Health New Orleans faculty take care of patients in public and private hospitals and clinics throughout the region. In the vanguard of biosciences research in a number of areas in a worldwide arena, the LSU Health New Orleans research enterprise generates jobs and enormous economic impact. LSU Health New Orleans faculty have made lifesaving discoveries and continue to work to prevent, advance treatment, or cure disease. To learn more, visit http://www.lsuhsc.edu, http://www.twitter.com/LSUHealthNO, or http://www.facebook.com/LSUHSC.
LSU Health New Orleans describes a causal mechanism of link between cancer and obesity
2021-05-27
(Press-News.org) New Orleans, LA - A review study led by Maria D. Sanchez-Pino, PhD, an assistant research professor in the departments of Interdisciplinary Oncology and Genetics at LSU Health New Orleans' School of Medicine and Stanley S. Scott Cancer Center, advances knowledge about the connection between obesity-associated inflammation and cancer. The researchers suggest that inflammatory cells with immunosuppressive properties may act as a critical biological link between obesity and cancer risk, progression, and metastasis. The paper is published in the June 2021 issue of Obesity, available here.
Despite evidence showing that obesity increases the risk of cancer progression, efforts are needed to identify the causal relationship between immunosuppressive cells and the response of immunotherapy in patients with obesity.
The function of myeloid cells is shaped by the metabolic microenvironment. Along with macrophages, myeloid cells with immunosuppressive properties called Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are generated in obesity. One of the major factors associated with the metabolic inflammation of obesity is the expansion of MDSCs. In cancer patients, MDSCs are associated with poor survival and resistance to immunotherapy.
Although there is tremendous cross-talk between inflammation and metabolic/endocrine disturbances that promote tumor growth in obesity, the biological and molecular mechanisms are not completely understood. The researchers reviewed the literature and explain that altered metabolic factors such as lipids, insulin, and leptin in obesity contribute to the activation of immunosuppressive and cancer developing capabilities of myeloid cells.
"Deciphering the molecular mechanisms by which obesity-associated metabolic factors activate or enhance the function of Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells and immunosuppressive macrophages will allow us to identify biomarkers for prognosis and therapeutic responses," notes Dr. Sanchez-Pino. "It will also lead to the discovery of potential targets for pharmacological therapies that may disrupt the pathophysiologic inflammatory link between obesity and cancer."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
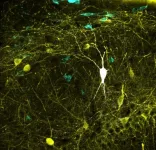
Study upgrades one of the largest databases of neuronal types
2021-05-27
The study, which is published in the journal PLOS Biology, represents the most comprehensive mapping performed to date between neural activity recoded in vivo and identified neuron types. This major breakthrough may enable biologically meaningful computer modeling of the full neuronal circuit of the hippocampus, a region of the brain involved in memory function.
Circuits of the mammalian cerebral cortex are made up of two types of neurons: excitatory neurons, which release a neurotransmitter called glutamate, and inhibitory neurons, which release GABA (gamma-aminobutanoic acid), the main inhibitor of the central nervous system. "A balanced dialogue between the 'excitatory' and 'inhibitory' activities is critical for brain function. ...
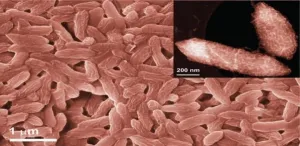
Recruiting bacteria to build catalysts atom by atom
2021-05-27
Exploiting the unusual metal-reducing ability of the iron-breathing bacterium Geobacter sulfurreducens, KAUST researchers have demonstrated a cheap and reliable way to synthesize highly active single-atom catalysts. The innovation, which could dramatically improve the efficiency and cost of hydrogen production from water, highlights the role nature can play in the search for new energy systems.
Many chemical reactions require a catalyst as a reactive surface where atoms or molecules are brought together with the right amount of energy to spark a chemical change. Water, for example, can be split into hydrogen and oxygen atoms by reacting on a pair of electrodes made of platinum and iridium oxide. The efficiency of the reaction, however, depends largely ...
It takes some heat to form ice!
2021-05-27
Water freezes and turns to ice when brought in contact with a cold surface - a well-known fact. However, the exact process and its microscopic details remained elusive up to know. Anton Tamtögl from the Institute of Experimental Physics at TU Graz explains: "The first step in ice formation is called 'nucleation' and happens in an incredibly short length of time, a fraction of a billionth of a second, when highly mobile individual water molecules 'find each other' and coalesce." Conventional microscopes are far too slow to follow the motion of water molecules and so it is impossible to use them to 'watch' how molecules combine on top of solid surfaces.
Findings turn previous understanding of ice formation upside down
With the help ...
Sometimes, even 3-year-olds just want to fit in with the group
2021-05-27
DURHAM, N.C. -- What makes preschoolers eat their veggies? Raise their hand? Wait their turn? "Because I say so" is a common refrain for many parents. But when it comes to getting kids to behave, recent research suggests that the voice of adult authority isn't the only thing that matters. Around age three, fitting in with the group starts to count big too.
That's the finding of a new study by Duke University researchers showing that, by their third birthday, children are more likely to go along with what others say or do for the sake of following the crowd, rather than acting out ...
Cell mechanics research is making chemotherapy friendlier
2021-05-27
Malignant tumour cells undergo mechanical deformation more easily than normal cells, allowing them to migrate throughout the body. The mechanical properties of prostate cancer cells treated with the most commonly used anti-cancer drugs have been investigated at the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Cracow. According to the researchers, current drugs can be used more effectively and at lower doses.
In cancer, a key factor contributing to the formation of metastasis is the ability of the neoplastic cells to undergo ...
Pertussis more common in Europe than previously thought
2021-05-27
Although vaccination programmes against pertussis are very effective in Europe, new Finnish study shows that the disease is still very common among middle-aged adults in various European countries. At the same time, the results show that the disease is underdiagnosed as the annually reported figures are considerably lower than those discovered in the study.
The primary cause of pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is the Bordetella pertussis agent which spreads through the respiratory mucosa and produces toxins that damage the mucous membrane. These toxins incapacitate the body's ...
Vaccine target for devastating livestock disease could change lives of millions
2021-05-27
The first ever vaccine target for trypanosomes, a family of parasites that cause devastating disease in animals and humans, has been discovered by scientists at the Wellcome Sanger Institute. By targeting a protein on the cell surface of the parasite Trypanosoma vivax, researchers were able to confer long-lasting protection against animal African trypanosomiasis (AAT) infection in mice.
The study, published today (26 May 2021) in Nature, is the first successful attempt to induce apparently sterile immunity against a trypanosome parasite. A vaccine was long thought impossible due to the sophisticated ability of the parasites to evade the host immune system. As well as a strong ...
Global microbiome study discovers thousands of new species, maps urban antimicrobial resistance and reveals new drug candidates
2021-05-27
NEW YORK (May 26, 2021) -- About 12,000 bacteria and viruses collected in a sampling from public transit systems and hospitals around the world from 2015 to 2017 had never before been identified, according to a study by the International MetaSUB Consortium, a global effort at tracking microbes that is led by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators.
For the study, published May 26 in Cell, international investigators collected nearly 5,000 samples over a three-year period across 60 cities in 32 countries and six continents. The investigators analyzed the samples using a genomic sequencing ...
Checking out plastic surgeons on Instagram? Your perception may be biased
2021-05-27
May 26, 2021 - Social media sites - especially Instagram - have revolutionized the way plastic surgeons market their practice. These platforms allow surgeons to post testimonials, educational videos, and before-and-after photos. This information can help to guide patients in making decisions about whether to undergo cosmetic surgery and which plastic surgeon to choose, based on factors like the surgeon's experience and results achieved.
However, patient perceptions of plastic surgeons' skills may also be affected by implicit bias - based solely on the ethnicity of the surgeon's name. "In our survey of responses to otherwise-identical Instagram ...
Magnetized threads weave spectacular galactic tapestry
2021-05-27
Threads of superheated gas and magnetic fields are weaving a tapestry of energy at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. A new image of this new cosmic masterpiece was made using a giant mosaic of data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and the MeerKAT radio telescope in South Africa.
The new panorama of the Galactic Center builds on previous surveys from Chandra and other telescopes. This latest version expands Chandra's high-energy view farther above and below the plane of the Galaxy - that is, the disk where most of the Galaxy's stars reside - than previous imaging campaigns. In the image featured in our main graphic, X-rays from Chandra are orange, green, blue and purple, showing different X-ray energies, and the ...