(Press-News.org) Invasive species, beware: Your days of hiding may be ending.
Biologists led by the University of Iowa discovered the presence of the invasive New Zealand mud snail by detecting their DNA in waters they were inhabiting incognito. The researchers employed a technique called environmental DNA (eDNA) to reveal the snails' existence, showing the method can be used to detect and control new, unknown incursions by the snail and other invasive species.
"eDNA has been used successfully with other aquatic organisms, but this is the first time it's been applied to detect a new invasive population of these snails, which are a destructive invasive species in fresh waters around the world," says Maurine Neiman, associate professor in the Department of Biology and the study's co-author. "eDNA can be used to find organisms at really early stages of invasion, so it can detect a population even when there are so few of the organisms that traditional methods would never find them."
The biologists traveled to central Pennsylvania seeking evidence of the presence of the mud snail, which for decades has been spreading in fresh waters in the continental United States, beginning in the Northwest, moving to the Great Lakes, and now migrating along the Eastern Seaboard. The tiny aquatic snails' population densities can balloon to more than 500,000 individuals in a square yard, covering the water bottom and crowding out native species.
The researchers collected samples from eight sites spread across six rivers in the Susquehanna River watershed, which feeds into Chesapeake Bay and the Mid-Atlantic watershed. Six of the sites had no reported cases of the mud snail, despite physical surveys, while the other two locations had not been studied.
The researchers used the eDNA technique to look for DNA the snails would leave as tracers in sloughed-off skin cells or bodily waste. They discovered the snails were there, after all: The eDNA results confirmed the mud snails were at one site where none had been detected previously, and were likely at low population levels at other sites as well.
"This study presents an important step forward in demonstrating that eDNA can be successfully applied to detect new P. antipodarum invasions and will allow us to more accurately track and potentially halt ongoing range expansion of this destructive invasive species," wrote James Woodell, a research support technician at University of Hawai?i at Mānoa who performed the research while a master's student in biology at Iowa and is the study's corresponding author.
The eDNA technique was developed less than a decade ago. It has been used to ferret out invasive species, including fish, frogs, and crustaceans, in aquatic ecosystems. For this study, the biologists refined the filtering protocols from an existing eDNA sampling system for mud snail detection and tested it for the first time in the field.
INFORMATION:
The study, "Matching a snail's pace: Successful use of environmental DNA techniques to detect early stages of invasion by the destructive New Zealand mud snail," was published online on June 1 in the journal Biological Invasions.
Edward Levri, from Pennsylvania State University-Altoona, led the project proposal and is a study co-author. The Mid-Atlantic Panel on Aquatic Invasive Species funded the research.
How old is your brain compared to your chronological age? A new measure of brain health developed by researchers at Rush University Medical Center may offer a novel approach to identifying individuals at risk of memory and thinking problems, according to research results published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association on June 1.
Dubbed the "cognitive clock" by the researchers, the tool is a measure of brain health based on cognitive performance. It may be used in the future to predict the likelihood of memory and thinking problems that develop ...
Rare disease experts detail the first results of an unprecedented collaboration to diagnose people living with unsolved cases of rare diseases across Europe. The findings are published today in a series of six papers in the European Journal of Human Genetics.
In the main publication, an international consortium, known as Solve-RD, explains how the periodic reanalysis of genomic and phenotypic information from people living with a rare disease can boost the chance of diagnosis when combined with data sharing across European borders on a massive scale. Using this new approach, a preliminary reanalysis of data from 8,393 individuals resulted in 255 new diagnoses, some with atypical manifestations of known diseases.
A complementary study ...
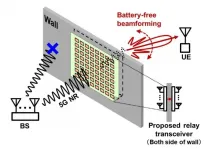
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) have developed a wirelessly powered relay network for 5G systems. The proposed battery-free communication addresses the challenges of flexible deployment of relay networks. This design is both economical and energy-efficient. Such advances in 5G communications will create tremendous opportunities for a wide range of sectors.
The ever-increasing demand for wireless data bandwidth shows no sign of slowing down in the near future. Millimeter wave, a short wavelength spectrum, has shown great potential in 5G communications and beyond. To leverage ...
Sophia Antipolis - 1 June 2021: A study in 5.8 million children has found a higher incidence of stroke four decades later in those whose mother had high blood pressure or pre-eclampsia while pregnant. The research is presented at ESC Heart & Stroke 2021, an online scientific conference of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
"Our findings indicate that hypertensive disorders during pregnancy are associated with increased risks of stroke and potentially heart disease in offspring up to the age of 41 years," said study author Dr. Fen Yang, PhD student, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden. "Studies with longer follow-up are needed to confirm the results and ...
VANCOUVER, Wash. - A new study in Global Biogeochemical Cycles shows per-area greenhouse gas emissions from the world's water reservoirs are around 29% higher than suggested by previous studies, but that practical measures could be taken to help reduce that impact.
Much of the increase in emissions comes from previously unaccounted for methane degassing, a process where methane passes through a dam and bubbles up downstream, according to the analysis by Washington State University and University of Quebec at Montreal scientists.
Overall, the researchers found ...
PULLMAN, Wash. - No billionaires live among the Tsimane people of Bolivia, although some are a bit better off than others. These subsistence communities on the edge of the Amazon also have fewer chronic health problems linked to the kind of dramatic economic disparity found in industrialized Western societies.
For a study in the journal eLife, a research team led by Aaron Blackwell of Washington State University and Adrian Jaeggi of University of Zurich tracked 13 different health variables across 40 Tsimane communities, analyzing them against each person's wealth and the degree of inequality in each community. While some have theorized that inequality's health impacts are universal, the researchers found only two robustly associated outcomes: higher blood pressure and ...
Electrical engineers at the University of California San Diego developed a technology that improves the resolution of an ordinary light microscope so that it can be used to directly observe finer structures and details in living cells.
The technology turns a conventional light microscope into what's called a super-resolution microscope. It involves a specially engineered material that shortens the wavelength of light as it illuminates the sample--this shrunken light is what essentially enables the microscope to image in higher resolution.
"This material converts low resolution light to high resolution light," said Zhaowei Liu, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at UC San Diego. "It's very simple ...
An enhanced learning environment during the first five years of life shapes the brain in ways that are apparent four decades later, say Virginia Tech and University of Pennsylvania scientists writing in the June edition of the Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience.
The researchers used structural brain imaging to detect the developmental effects of linguistic and cognitive stimulation starting at six weeks of age in infants. The influence of an enriched environment on brain structure had formerly been demonstrated in animal studies, but this is the first experimental study to find a similar result in humans.
"Our research shows a relationship between brain structure and five years of high-quality, educational and social experiences," said Craig Ramey, ...
New research has shown that if people achieve and maintain substantial weight loss to manage their type 2 diabetes, many can also effectively control their high blood pressure and stop or cut down on their anti-hypertensive medication.
A weight management programme, developed by researchers at the Universities of Glasgow and Newcastle for the Diabetes UK-funded DIabetes REmission Clinical Trial (DIRECT), has proved effective at lowering blood pressure and reducing the need for anti-hypertensive medications, as well as bringing remission of type 2 diabetes.
The programme involves an initial 12 weeks on a nutritionally complete formula diet (low calorie soups and shakes) which will induce weight loss ...
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. Tai chi about equal to conventional exercise for reducing belly fat in middle-aged and older adults
HD video soundbites ...