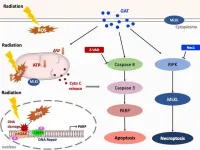
Ganoderic acid increases radiosensitivity of cancer cell
2021-06-01
(Press-News.org) Recently, the research team led by Prof. KONG Lingtao from Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) prepared a highly active single iron atom catalyst (Fe-ISAs@CN) which can activate H2O2 to generate free radicals, achieving rapid removal of sulfadiazine pollutants in aqueous. The relevant results were published in Journal of Colloid and Interface Science.
Sulfadiazine (SDZ), a kind of synthetic sulfadiazine antibiotic, is widely used in clinical and animal husbandry industries. However, due to its large-scale use and unqualified discharge of wastewater, more and more antibiotic residues are detected in the water environment. These antibiotics are still highly toxic at very low concentrations. Due to the stable chemical structure of sulfadiazine, it is difficult to solve the residual problem with conventional processing technology.
In this research, researchers synthesized the Fe(acac)3@ZIF8 precursor using a solvothermal method, and then calcined at a high temperature of 930? to prepare a dodecahedral Fe-ISAs@CN catalyst with uniform morphology and good dispersion. Its rough surface and hollow structure provide a large specific surface area and expose a large number of adsorption sites.
The results of degradation experiments showed that 0.1g/L Fe-ISAs@CN could remove 91% of 20 mg/L SDZ within 60 minutes under acid pH conditions.
"We looked into the mechanism, and found those active sites could rapidly activate H2O2 in a short time," said YANG Wu, leading scientist of the research, "It produced a large number of active substances with stronger oxidizing energy, and the adsorption site could adsorb SDZ to assist the degradation process."
The result proved the rapid degradation of sulfadiazine in the restricted range. Combined with the LC-MS data, they proposed the possible degradation pathways. After five cycles, the removal rate of sulfadiazine was still greater than 80%, and the loss of iron in the catalyst was rather small, indicating good stability of the material.
This work breaks through the traditional Fenton's stringent pH restrictions and provides new ideas for the rapid and deep removal of micro-pollutants in water by nanomaterials.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-01
Graphene-based materials can be obtained using various reducing agents, many of which are dangerous and toxic chemicals, and the obtained graphene-based materials are prone to aggregation, limiting their practical applications.
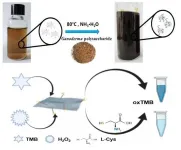
Recently, a research group of Prof. HUANG Qing from the Institute of Intelligent Machines, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), prepared graphene-based nanozymes through a simple and green preparation method, and verified that it can be used to detect L-cysteine in serum.
The study, published in Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation ...
2021-06-01
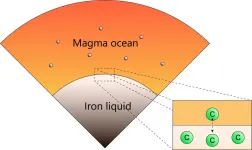
According to the theory of planet formation, rocky bodies such as the Earth were formed by repeating collisions from dusty materials. In this process, a number of Mercury- or Mars-sized planetary embryos, were formed, and eventually these bodies merged together and formed terrestrial planets in our solar system. During the formation of the planetary embryos, the interior of these bodies was likely to be molten due to the heat by radiative-decay elements and a collisional energy of the planetary embryos. At this stage, iron and silicate separate, and form the metallic core and ...
2021-06-01
It might seem like a given that mothers take extra risks to protect their children, but have you ever wondered why? A new study led by Kumi Kuroda at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan shows that in mice, this and other nurturing behaviors are driven in part by neurons in a small part of the forebrain that contain a protein called the calcitonin receptor. The study was published in Cell Reports.
Many simple behaviors, such as eating and drinking, are driven by different parts of the brain's hypothalamus. The new study focused on identifying the part that drives a much more complicated behavior: caring for infants. As Kuroda explains, "we were able to narrow down the brain cells necessary ...
2021-06-01
Most prescriptions for the drug buprenorphine, used to treat opioid use disorder, are written by a small number of the health care providers, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Published in the June 1 edition of the Journal of the American Medical Association, the study found that half of all patient-months of buprenorphine treatment during 2016 and 2017 were prescribed by just 4.9% of the physicians and other providers who prescribed the drug during the period.
"These findings have important implications for efforts to increase buprenorphine access," said Dr. Bradley D. Stein, the study's lead author and a senior physician researcher at RAND, a nonprofit research organization. "Our study suggests that targeted efforts to encourage more current prescribers to become high-volume ...
2021-06-01
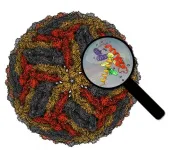
In a recent study, Australian scientists used an original approach to resolve the 3D structure of flaviviruses with an unprecedented level of detail, identifying small molecules known as 'pocket factors' as new therapeutic targets.
Flaviviruses infect humans by mosquito or tick bite, with symptoms ranging from fever and myalgia to life-threatening neurological and congenital conditions. Flaviviruses such as dengue, yellow fever and Zika threaten almost a third of the world's population, and new flaviviruses emerge regularly from animal reservoirs with the potential to cause epidemics. ...
2021-06-01
A research team led by scientists at Université de Montréal has developed a unique observational tool for assessing children up to 5 years of age who have had a concussion. The work is explained in a study published in the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation.
Pediatric traumatic brain injury (TBI) is particularly prevalent in toddlers; they're more likely to be injured because they have a lower sense of danger and are still developing physically. But parents and clinicians have trouble detecting symptoms of trauma, given the toddler's limited verbal skills.
"A young child will not tell you that they have a headache or feel dizzy," said Dominique Dupont, an UdeM postdoctoral student in neuropsychology and first author of the study.
"But assessing post-concussion symptoms ...
2021-06-01
PHILADELPHIA--An odor-based test that sniffs out vapors emanating from blood samples was able to distinguish between benign and pancreatic and ovarian cancer cells with up to 95 percent accuracy, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Pennsylvania and Penn's Perelman School of Medicine.
The findings suggest that the Penn-developed tool -- which uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to decipher the mixture of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitting off cells in blood plasma samples -- could serve as a non-invasive approach ...
2021-06-01
Our lives today are governed by electronics in all shapes and forms. Electronics, in turn, are governed by their batteries. However, the traditional lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), that are widely used in electronic devices, are falling out of favor because researchers are beginning to view lithium metal batteries (LMBs) as a superior alternative due to their remarkably high energy density that exceeds LIBs by an order of magnitude! The key difference lies in the choice of anode material: LIBs use graphite, whereas LMBs use lithium metal.
Such a choice, however, comes with its own challenges. Among the most prominent ones is the formation ...
2021-06-01
Singapore, 1 June 2021 - The discovery and development of new small-molecule compounds for therapeutic use involves a huge investment of time, effort and resources. Giving a new spin to conventional chemical synthesis, a team of researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) has developed a way to automate the production of small molecules suitable for pharmaceutical use. The method can potentially be used for molecules that are typically produced via manual processes, thereby reducing the manpower required.
The research team that achieved this technological breakthrough was led by Assistant Professor Wu Jie from the NUS Department of Chemistry as well as Associate Professor Saif A. Khan from ...
2021-06-01
Bribery in the public healthcare does not solve the problem of poor quality of services, and even exacerbates it, researchers argue. The same can be said about the well-being of patients and their own assessment of health. In other words, bribes in the healthcare do not provide good quality services and do not pay off. Such conclusions were reached by an international team of researchers, including Olga Popova, the article's co-author, an associate professor at the Ural Federal University (UrFU, Russia).
Researchers examined survey data on 41,000 citizens from 28 post-communist countries in Central and Eastern Europe, as well as ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ganoderic acid increases radiosensitivity of cancer cell