(Press-News.org) SAN FRANCISCO, CA (June 3, 2021) -- Since arriving to the northern Atlantic Ocean less than 30 years ago, lionfish have quickly become one of the most widespread and voracious invasive species, negatively impacting marine ecosystems--particularly coral reefs--from the northeast coast of the United States to the Caribbean Islands. In a new study, an international research team including the California Academy of Sciences presents four new records of lionfish off the coast of Brazil, confirming the invasion of the predatory fish into the South Atlantic for the first time. Their findings, published today in Biological Invasions, discuss how the lionfish may have arrived in the region, and hold important insights on how Brazil's diving and fishing communities can help manage the invasion before it potentially devastates local ecosystems.
"For a while it was uncertain whether or not lionfish would extend into the South Atlantic," says Academy Curator of Ichthyology and study co-author Luiz Rocha. "Now that we know they are here, it is imperative that we uncover how they arrived and work with local communities to keep the population under control. If left unchecked, lionfish could have a huge impact on local species, particularly those that exist solely in the reefs surrounding Brazil's oceanic islands."
Sporting maroon stripes and more than a dozen venomous spines, lionfish have long been a staple in the hobbyist aquarium trade. Like other popular aquarium fish, however, they are sometimes irresponsibly released into the wild. Indeed, it is likely that the invasion of lionfish in the Atlantic Ocean began that way.
Once they enter new waters, lionfish can quickly disrupt local ecosystems and disperse to other locations. Due to their broad diet, lack of natural predators, unique hunting style, and year-round reproduction of buoyant eggs that can travel long distances on ocean currents, lionfish have expanded faster than any other invasive marine species.
Despite those traits, lionfish have been noticeably absent in the South Atlantic--a phenomenon that the researchers attribute to the northerly flowing currents at the oceanic boundary between Brazilian and Caribbean waters. But in 2015, a local diver photographed a lionfish swimming off the southern coast of Brazil and alerted the researchers, who 11 months later found and collected the specimen confirming the species' expansion into Brazil.
After that initial discovery, the researchers--with help from local fisherman and divers--were able to track down three additional lionfish in Brazil's waters: two from deep coral reefs known as mesophotic reefs and one from reefs surrounding the Fernando de Noronha Archipelago around 200 miles off the country's northeastern coast.
Though all of the incidents are troubling, the researchers say that the Fernando de Noronha record is of particular concern. "The arrival of lionfish to Brazil's oceanic islands is especially worrying," says marine biologist and study co-author Clara Buck. "These unique ecosystems have a high number of endemic species found nowhere else on Earth making them much more sensitive to adverse impacts."
To curb the invasion before it accelerates, it is crucial to know how the lionfish are arriving in the region in the first place. In their study, the researchers propose that the lionfish found in the mesophotic reefs may have arrived in a stepping-stone fashion, utilizing deeper reefs under the Amazon plume to slowly push southwards from the Caribbean.
In contrast, they suggest that the individual found at Fernando de Noronha arrived by more conventional means, traveling along the currents between the islands and the Caribbean as a larva. Since the archipelago is distant from the mainland, lionfish larva can subvert the oceanic boundary that exists closer to the coastline.
Finally, while the lionfish off the southern coast was too far away from the Caribbean to have arrived there by dispersal or mesophotic reef hopping, the researchers were able to confirm through a DNA analysis that it originated from the Caribbean population, suggesting it may have been removed from the Caribbean and introduced to Brazilian waters through the aquarium trade.
Regardless of how they arrived, now that the lionfish are there the researchers urge the Brazilian government and local communities to stem the invasion. While efforts elsewhere in the Atlantic have shown that full eradication of the lionfish is unlikely, the researchers say that keeping population numbers low could buy precious time for local species to adapt to the voracious fish and ultimately avoid predation.
From spearing the lionfish they come across to alerting researchers of emerging populations, local fishermen and divers--like those who assisted with this study--will play a critical role in managing the invasion, and protecting the coral reefs and local species that sustain their livelihoods.
Despite the challenges they face, Rocha is optimistic they can succeed. "Brazil, and Fernando de Noronha in particular, have robust local diving and fishing communities," he says. "If we put the right tools in their hands, it is absolutely possible to keep the invasion under control."
INFORMATION:
About Research at the California Academy of Sciences
The Institute for Biodiversity Science and Sustainability at the California Academy of Sciences is at the forefront of efforts to understand two of the most important topics of our time: the nature and sustainability of life on Earth. Based in San Francisco, the Institute is home to more than 100 world-class scientists, state-of-the-art facilities, and nearly 46 million scientific specimens from around the world. The Institute also leverages the expertise and efforts of more than 100 international Associates and 450 distinguished Fellows. Through expeditions around the globe, investigations in the lab, and analysis of vast biological datasets, the Institute's scientists work to understand the evolution and interconnectedness of organisms and ecosystems, the threats they face around the world, and the most effective strategies for sustaining them into the future. Through innovative partnerships and public engagement initiatives, they also guide critical sustainability and conservation decisions worldwide, inspire and mentor the next generation of scientists, and foster responsible stewardship of our planet.
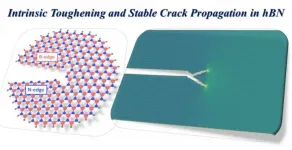
A team of scientists led by Nanyang Technological University (NTU Singapore) and Rice University in the US, has uncovered the key to the outstanding toughness of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN). h-BN can withstand ten times the amount of force that graphene can, which is known as one of the toughest materials on Earth.
A two-dimensional (2D) material, h-BN has a thickness of just one atom. First used in cosmetics in the 1940s, it was soon abandoned due to its high price, making a resurgence in the late 1990s after technology made its production cheaper.
Today, it is used by nearly all leading producers of cosmetic products because of its ability to absorb excess facial sebum and disperse pigment evenly, ...
Mangrove vegetation, which grows naturally in subtropical shorelines, provides a wide range of ecosystem functions such as reducing coastal erosion, promoting biodiversity, and removing nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon dioxide. These vital ecological functions are influenced by the water flow around the intricate mangrove roots, which create a complex energetic process that mixes up sediments and generates a depositional region behind the roots. How these mangrove roots interact with water flow is believed to be a key element in mitigating coastal erosion.
Accurately projecting hydrodynamic erosion and the essential amount of mangrove species has been a challenge for managers and restoration experts to forecast a successful component of project designs. That is because ...
WASHINGTON (June 3, 2021) - Nearly three-quarters of breast cancer patients (73%) report using at least one type of complementary medicine after cancer diagnosis, while oncologists believe that less than half (43%) of patients are using these approaches during cancer care. These and other findings from a national survey of oncologists and breast cancer patients were released in conjunction with the 2021 ASCO Annual Meeting. The study found that doctors report discussing integrative health with only about half of patients, leading patients to seek information outside the clinic.
"Cancer is a complex ...
Astronomers studying the fast-moving jet of material ejected by a still-forming, massive young star found a major difference between that jet and those ejected by less-massive young stars. The scientists made the discovery by using the U.S. National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) to make the most detailed image yet of the inner region of such a jet coming from a massive young star.
Both low- and high-mass young stars, or protostars, propel jets outward perpendicular to a disk of material closely orbiting the star. In stars with masses similar to the Sun, these jets are narrowed, or focused, relatively tightly near to the star in a process called collimation. Because most high-mass protostars are more distant, studying ...
New research into Alzheimer's disease (AD) suggests that secondary infections and new inflammatory events amplify the brain's immune response and affect memory in mice and in humans - even when these secondary events occur outside the brain.
Scientists believe that key brain cells (astrocytes and microglia) are already in an active state due to inflammation caused by AD and this new research shows that secondary infections can then trigger an over-the-top response in those cells, which has knock-on effects on brain rhythms and on cognition.
In the study, just published in Alzheimer's & Dementia, the journal ...
Facing the triple threat of climate change, loss of nature and pollution, the world must deliver on its commitment to restore at least one billion degraded hectares of land in the next decade - an area about the size of China. Countries also need to add similar commitments for oceans, according to a new report by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN (FAO), launched as the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration 2021-2030 gets underway.
The report, #GenerationRestoration: Ecosystem restoration for People, Nature and Climate, highlights that humanity is using about 1.6 times the amount of services that nature can provide sustainably.
That ...
June 3, 2021 - LA JOLLA, CA--Mining the world's most comprehensive drug repurposing collection for COVID-19 therapies, scientists have identified 90 existing drugs or drug candidates with antiviral activity against the coronavirus that's driving the ongoing global pandemic.
Among those compounds, the Scripps Research study identified four clinically approved drugs and nine compounds in other stages of development with strong potential to be repurposed as oral drugs for COVID-19, according to results published June 3 in the journal Nature Communications.
Of the drugs that prevented the coronavirus from replicating in human cells, 19 were found to work in concert with or boost the activity of remdesivir, an antiviral therapy approved ...
MIT researchers have created the first fiber with digital capabilities, able to sense, store, analyze, and infer activity after being sewn into a shirt.
Yoel Fink, who is a professor of material sciences and electrical engineering, a Research Laboratory of Electronics principal investigator, and the senior author on the study, says digital fibers expand the possibilities for fabrics to uncover the context of hidden patterns in the human body that could be used for physical performance monitoring, medical inference, and early disease detection.
Or, you might someday store your wedding music in the gown you wore on the big day -- more on that later.
Fink and his colleagues describe the features of the digital fiber in Nature Communications. Until now, electronic fibers ...
The number of people engaging with life-enhancing cardiac rehabilitation clinics has declined during the pandemic, according to a BMJ clinical update which makes the case for more home-based and virtual alternatives.
Before the covid-19 pandemic, 100?000 people were admitted to hospital with heart attacks and approximately 200?000 were diagnosed with heart failure annually in the UK. There was a 40% decline in the number of patients admitted with heart attacks (acute coronary syndromes ) in 2020.
Cardiac rehabilitation is crucial to helping people who have encountered a heart attack or heart failure have a better quality of life. Now, a new review, undertaken by cardiac rehabilitation experts based at the ...
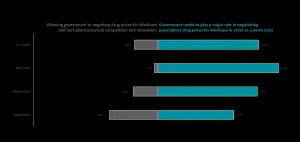
WASHINGTON, DC - JUNE 3, 2021 -- A new West Health/Gallup survey finds nearly all Democrats (97%) and the majority of Republicans (61%) support empowering the federal government to negotiate lower prices of brand-name prescription drugs covered by Medicare. Overall, 8 in 10 Americans prefer major government action to control prices over concerns about it hurting innovation and competition from the pharmaceutical industry. The results come from a nationally representative poll of more than 3,700 American adults.
While President Joe Biden, Democrats in Congress and former President Donald Trump have called for such negotiation, ...