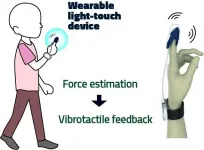
Wearable accelerometer and vibrator 'thimble' could reduce falls amongst seniors
Researchers have developed a device using accelerometers and vibrators, similar to those found in mobile phones, that can be worn on the fingertips like a thimble to help reduce 'postural sway' and improve balance amongst seniors
2021-06-03
(Press-News.org) Japanese researchers have developed and tested a prototype device -- wearable on the fingertips -- that incorporates the concept of 'light touch' to enhance the sense of balance. If widely implemented, the device should significantly reduce incidence of falls amongst seniors.
The findings are published in the journal Scientific Reports on April 1.
As we age, our sense of balance can become impaired. The resulting increase in postural sway in turn increases the risk of falls and consequent injuries. Meanwhile, older people make up a large and increasing proportion of the population in highly developed countries. This makes efforts to reduce the effects of postural sway ever more imperative.
Aids such as canes and walking frames help a great deal, but research suggests their use or misuse in certain circumstances such as on stairs or stepping into or out of vehicles can actually exacerbate the problem with sense of balance and increase the risk of injury.
In order to address the challenge of human balance in the elderly, in recent years a great deal of research has focussed on the phenomenon known as 'light touch.' Even with eyes closed, a subject that lightly touches a curtain or piece of paper draped in front of them with just their fingertips is given enough of a stimulus cue to reduce their swaying. This happens even though a curtain or piece of paper cannot deliver any postural support in the way that a cane or walking frame can.
Researchers with Yokohama National University (YNU) and the Prefectural University of Hiroshima wanted to test a way to create a 'virtual light touch' (VLT) system to achieve the same result--in effect creating a virtual curtain.
The first step was a basic VLT system that incorporated a small device that fits over a fingertip of a subject--much like wearing a thimble--and delivers a vibrotactile 'nudge' when they begin to sway. Assessment of swaying in this first attempt at a VLT was performed by a 3D motion capture system akin to what is used by special effects professionals in the movie industry.
Initial tests on subjects with this proof-of-concept system showed results equivalent to the use of a physical curtain.
"The use of such a large and complex motion capture system is no more practical in daily life than a curtain," said Keisuke Shima, Associate Professor at faculty of engineering of YNU and lead author of the study.
"But the tests on live subjects showed that the concept worked," added YNU researcher Mami Sakata, a co-author of the paper. "The next step was to transform the VLT into a system that could be used in everyday life."
The researchers swapped out the motion capture system for an accelerometer--an electromechanical device that measures acceleration forces--similar to what is found in most smartphones. The vibrotactile nudges were still delivered by the vibrotactile thimble device.
The accelerometer-and-vibrotactile-thimble VLT system was then tested on 150 volunteers ranging in age from their sixties to their nineties and again found that postural sway was reduced as significantly as a physical curtain.
The acceleration-based VLT set-up is immediately practical as a balance aid in everyday life as it involves a simple, lightweight and compact sensor and motor. It should enjoy widespread adoption amongst elderly people.
However, the researchers want to improve their system further by making the device even more lightweight and compact, and to enhance its reduction of postural sway. For this latter enhancement, they will need to explore precisely how the still poorly understood light-touch effect works to support human balance.
INFORMATION:
Yokohama National University (YNU or Yokokoku) is a Japanese national university founded in 1949. YNU provides students with a practical education utilizing the wide expertise of its faculty and facilitates engagement with the global community. YNU's strength in the academic research of practical application sciences leads to high-impact publications and contributes to international scientific research and the global society. For more information, please see: https://www.ynu.ac.jp/english/
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-03
Research involving scientists from the University of A Coruña has succeeded in sequencing the oldest mitochondrial genome of the immediate ancestor of modern cows that has been analysed to date. The remains, some 9,000 years old, were found next to a woman. Why were they with her if cattle had not yet been domesticated? Do they belong to ancestors of today's Iberian cows?
Humans have maintained a very close relationship with aurochs (Bos primigenius) since their beginnings, first by hunting them and then by breeding and selecting them.
This extinct species of mammal is little known in the Peninsula because its skeletal remains are difficult to distinguish from bison. In fact, there have been references to the presence of "large bovids" in many sites because ...
2021-06-03
Interactions in the network can lower the critical temperature thresholds beyond which individual tipping elements begin destabilizing on the long-run, according to the study - the risk already increases significantly for warming of 1.5°C to 2°C, hence within the temperature range of the Paris Agreement.
"We provide a risk analysis, not a prediction, yet our findings still raise concern," says Ricarda Winkelmann, Lead of FutureLab on Earth Resilience in the Anthropocene at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK). "We find that the interaction of these four tipping elements can make them overall more vulnerable due to mutual destabilization on the long-run. The feedbacks between them tend to lower the critical temperature ...
2021-06-03
A new study looking at the benefits of good farmer seed production suggests women need more support to participate in contract farming - to the same extent as their male counterparts - and have more equality along the whole food value chain.
The CABI-led research - which sought to assess the benefits of good farmer seed production through a case study of the Good Seed Initiative in Tanzania - reveals that while around 70% of the labour to grow African Indigenous Vegetables (AIVs) is provided by women only 10 to 30% are contract farmers who own the fields, make decisions on sales and control revenues.
The paper, led by Dr Monica Kansiime ...
2021-06-03
Philadelphia, June 3, 2021 - Researchers at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have demonstrated how to use standardized reporting of clinical data for seizures caused by a variety of neurological disorders, providing fundamental baseline information that can determine what methods work best for keeping seizures under control. The findings were published today in the journal Epilepsia.
In order to make improvements in epilepsy care, clinicians need a reliable and efficient method to measure outcomes. While Electronic Medical Records (EMR) are being used more frequently for research and quality improvement, important epilepsy outcome measures such ...
2021-06-03
MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researchers are finding solutions to the aging-related changes that reduce anti-cancer immunity. Besim Ogretmen, Ph.D., and colleagues found a novel link between aging, metabolism and anti-cancer T-cell function. Their work, published in Cell Reports, sheds light on an important pathway that cannot be ignored during cancer treatment.
Two broad questions in cancer research are: How can cancer treatments be improved, and what is the link between cancer and aging?
"We know that the protective T-cell response deteriorates with age. Mitochondrial function is now thought to be one of the central regulators of the aging process. Our experiments connected the dots with what was previously shown and highlighted some ...
2021-06-03
Thursday, June 3, 2021, CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study shows that survivors of COVID-19 who have moderate or severe obesity may have a greater risk of experiencing long-term consequences of the disease, compared with patients who do not have obesity. The study was recently published online in the journal of Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.
Multiple studies have identified obesity as a risk factor for developing a severe form of COVID-19 that may require hospital admission, intensive care, and ventilator support in the early phase of the disease. Obesity, which is a complex disease caused by multiple factors, is associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular ...
2021-06-03
DURHAM, N.H.-- Bears are known for being devoted and protective of their baby cubs, but research from the University of New Hampshire shows that they may also play a significant role in shielding gray fox from predators like coyotes, who compete with the fox for food and space. The research is one of the first studies to show how black bears provide a buffer to allow other, smaller carnivores to safely co-exist.
"Even though black bears and coyotes are the two most common carnivores in North America, we're still learning how they affect the ecosystems around them," said Rem Moll, assistant professor of wildlife ecology and lead author ...
2021-06-03
The fabrication device for the battery revolution looks quite unconspicuous: It is a modified, commercially available 3D printer, located in a room in the Empa laboratory building. But the real innovation lies within the recipe for the gelatinous inks this printer can dispense onto a surface. The mixture in question consists of cellulose nanofibers and cellulose nanocrystallites, plus carbon in the form of carbon black, graphite and activated carbon. To liquefy all this, the researchers use glycerin, water and two different types of alcohol. Plus a pinch of table salt for ionic conductivity.
A sandwich of four layers
To build a functioning supercapacitor from these ingredients, four layers are needed, all flowing out of the 3D printer one after the ...
2021-06-03
Left- or right-handedness is a symmetry property that many macroscopic objects also exhibit and which is of immense importance, particularly for the bioactivity of organic molecules. Chirality is also relevant for physical or chemical properties such as optical activity or enantioselectivity of crystalline solids or their surfaces. In the case of chiral metallic phases, unconventional superconductivity and unusual magnetic ordered states are linked to the chirality of the underly-ing crystal structure. Despite this connection between chirality and the properties of a material, detection is often difficult because left-handed and righthanded ...
2021-06-03
The expansion of wind energy in the German Bight and the Baltic Sea has accelerated enormously in recent years. The first systems went into operation in 2008. Today, wind turbines with an output of around 8,000 megawatts rotate in German waters, which corresponds to around eight nuclear power plants. But space is limited. For this reason, wind farms are sometimes built very close to one another. A team led by Dr. Naveed Akhtar from Helmholtz Zentrum Hereon has found that wind speeds at the downstream windfarm are significantly slowed down. As the researchers now write in the journal Nature Scientific Reports, this braking effect results in astonishingly large-scale low wind pattern noticeable in mean ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Wearable accelerometer and vibrator 'thimble' could reduce falls amongst seniors
Researchers have developed a device using accelerometers and vibrators, similar to those found in mobile phones, that can be worn on the fingertips like a thimble to help reduce 'postural sway' and improve balance amongst seniors