A genomic single-cell map explains neuronal death in epilepsy
An interdiscipinary collaboration lead by CSIC deciphers the genetic map of hippocampal sclerosis, a key finding for the diagnosis of temporal lobe epilepsy
2021-06-08
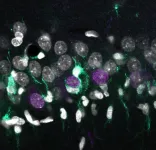
(Press-News.org) A multidisciplinary team led by researchers from the Spanish Research Council (CSIC) identifies the genomic cellular map associated with hippocampal sclerosis, a major histopathological condition of temporal lobe epilepsy. The study, published in Cell Reports, identifies cell-type specific transcriptional signatures of hyper-excitability and neurodegeneration, providing grounds for improved diagnosis. While the presence of sclerosis is essential for identifying temporal lobe epilepsy (the most common form of drug-resistant epilepsy), it is also detected in some cases of dementia associated with Alzheimer's disease.
Hippocampal sclerosis is characterized by the loss of specific neuronal populations and exacerbated activation of other cell types resident in the brain, such as microglia and astrocytes. However, understanding why some neuronal types are more vulnerable than others has remained largely unclear.
In this work, the researchers have developed a transcriptional map that identifies the precise genetic code of all cell types specifically affected in the disease. "With these maps we seek to match different genes with specific biological elements. In the case of the brain, we aim linking expression of some specific genes with different cell types, such as neurons, astrocytes and microglia", explains Liset Menéndez de la Prida, a scientist at the Cajal Institute of the CSIC, who lead the study together with José López-Atalaya, from the Institute of Neurosciences (CSIC-UMH) in Alicante.
To do this, researchers applied two advanced procedures for biological sampling: laser micro-dissection of localized brain tissue and sorting of individual cell nuclei extracted from rats and mice. Using cutting-edge genomic and bioinformatic approaches allowed them to identify specific genetic signatures of degenerative processes.
"When neurons begin to degenerate, they release some signals that can be detected by microglia, which are mediating the inflammatory and neurotoxic response. Each of these processes involve the activation or inactivation of some genetic programs defining a specific genetic signature. We identify some of these genetic signatures associated to neuronal types", explains López-Atalaya.
Researchers also recorded the electrical activity of individual neurons in vivo and found signs of epileptiform activities in some of them. These more hyperexcitable neurons tended to be located in a specific sublayer within the hippocampal region (the superficial sublayer) and expressed some characteristic genes. "Very strikingly, we found that the hyperexcitability map perfectly matched neurodegeneration signatures" adds de la Prida.
To ease dissemination amongst the neuroscience and clinical communities, researchers have made the data associated with this study accessible as a public resource though two interactive websites.
Temporal lobe epilepsy and Alzheimer's
Temporal lobe epilepsy is associated to many causes, from brain infection, injuries caused by trauma, tumors or various genetic factors associated with anatomical changes of the laminar organization of the cerebral cortex. Something common to this heterogeneous group of disorders is the origin of seizures in the temporal lobe, associated with hippocampal atrophy and sclerosis.
In Alzheimer's disease, which affects similar structures of the temporal lobe, electrographic seizures comparable to those of temporal lobe epilepsy have been described. Both diseases are associated with episodic memory deficits, which involve the hippocampus. In some cases of Alzheimer's, atrophy of the hippocampus is also observed, so the results of this study could be of relevance to identify their underlying commonalities.
The work, funded by prestigious national and international grants, involves multidisciplinary collaborations of researchers from several institutions, including the Hospital de San Pau in Barcelona, the Universidad Europea in Madrid, as well as the Riken Brain Institute and the University of Kyoto in Japan.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-08
Since March 2020 the Cancer Genomics and BioComputing of Complex Diseases Laboratory at the Azrieli Faculty of Medicine of Bar-Ilan University has been dedicated to the study of COVID-19. Motivated in particular to study the evolution of coronaviruses, the lab, led by Dr. Milana Frenkel-Morgenstern, has characterized and compared sequences of numerous relevant viruses.
In their most recent study, published in the journal of the Federation of European Biochemical Societies (FEBS), the research team focused on patterns of genetic coding used by viruses which infect a single or narrow range of hosts compared to those which infect a multiple or broad range of hosts.
It was discovered that "promiscuous", or multiple-host, viruses utilize significantly non-optimal codons (the DNA ...
2021-06-08
Mobility analyses show: Only a small proportion of all vehicles are responsible for the majority of the kilometers driven. We are talking above all about long-distance trucks that transport goods all over Europe. If these continue to be fueled with fossil energy, it will hardly be possible to sufficiently reduce CO2 emissions in road traffic. Synthetic fuels from surplus renewable electricity can make a significant contribution to such frequent driver applications.
With electric mobility, hydrogen mobility and synthetic fuels, Empa's future mobility demonstrator, "move", is investigating ...
2021-06-08
In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers from Tel Aviv University and the Academic College of Tel Aviv-Yaffo used smart watches and a dedicated app to monitor 169 subjects before and during Israel's second COVID-19 lockdown (October 2020). The watches and app provided the researchers with accurate daily data for measuring quality of life parameters, such as mood, stress, duration and quality of sleep, heart rate at rest, meeting others and physical exercise.
The study was conducted by a group of experts from the Iby and Aladar Fleischman Faculty of Engineering at Tel Aviv University led by Dr. Erez Shmueli, Dr. Dan Yamin, Shay Oved and Merav Mofaz, in collaboration with TAU's Prof. Noga Kronfeld Schor of the School of Zoology at the George S. Wise ...
2021-06-08
BOSTON - Last year, people who smoked had a variety of responses to the COVID-19 pandemic, with some increasing their smoking to help them cope and others quitting to potentially lessen their vulnerability to COVID-19. That's the finding of new research published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine and conducted by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), Vanderbilt University Medical Center and the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine.
"Studies have shown that alcohol and opioid use increased during the pandemic, but little is known about how smokers responded," says lead author Nancy A. Rigotti, MD, director of MGH's Tobacco Research and Treatment Center and professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. "They might have increased ...
2021-06-08
Rising temperatures are increasingly affecting the quality of life in many regions, setting new challenges for architects, urban planners and healthcare systems. Researchers at KAUST have analyzed discomfort due to outdoor heat across Saudi Arabia and neighboring regions to help understand and combat the problem.
"Living conditions in the Kingdom have been particularly affected by the changing climate," says Hari Dasari, first author of the paper. He also emphasizes the unique challenges facing the Hajj pilgrimage visits by several million people each year. Between 2014 and 2018, the Hajj occurred in summer months when the ...
2021-06-08
UNF archaeology researchers are uncovering the lost Indigenous NE Florida settlement of Sarabay
Jacksonville, Fla. - The University of North Florida archaeology team is now fairly confident they have located the lost Indigenous northeast Florida community of Sarabay, a settlement mentioned in both French and Spanish documents dating to the 1560s but had not been discovered until now.
The type and amounts of Indigenous pottery the team is finding combined with the type and dates for European artifacts as well as cartographic map evidence strongly supports this location as the late 16th/early 17th century Mocama settlement.
The researchers have opened large excavation blocks with many exciting ...
2021-06-08
The "miracle of life" is most obvious at the very beginning: When the fertilized egg cell divides by means of furrows into blastomeres, envelops itself in an amniotic sac, and unfolds to form germ layers. When the blastomeres begin to differentiate into different cells - and when they eventually develop into a complete organism.
"We wanted to find out whether the later differences between the various cells are already partly hard-wired into the fertilized egg cell," says Dr. Jan Philipp Junker, who heads the Quantitative Developmental Biology Lab at the ...
2021-06-08
Researchers from Skoltech and Ludwig Maximilians-Universität (LMU) in Germany have studied the fundamental properties of halide perovskite nanocrystals, a promising class of optoelectronic materials. Using a combination of theory and experiment, they were able to show and explain an intricate connection between composition, light-induced lattice dynamics, and stability of the materials. The paper was published in the journal Nature Communications.
Perovskite nanocrystals (PNCs) are semiconductor nanocrystals that, thanks to their unique properties, have found a number of applications in optoelectronics, for instance, in lasers and LEDs. PNCs have a much higher photoluminescence quantum ...
2021-06-08
Accelerated cognitive decline in patients with and without existing dementia is one of the most disturbing outcomes of hospitalizations for older adults, affecting at least 2.6 million Americans every year.
But the condition, known as delirium, is believed to be preventable in up to 40 percent of hospital-acquired cases, and researchers at UC San Franciso wanted to see if simple tweaks, like avoiding nighttime interruptions to promote sleep, nixing certain prescription drugs, and promoting exercise and social engagement, could decrease its incidence.
In a June 8, 2021, study in the Journal of Hospital Medicine, the researchers followed approximately 22,700 inpatients aged 50 and ...
2021-06-08
MELVILLE, N.Y., June 8, 2021 -- As face coverings have become more and more ubiquitous during the coronavirus pandemic, their effects on nearly every aspect of life have been called into question. For one, a better understanding of the impacts of face masks and shields on acoustic transmission in classrooms could help optimize educational settings.
During the 180th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, which will be held virtually June 8-10, Laura and Rich Ruhala, from Kennesaw State University, will talk about how various types of face coverings may affect ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A genomic single-cell map explains neuronal death in epilepsy
An interdiscipinary collaboration lead by CSIC deciphers the genetic map of hippocampal sclerosis, a key finding for the diagnosis of temporal lobe epilepsy





