How different beliefs and attitudes affect college students' career aspirations
2021-06-09
(Press-News.org) A study published in Career Development Quarterly has looked at whether beliefs and attitudes influence career aspirations of college students with different genders and sexual orientations.
Among 1,129 college students at a midwestern urban university, stronger self-efficacy beliefs--or perceptions about whether a person has the ability to achieve a desired outcome--led both male and lesbian, gay, bisexual, queer, intersex, and questioning (LGBQIQ) students to seek out leadership positions within their chosen career field. Stronger feminist attitudes were associated with an increase in achievement efforts for LGBQIQ college students, but not for heterosexual students.
"The results of the study not only demonstrate that beliefs and attitudes influence college students' career aspirations, but also underscore the moderating effects of gender and sexual orientation on these relationships", said lead author Darrick Tovar-Murray, PhD, of DePaul University. "Career counselors and other professionals might consider using these findings to support college students in their occupational goals and also encourage them to accomplish their vocational dreams."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-09
New research reveals that only a minority of U.S. Medicare beneficiaries with knee osteoarthritis in 2005-2010 used non-surgical care such as physical therapy and knee injections, and few were treated by rheumatologists, physiatrists, or pain specialists. The study, which is published in END ...
2021-06-09
Oncotarget published "Differential expression of Vitamin D binding protein in thyroid cancer health disparities" which reported that thyroid cancer incidence, recurrence, and death rates are higher among Filipino Americans than European Americans.
In this study, the authors determined the correlation between differential DBP expression in tumor tissues and cancer staging in Filipino Americans versus European Americans.
The majority of Filipino Americans presented with advanced tumor staging. In contrast, European Americans showed early staging and very few advanced tumors.
On the contrary, in the tumor tissues derived from European Americans, moderate to strong DBP staining was detected ...
2021-06-09
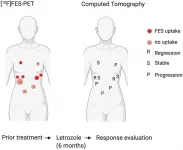
Oncotarget published "[18F]FDG and [18F]FES positron emission tomography for disease monitoring and assessment of anti-hormonal treatment eligibility in granulosa cell tumors of the ovary" which reported that the authors evaluated 22 PET/CTs from recurrent Anti-hormonal granulosa cell tumors (AGCT) patients to determine tumor FDG and FES uptake by qualitative and quantitative analysis.
They included all consecutive patients from two tertiary hospitals between 2003-2020.
Expression of ERα and ERβ and mitoses per 2 mm2 were determined by immunohistochemistry and compared to FES and FDG uptake, respectively.
Qualitative assessment showed low-to-moderate FDG uptake in most patients, and intense uptake in ...
2021-06-09
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Women's mental health likely has a higher association with dietary factors than men's, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
Lina Begdache, assistant professor of health and wellness studies at Binghamton University, had previously published research on diet and mood that suggests that a high-quality diet improves mental health. She wanted to test whether customization of diet improves mood among men and women ages 30 or older.
Along with research assistant Cara M. Patrissy, Begdache dissected the different food groups that are associated with mental distress in men and women ages 30 years and older, as well as studied ...
2021-06-09
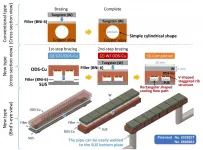
The oxide dispersion strengthened copper alloy (ODS-Cu) is superior in thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, heat resistance and friction tolerance, etc. Although the ODS-Cu can be expected to have various industrial applications, its joint with other materials is extremely difficult because of its intrinsic poor weldability. The research group of Dr. Masayuki Tokitani in the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) National Institute for Fusion Science (NIFS) has developed an extremely novel joint technique that enables us to fabricate any component made of ODS-Cu. This technique highly contributes to producing the efficient heat removal component for the fusion reactor.
Copper ...
2021-06-09
Microphones are perhaps the most common electronic sensor in the world, with an estimated 320 million listening for our commands in the world's smart speakers. The trouble is that they're capable of hearing everything else, too.
But now, a team of University of Michigan researchers has developed a system that can inform a smart home--or listen for the signal that would turn on a smart speaker--without eavesdropping on audible sound.
The key to the device, called PrivacyMic, is ultrasonic sound at frequencies above the range of human hearing. Running dishwashers, computer monitors, even finger snaps, all generate ultrasonic sounds, which have a frequency of 20 kilohertz ...
2021-06-09
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Scientists working to understand the cellular processes linking high cholesterol to breast cancer recurrence and metastasis report that a byproduct of cholesterol metabolism causes some cells to send out cancer-promoting signals to other cells. These signals are packaged in membrane-bound compartments called extracellular vesicles.
Reported in the journal Endocrinology, the discovery could lead to the development of new anti-cancer therapies, researchers say.
"Extracellular vesicles play an important role in normal physiology, but they also have been ...
2021-06-09
A population-based study, published today in JAMA, has found flu vaccination during pregnancy does not lead to an increased risk of adverse early childhood health outcomes.
Although pregnant people are not more susceptible to acquiring influenza infection, they are at an increased risk of severe illness and complications if they get the flu during pregnancy. For this reason, all pregnant people are advised to receive a flu shot each year, yet only 36 percent received it according to a study monitoring four flu seasons in Nova Scotia. Safety concerns are reportedly a leading reason people may not receive influenza ...
2021-06-09
DARIEN, IL - Dreams result from a process that often combines fragments of multiple life experiences and anticipates future events, according to novel evidence from a new study.
Results show that 53.5% of dreams were traced to a memory, and nearly 50% of reports with a memory source were connected to multiple past experiences. The study also found that 25.7% of dreams were related to specific impending events, and 37.4% of dreams with a future event source were additionally related to one or more specific memories of past experiences. Future-oriented dreams became proportionally more common later in the night.
"Humans ...
2021-06-09
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Mayo Clinic researchers and colleagues at the University of Minnesota showed that COVID-19 exacerbates the damaging impact of senescent cells in the body. In preclinical studies, the senolytic drugs discovered at Mayo significantly reduced inflammation, illness, and mortality from COVID infection in older mice. The findings appear in the journal Science.
Senescent cells (damaged or non-functioning cells that persist in the body) contribute to many aspects of aging and illness, including inflammation and multiple chronic diseases. Based on the "Amplifier/Rheostat Hypothesis" of senescent ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How different beliefs and attitudes affect college students' career aspirations