INFORMATION:
Researchers realize unconventional coherent control of solid-state spin qubits
2021-06-09
(Press-News.org) The research team led by Prof. GUO Guangcan from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), together with Prof. Adam Gali from Wigner Research Centre for Physics, realized robust coherent control of solid-state spin qubits using anti-Strokes (AS) excitation, broadening the boundary of quantum information processing and quantum sensing. This study was published in Nature Communications.
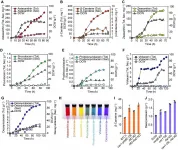
Solid-state color center spin qubits play an important role in quantum computing, quantum networks and high-sensitivity quantum sensing. Considered as the basis of quantum technology application, optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) technology offers a readout approach to detect the spin state. Conventional ODMR detection of solid-state spin states is almost all under Strokes excitation, which requires that the excitation laser has higher energy than emitted photons.
To extend the scope of solid-state quantum technologies, the researchers first realized the AS excited ODMR detection of silicon vacancy defect spin in silicon carbide (SiC), where the energy of exciting laser is lower than that of the emission photons.
By investigating the dependence of laser power and temperature on AS excited ODMR signals, the researchers proved that the AS photoluminescence (PL) was induced by phonon-assisted single photon absorption process, and was applicable to all-optical high-temperature temperature sensing.
On the basis of this, they found that AS and Strokes excited ODMR followed similar behavior facing the change of laser power, microwave (MW) power and temperature, while the AS ODMR contrast remained approximately three times larger than the Strokes one.
Furthermore, the researchers realized the coherent manipulation of solid-state spin states in SiC under AS excitation. The results showed that the AS excitation method increased the signal contrast by around three times, enabling the potential applications of AS excited ODMR approach to quantum information processing and quantum sensing.
This study improves any ODMR-based measurement. This AS demonstration can be used in yet unforeseen development.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Machine learning speeds up simulations in material science
2021-06-09
Research, development, and production of novel materials depend heavily on the availability of fast and at the same time accurate simulation methods. Machine learning, in which artificial intelligence (AI) autonomously acquires and applies new knowledge, will soon enable researchers to develop complex material systems in a purely virtual environment. How does this work, and which applications will benefit? In an article published in the Nature Materials journal, a researcher from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and his colleagues from Göttingen and Toronto explain it all. (DOI: 10.1038/s41563-020-0777-6)
Digitization and virtualization are becoming increasingly important in a wide range of scientific disciplines. One of these disciplines ...
Identifying the main culprit of the COVID-19 disaster
2021-06-09
A research team led by Professor Jianping Huang from Lanzhou University has launched a Global Prediction System for COVID-19 pandemic. Their recent work explored the periodicity and mutability in the evolutionary history of the COVID-19 pandemic and investigated the principle mechanisms behind them. They attributed the periodic oscillations of COVID-19 daily cases to seasonal modulations and reporting bias, and identified the unrestricted mass gatherings as the main culprit of the COVID-19 disaster.
Their findings, entitled "The oscillation-outbreaks characteristic of the COVID-19 pandemic", were published in National Science Review.
In this study, the influence ...
The iron jaws of the bristle worm
2021-06-09
Bristle worms are found almost everywhere in seawater, they have populated the oceans for hundreds of millions of years. Nevertheless, some of their special features have only now been deciphered: Their jaws are made of remarkably stable material, and the secret of this stability can now be explained by experiments at TU Wien in cooperation with Max Perutz Labs.
Metal atoms, which are incorporated into the protein structure of the material, play a decisive role. They make the material hard and flexible at the same time - very similar to ordinary metals. Further ...
A new approach will help save X-ray studies from failing results
2021-06-09
X-rays are widely used to study the structures of various objects. New sources of x-rays, like Free Electron Lasers and 4th generation synchrotrons are being built around the Globe. The best optics for the new sources is usually made of the single crystal materials, such as silicon, germanium or diamond. However, the ideal periodicity of crystals leads to some unwanted diffraction losses - X-ray glitches. This effect causes dips in the intensity of the radiation transmitted through the optical element, down to zero. Scientists from the Immanuel Kant Baltic ...
Language extinction triggers loss of unique medicinal knowledge
2021-06-09
Language is one of our species' most important skills, as it has enabled us to occupy nearly every corner of the planet. Among other things, language allows indigenous societies to use the biodiversity that surrounds them as a "living pharmacy" and to describe the medicinal properties of plants. Linguists estimate that there are nearly 7,400 languages in the world today.
Most of these languages, however, are not recorded in writing, and many languages are not being passed on to the next generation. This has led linguists to estimate that 30 percent of all languages will disappear by the end of the 21st century. For indigenous cultures who mostly transmit knowledge orally, this ...
Microbial production of natural rainbow colorants
2021-06-09
A research group at KAIST has engineered bacterial strains capable of producing three carotenoids and four violacein derivatives, completing the seven colors in the rainbow spectrum. The research team integrated systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering strategies for the production of seven natural rainbow colorants in engineered Escherichia coli strains. The strategies will be also useful for the efficient production of other industrially important natural products used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Colorants are widely used in our lives and are directly related to human health when we eat food additives and wear cosmetics. However, most of these colorants are made from petroleum, causing unexpected side effects and health problems. Furthermore, ...
COVID-19 lockdowns lead Aussie and UK women to drink more
2021-06-09
Feelings of anxiety, pessimism and depression during the COVID-19 pandemic led middle-aged women in both Australia and the UK to stock up on alcohol, which was associated with drinking more, a new Flinders University-led study has found.
The research, led by Dr Emma Miller in Flinders University's College of Medicine and Public Health, also found women in the UK were more likely to drink at risky levels than their Australian counterparts during lockdown, and were more likely to have stockpiled alcohol.
Despite these differences, the research found the emotional responses to ...
Transformation toughening of ceramics made crystal clear
2021-06-09
Tsukuba, Japan - Ceramic materials that are resistant to cracking are used in a variety of industries from aerospace engineering to dentistry. Toughening them to improve their efficiency and safety is therefore an important area of investigation. Researchers from the University of Tsukuba have used time-resolved X-ray diffraction to observe transformation toughening in zirconia ceramics during dynamic fracture. Their findings are published in Applied Physics Letters.
Current methods of observation allow the formation of cracks in materials to be observed in situ while loads are applied. These close-up analyses ...
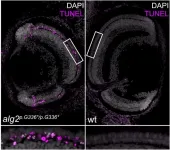
Rice fish model of a rare metabolic disorder
2021-06-09
Human cells are kept healthy by the activity of millions of proteins. These proteins are modified in different ways, such as by adding sugar molecules to them, which can be crucial for them to function properly. Given this importance, defects in the sugar-adding process are often lethal at the very early stages of development. In rare cases, however, patients can develop sugar-adding deficiencies that result in a range of metabolic diseases, known collectively as 'congenital disorders of glycosylation' (CDG). These disorders are caused by defects in the enzymes involved in the sugar-adding process. For example, ALG2-CDG (or CDG-Ii) is a disorder caused by mutations in the ALG2 enzyme, ...
Personalized soundscape could help people with dementia with time, place recognition
2021-06-09
MELVILLE, N.Y., June 9, 2021 -- Designing a soundscape to improve the quality of life for an individual is centered on putting their perception at the heart of the process. It becomes trickier for people who have diminished cognitive capacities.
During the 180th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, which will be held virtually June 8-10, Arezoo Talebzadeh, from Ghent University, will show how a personalized soundscape can help those with dementia by providing clues regarding time of day and place. The session, "Soundscape design for people with dementia; the correlation between psychoacoustic parameter and human perception," will take place Wednesday, June 9, ...