(Press-News.org) Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men, according to the American Cancer Society. It's also one of the trickiest cancers to diagnose and treat.
But new research from the University of Georgia has identified a protein that appears to prevent the cancer from spreading to and colonizing the bone, providing a new target for future therapeutics.
"Unfortunately, prostate cancer that has spread to the bone is very aggressive, often lethal and very difficult to treat," said Brian Cummings, corresponding author of the study and head of the College of Pharmacy's pharmaceutical and biomedical sciences department. "Even in cases of successful treatment, the patient's quality of life is severely lessened due to bone loss."
Prostate cancer that hasn't spread beyond nearby organs has nearly a 100% survival rate, meaning almost all of these patients will live at least another five or more years after their initial diagnosis and treatment. But for men whose cancer has spread to other organs or the bone, that five-year survival rate plummets to 30%, according to the American Cancer Society. In the U.S., about one in every eight men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer and more than 34,000 men die each year from the disease.
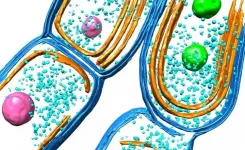
The new study, published by Scientific Reports, focused on cancer-associated fibroblasts, which are the most abundant type of cell in tumors and are responsible for cancer growth and spread. The researchers found that knocking out a specific protein, called glypican-1, could prevent tumor cells from spreading into nearby bone.
The study supports a previous report from Cummings' laboratory suggesting that this protein may prevent tumor growth. The researchers found that the protein doesn't alter the cancer cells themselves. Instead it affects a group of neighboring cells called fibroblasts.
Fibroblasts are cells that help make up connective tissues in people and animals. But fibroblasts can also be present in cancerous tumors, where they facilitate cancer growth and spread.
To determine the glypican-1 protein's role in helping cancer spread, the researchers combined human prostate cancer cells and human bone-derived cells to examine how the cancer cells transformed the fibroblast. Then they genetically modified the cancer cells and the fibroblast to knock out the protein.
Without the protein, the prostate cancer cells had problems transforming the fibroblast.
The study was the first to demonstrate such a role for glypican-1 and suggests that this protein may have the same effect on tumor growth in people.
"Part of the significance of this study is that it demonstrates how cancer cells are able to change their environment in ways to facilitate their own growth," Cummings said. "Prostate cancer cells alter their environment so that they can colonize bone. This study identifies a role for a protein that appears to inhibit the harmful changes that prostate cancer makes to the bone."
"This protein appears to stop the ability of cancer cells to change their environment, which decreases the cancer's aggressiveness. The fact that this protein is found in the bone, where many aggressive prostate cancer cells reside, further increases the potential impact of this work."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors on the study included Som Shenoy, a professor in the Department of Clinical and Administrative Pharmacy; Arti Verma, a postdoctoral fellow in Shenoy's laboratory; Lillie Barnette, a graduate student in Cummings' laboratory; and Sukhneeraj Kaur, a former graduate student in Cummings' laboratory, who was the first author.
There are still many unsolved mysteries about the human brain and its development. Now, a novel study published in Frontiers in Psychiatry sheds new light on the neurobiological origins of our individual traits.
Functional connectivity is the coordinated activity - activation or deactivation - through time between separate brain regions, regardless of their physical closeness or the type of neural connections between them. Changes in functional connectivity can be a sign of mental health disorders such as depression, eating disorders, and schizophrenia, and are thought to have developmental origins.
We know that mental health is characterized by three functional brain networks. The first is hypoconnectivity ...
People who have a high sensation-seeking personality trait may be more likely to develop an addiction to cocaine, according to a Rutgers study.
"Although many people try illicit drugs like cocaine or heroin, only a small proportion develop an addiction," said lead author Morgan James, a member of the Rutgers Brain Health Institute and an assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. "The interaction found between sensation-seeking traits and the drug-taking experience show that predisposition to addiction has a genetic basis, and that this interacts with environmental factors such as patterns of drug use. The sensation-seeking trait was predictive of rats' likelihood to exhibit stronger ...
For older adults, participating in social activities can protect against physical and mental signs of aging, but it may also pose risks, especially for women.
A new analysis of national data led by UC San Francisco found that older women who were broadly engaged in social activities before the COVID pandemic had 76 percent higher odds of experiencing emotional abuse or mistreatment than women who were less engaged.
The paper is published June 9, 2021 in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
"Given widespread discussion about the negative effects of social isolation of ...
Research from the University of Washington shows that endangered blue whales are present and singing off the southwest coast of India. The results suggest that conservation measures should include this region, which is considering expanding tourism.
Analysis of recordings from late 2018 to early 2020 in Lakshadweep, an archipelago of 36 low-lying islands west of the Indian state of Kerala, detected whales with a peak activity in April and May.
The study was published in May in the journal Marine Mammal Science.
"The presence of blue whales in Indian waters is well known from several strandings and some live sightings of blue whales," said lead author Divya Panicker, a ...
A new study conducted by the researchers at the University of Liverpool reveals how the ancient photosynthetic organisms - cyanobacteria - evolve their photosynthetic machinery and organise their photosynthetic membrane architecture for the efficient capture of solar light and energy transduction.
Oxygenic photosynthesis, carried out by plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, produces energy and oxygen for life on Earth and is arguably the most important biological process. Cyanobacteria are among the earliest phototrophs that can perform oxygenic photosynthesis and make significant contributions to the Earth's atmosphere and primary production.
Light-dependent photosynthetic reactions are performed by a set of photosynthetic ...
Laser-produced high energy density plasmas, akin to those found in stars, nuclear explosions, and the core of giant planets, may be the most extreme state of matter created on Earth. Now scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), building on nearly a decade of collaboration with the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at the DOE's Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), have designed a novel X-ray crystal spectrometer to provide high-resolution measurements of a challenging feature of NIF-produced HED plasmas.
Most powerful lasers
The ...
An international research team led by members from the Technical University of Munich, the Deutsches Museum, Munich, and the Swedish Linköping University has developed a method to manufacture two-dimensional polymers with the thickness of a single molecule. The polymers are formed on a surface by the action of light. The discovery paves the way to new ultrathin and functional materials.
The quest for new two-dimensional materials has rapidly intensified after the discovery of graphene - a supermaterial whose excellent properties include high conductivity and strength, making it incredibly versatile.
Two main ...
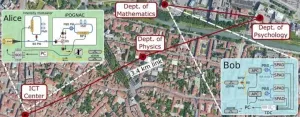
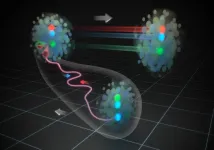
WASHINGTON -- In a new study, researchers demonstrate an automated, easy-to-operate quantum key distribution (QKD) system using the fiber network in the city of Padua, Italy. The field test represents an important step toward implementing this highly secure quantum communication technology using the type of communication networks already in place in many regions around the world.
QKD offers impenetrable encryption for data communication because it uses the quantum properties of light to generate secure random keys for encrypting and decrypting data.
"QKD can be useful in any situation where security is paramount because it offers unconditional security for the key exchange process," ...
Two gene variants found in African American women may explain why they are more likely to be diagnosed with triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) than white women of European ancestry, according to Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian investigators. The study findings may have implications for developing better risk assessment tools for TNBC in African American women and for understanding why they have poorer TNBC outcomes.
In a study, published April 29 in Scientific Reports, the investigators found that a version of the ANKLE1 gene that can be protective against TNBC is less likely to be found in African American women than white women of European ancestry. In addition, African American women with a mutation in the Duffy gene, which plays a role in inflammation, ...
Inside each proton or neutron there are three quarks bound by gluons. Until now, it has often been assumed that two of them form a "stable" pair known as a diquark. It seems, however, that it's the end of the road for the diquarks in physics. This is one of the conclusions of the new model of proton-proton or proton-nucleus collisions, which takes into account the interactions of gluons with the sea of virtual quarks and antiquarks.
In physics, the emergence of a new theoretical model often augurs badly for old concepts. This is also the case with the description of collisions of protons with protons or atomic nuclei, proposed by scientists from the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IFJ PAN) ...