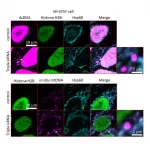
LIM domain only 1: One gene, many roles in cancer
Researchers detail another gene target that could be the crucial link to curing different cancers
2021-06-10
(Press-News.org) Humans have been plagued by a myriad of deadly cancers since ages. Parallelly, they have also been attempting different permutations and combinations of treatments to cure the disease. Part of these attempts involving biomolecular targets have come to the fore in recent years. Like a broad-spectrum antibiotic that can attack and eliminate several microbes at a time, some of these biomolecular targets, when manipulated appropriately, can alleviate different cancers. One such biomolecular target of interest is LIM domain only 1 gene (LMO1).
LMO1 codes for a protein 'connector' that helps in the assembly of biomolecules involved in the production of RNA molecules, which in turn, leads to the synthesis of proteins implicated in cancer formation. This generates hope for devising ways to manipulate LMO1, which could take modern medicine one step closer to curing cancer. As such, a group of medical researchers from Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University in China, and Texas State University in USA, took it upon themselves to answer this question better, through a review published in Chinese Medical Journal.
The researchers scanned several studies on LMO1 to determine its key molecular features. On the question of why they narrowed their focus on LMO1, Professor You-Chao Jia of Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, who led the study, explains, "Unique biological features of LMO1 distinct from other LMO members, such as its tissue-specific expression patterns, interacting proteins, and transcriptional targets, have been increasingly recognized. Studies indicated that LMO1 plays a critical oncogenic role in various types of cancers, including T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, neuroblastoma, gastric cancer, lung cancer, and prostate cancer."
The protein 'connectors' that LMO1 codes for are called as transcription cofactors (COF). Much like a puppeteer who manipulates strings to move the puppets in different ways, the LMO1 COF acts through its protein products to effect various cancer-causing changes in the cell. Here, it is important to note that these protein products regulate expression by binding to the DNA. So, through their DNA-binding protein counterparts, LMO1 COF extensively interacts with other important components of the cell and facilitates production of other proteins, essentially functioning as a carcinogenic 'power-broker' of sorts. Accordingly, the researchers stress the importance of better studying the LMO1 interactome and transcriptome in the review.
Moving to a higher level of organization, the researchers also looked into the tissue-specific expression of LMO1 in cancer. Here again, they identified the mediation of LMO1 activities through its DNA-binding 'partners'. So, they propose that the analysis of cancer condition should incorporate not only LMO1 expression, but also nuances in their partners' expression. They observed similar correlations at the epigenetic level too.
Further, the researchers highlight the role of random unique genetic changes called single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the LMO1 as possible contributors to carcinogenesis. They specifically identified LMO1 SNP contributions to T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and neuroblastoma.
Needless to say, the researchers highlight the diagnostic value of LMO1 expression levels. They observed from several studies that the overexpression of LMO1 is implicated in poor patient clinical outcomes in different cancers. Therefore, they believe that with a little more analysis, LMO1 expression levels could well become the clinical determiner of cancer progression in affected patients. Also, they implied that further research into the gene could lead to targeted therapy for these cancers.
Overall, the researchers have made a convincing argument to take a better look at LMO1 for devising more effective cures for different cancers. In this regard, Professor Jia hopes, "LMO1 is an oncogene or a key factor in carcinogenesis in many kinds of cancers. We hope that more studies will be carried out to explore its application value in clinical treatment of tumors." The world can indeed be optimistic about a possible breakthrough in cancer cure, through this review.
INFORMATION:
Reference
Title of original paper: LIM domain only 1: an oncogenic transcription cofactor contributing to the tumorigenesis of multiple cancer types.
Journal: Chinese Medical Journal
DOI: http://doi.org/10.1097/CM9.0000000000001487
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-10
Increasing evidence shows that physical activity and exercise training may delay or prevent the onset of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In aging humans, aerobic exercise training increases gray and white matter volume, enhances blood flow, and improves memory function. The ability to measure the effects of exercise on systemic biomarkers associated with risk for AD and relating them to key metabolomic alterations may further prevention, monitoring, and treatment efforts. However, systemic biomarkers that can measure exercise effects on brain function and that link to relevant metabolic responses are lacking.
To address this issue, Henriette van Praag, Ph.D., from Florida Atlantic University's ...
2021-06-10
Highly dispersed platinum catalysts provide new possibilities for industrial processes, such as the flameless combustion of methane, propane, or carbon monoxide, which has fewer emissions and is more resource efficient and consistent than conventional combustion. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, a team of researchers reports on which platinum species are active in high-temperature oxidations and what changes they can undergo in the course of the process--important prerequisites for the optimization of catalysts.
Individual metal atoms and clusters consisting of only a few metal atoms have interesting catalytic properties determined by the exact nature of the active metal species. Usually, these are highly dispersed and deposited on ...
2021-06-10
Black people have a higher risk of colorectal cancer than white people, but this risk is likely not due to genetics. Data from a recent study by researchers from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine adds more data to the existing evidence.
"The next step is determining what is behind this increased risk," said lead author Thomas Imperiale, M.D., Regenstrief Institute research scientist, VA investigator and professor of gastroenterology and hepatology at IU School of Medicine. "Lifestyle and healthcare-related behaviors may explain some of the difference." ...
2021-06-10
Washington, D.C. - June 9, 2021 - The Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine is protective against several SARS-CoV-2 variants that have emerged, according to new research presented in the journal mBio, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology. While this is good news, the study also found that the only approved monoclonal antibody therapy for SARS-CoV-2 might be less effective against SARS-CoV-2 variants in laboratory experiments.
"The vaccines provide very strong protection against the earlier forms of the virus as well as the newer variants. This is an important point because I have heard people say that they don't think there is a reason to get vaccinated, because the vaccine isn't going to ...
2021-06-10
Scientists say naked mole rats - a rodent native to West Africa - may hold the key to new treatments for degenerative diseases such as cancer and dementia.
The reclusive animals have a lifespan far in excess of other rodents - for example, mice and rats live about two years, whereas naked mole rats can live for 40 or 50 years.
Researchers at the University of Bradford say the animals have a unique DNA repair mechanism that enables them to prevent cancers and other degenerative conditions, including dementia.
Cancer resistant
Professor Sherif El-Khamisy, Director of the Institute of Cancer Therapeutics at the University, said: "Naked mole rats are fascinating ...
2021-06-10
Niigata, Japan - Researchers from Brain Research Institute, Niigata University, Japan may have unraveled a new approach that could revolutionize the treatment, prevention, and possibly reversal of the damages that could lead to Parkinson's Disease (PD). This novel finding utilizing the cellular and zebrafish models, demonstrated how the leakage of mitochondrial dsDNA into the cytosol environment of the cell can contribute to the impairment of brain tissue of patients with PD.
Parkinson's disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease, and its prevalence ...
2021-06-10
Surgeons can ease their patients' pain from common operations without prescribing opioids, and avoid the possibility of starting someone on a path to long-term use, a pair of new studies suggests.
Treating post-surgery pain with non-opioid pain medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen didn't lead to higher pain levels or more serious issues during recovery, and didn't dampen patients' satisfaction with their care, according to new results from a study of more than 22,000 patients who had one of seven common operations at 70 hospitals.
The team behind the study has also produced a free, evidence-based guide for surgeons and other acute care providers, ...
2021-06-10
People often think about human behavior in terms of what is happening in the present--reading a newspaper, driving a car, or catching a football. But other dimensions of behavior extend over weeks, months, and years.
Examples include a child learning how to read; an athlete recovering from a concussion; or a person turning 50 and wondering where all the time has gone. These are not changes that people perceive on a day-to-day basis. They just suddenly realize they're older, healed, or have a new development skill.
"The field of neuroscience looks at the brain in multiple ways," says Franco Pestilli, a neuroscientist at The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin). "For ...
2021-06-10
Researchers have discovered that the common bacteria E. coli can be deployed as a sustainable way to convert post-consumer plastic into vanillin, a new study reveals.
Vanillin is the primary component of extracted vanilla beans and is responsible for the characteristic taste and smell of vanilla.
The transformation could boost the circular economy, which aims to eliminate waste, keep products and materials in use and have positive impacts for synthetic biology, experts say.
The world's plastic crisis has seen an urgent need to develop new methods to recycle polyethylene terephthalate (PET) - the strong, lightweight plastic derived from non-renewable materials such as oil and gas and widely used for ...
2021-06-10
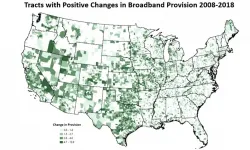
High-speed internet access has gone from an amenity to a necessity for working and learning from home, and the COVID-19 pandemic has more clearly revealed the disadvantages for American households that lack a broadband connection.
To tackle this problem, Michigan State University researchers have developed a new tool to smooth the collection of federal broadband access data that helps pinpoint coverage gaps across the U.S. The research was published May 26 In the journal PLOS ONE.
"Nearly 21% of students in urban areas are without at-home broadband, while 25% and 37% lack at-home broadband in suburban ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] LIM domain only 1: One gene, many roles in cancer
Researchers detail another gene target that could be the crucial link to curing different cancers