(Press-News.org) Neurons, nerve cells in the brain, are central players in brain function. However, a key role for glia, long considered support cells, is emerging. A research group at the University of Basel has now discovered two new types of glial cells in the brain, by unleashing adult stem cells from their quiescent state. These new types of glia may play an important role in brain plasticity and repair.
The brain is malleable well into adulthood. Brain plasticity is not only due to the formation of new nerve connections. Stem cells present in the adult brain also generate new nerve cells. For more than a hundred years, scientists have concentrated on investigating different types of nerve cells.
In the brain, however, another class of cells, called glia, are also essential for brain function. However, the importance of glial cells has been underestimated for decades. How many types of glia there are, how they develop and what roles they play are all still largely unexplored.
Stem cells - unleashed from quiescence
The research group of Prof. Fiona Doetsch at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel is investigating stem cells in the ventricular-subventricular zone in the adult mouse brain. In this region, many of the stem cells are in a quiescent state, sensing signals in the environment that stimulate them to awaken and transform into new nerve cells.
In their study in the journal Science, Doetsch's team identified a molecular signal that awakened the stem cells from their quiescent state, allowing them to uncover multiple domains that give rise to glial cells in this stem cell reservoir.
Stem cells - birthplace of glial cells
"We found an activation switch for quiescent stem cells," Doetsch explains. "It is a receptor that maintains the stem cells in their resting state. We were able to turn off this switch and thus activate the stem cells," Doetsch says. In addition, the researchers were able to visualize the development of the stem cells into different glial cells in specific areas of the stem cell niche.
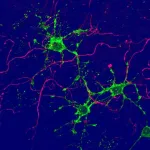
"Some of the stem cells did not develop into neurons, but into two different novel types of glial cells," Doetsch reports. This brain region studied is therefore a birthplace for different types of glial cells as well as its role as a breeding ground for neurons.
"What was very unexpected was that one glial cell type was found attached to the surface of the wall of the brain ventricle, rather than in the brain tissue." These cells are continuously bathed by cerebrospinal fluid and interact with axons from other brain areas, and therefore are poised to sense and integrate multiple long-range signals.
Glial cells - active in health and disease
The research team also found that both glial cell types were activated in a model of demyelination. These new glial cell types may therefore be a source of cells for repair in neurodegenerative diseases, such as multiple sclerosis or after injury.
As a next step, Doetsch would like to specifically trace these new glial cell types and to investigate their roles in normal brain function and how they respond in different physiological contexts. This will provide important clues to understanding brain plasticity and how the renewal and repair of neural tissue occurs.
INFORMATION:
Moreover, they identified a correlation between the progression of the disease and certain corpuscles in the cell nuclei. They published their report in the journal Acta Neuropathological Communications on 13 April 2021.
Aggregates seem to have a function
Affecting over 50 million people, Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia and primarily occurs in people over the age of 65. The pathology of the disease in the brain is mainly characterised by two factors: beta-amyloid plaques outside the nerve cells and tau proteins. The tau protein stabilises tube-like structures (microtubules) inside cells, which are relevant ...
With Oskar Aszmann and his team at the Department of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery, MedUni Vienna has long been regarded as a world leader in bionic limb reconstruction. It was only last year that the world's first fully integrated bionic arm prosthesis was developed at MedUni Vienna. This is ready-to-use and is described as "Plug and Play". Although all bionic aids have so far been used in humans, the technique known as osseointegration (direct skeletal attachment) has now been used for the very first time in a bearded vulture - the creature was given a new foot. A paper on this ground-breaking procedure has been published today (Friday) in the prestigious Journal Scientific Reports.
In large birds such as vultures, the loss of limbs results in the ...
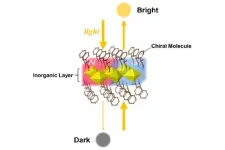
Researchers at Tohoku University have demonstrated the designability of novel magnets with magic mirror-like characteristics in organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite (OIHP)-type compounds.
OIHP-type compounds, a type of material used to construct solar cells, possess exceptional optical properties and have recently attracted worldwide interest. Researchers are keen to harness their structural diversity.
Although the superior optical properties of OIHPs have been mainly studied for their photoelectric characteristics, several OIHP-type compounds are known to function as magnets that transmit light. Combining the excellent optical ...
Not only the very concise 11-year cycle, but also all other periodic solar activity fluctuations can be clocked by planetary attractive forces. This is the conclusion drawn by Dr. Frank Stefani and his colleagues from the Institute of Fluid Dynamics at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) and from the Institute of Continuous Media Mechanics in Perm, Russia. With new model calculations, they are proposing a comprehensive explanation of all important known sun cycles for the first time. They also reveal the longest fluctuations in activity over thousands of years as a chaotic process. ...
On average the earliest memories that people can recall point back to when they were just two-and-a-half years old, a new study suggests.
The findings, published in peer-reviewed journal Memory, pushes back the previous conclusions of the average age of earliest memories by a whole year.
They are presented in a new 21-year study, which followed on from a review of already-existing data.
"When one's earliest memory occurs, it is a moving target rather than being a single static memory," explains childhood amnesia expert and lead author Dr Carole Peterson, from Memorial University of Newfoundland.
"Thus, what many people provide when asked for their earliest memory is not a boundary or watershed beginning, before which there are no memories. Rather, ...
Shifts in weather patterns induced by climate change will increase extreme heat and reduce rainfall across major crop growing regions, with impacts on agricultural production. Will this trigger a decline in the supply of calories needed to sustain the world's growing population?
According to a study published in the Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, global calorie supplies are subject to continuing or even increasing vulnerability to climate change. Climate change could reduce global crop yields by 10% by mid-century and 25% by century's end, under a vigorous warming scenario, if farmers cannot adapt better than they did historically. ...
Every day, around 15 000 children under the age of five die from causes that could have been prevented.
But the children of highly educated parents survive more often than others. This statistic applies worldwide, according to a newly published sweeping systematic review in The Lancet.
The mother's level of education is particularly important for her children's survival.
"One year of extra education for the mother is associated with an approximately three per cent reduction in mortality on average," says Professor Terje Andreas Eikemo at the Norwegian University of Science ...
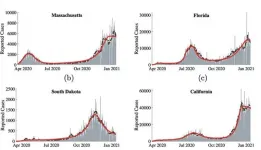
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- By adding behavioral components to an infectious disease model, Brown University researchers have developed a new modeling approach that captures the peaks and valleys in new COVID-19 cases seen over the past 16 months.
The approach, published in the journal Scientific Reports, could be useful in forecasting the future trends in the current pandemic, as well as in predicting the course of future ones.
"We know that people's behavior matters in terms of how an infection is spread," said Vikas Srivastava, an assistant professor of ...
Tsukuba, Japan - To study the immune system in human health and disease, scientists commonly use the genetic manipulation of mouse hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) as a powerful model system. These studies have been extremely valuable in the fight against a number of human diseases. However, the current procedures are complex, time-consuming, and expensive.
In a new study published in NATURE COMMUNICATIONS, researchers at the University of Tsukuba have developed a novel technique that has the potential to overcome the limitations associated with these models, which are known as bone marrow (BM) chimeric mice. This system allows scientists to observe and investigate how ...
SARS-CoV-2 outbreaks involving care homes with fully vaccinated residents have been reported across Germany. In order to gain a better understanding of this phenomenon, a team of researchers from Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin used an outbreak at a Berlin-based facility to analyze virus-related data and study the immune responses of elderly residents following vaccination. The researchers' data, which have been published in Emerging Infectious Diseases*, confirm vaccine effectiveness in the elderly. However, they also indicate a delayed and slightly reduced immune response. In light of their findings, the researchers emphasize the need to vaccinate both caregivers and close contacts in order to better protect this high-risk group.
The BioNTech/Pfizer ...