Can encroachment benefit hotel franchisees?
News from the Journal of Marketing
2021-06-15
(Press-News.org) Researchers from University of Texas at Dallas and Emory University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines the issue of encroachment in the hotel industry.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Can Encroachment Benefit Hotel Franchisees?" and is authored by TI Tongil Kim and Sandy Jap.
For decades, the issue of encroachment, or adding an outlet in proximity to existing outlets, has been contentious. A new outlet increases competition for customers, causing concerns for franchisors and franchisees that the existing outlet's sales will be cannibalized. Franchising is a key means for growth and market expansion for many companies. These organizations account for as much as $890 billion or 50% of all retail sales across 75 industries in the US (approximately 3% of the US gross domestic product). Therefore, encroachment is a big issue.
A new study in the Journal of Marketing suggests that cannibalization does not always have to be the case. Using five years of hotel sales data, an experiment, and a series of simulations, the research team finds that adding a new outlet in markets with few same brand outlets can modestly benefit existing locations. Specifically, the researchers find that revenues can increase an average of 1.7% (a 2.3% improvement in profits) - in other words, a sunny side to an issue that has historically dissolved in conflict.
Importantly, this positive impact does not happen when the new outlet is a different franchise brand. In other words, brands matter. Kim adds that "We also find that younger brands, cross-brands (e.g., Hyatt Place and Hyatt House), and brand bookings through online travel agencies also benefit from having more versus fewer locations." Customers appreciate and value additional outlets of a brand (up to a point) as well as when the brands are new or when they share a moniker with other franchise locations of the same brand. Customers also value multiple same brand options when booking through websites like Expedia or Kayak.
This means that when looking to expand, franchisors should prioritize markets with few same brand outlets, newer brands in their portfolio, cross brands, and online travel agency sales channels. These potentially represent win-win options in the conflict over encroachment.
Most of the work around network expansion has focused on the legalities of this process, codes of conduct, expectations, and compliance and monitoring practices. This research suggests that there may be alternate ways of tackling this thorny problem.
INFORMATION:
Full article and author contact information available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/00222429211008136
About the Journal of Marketing
The Journal of Marketing develops and disseminates knowledge about real-world marketing questions useful to scholars, educators, managers, policy makers, consumers, and other societal stakeholders around the world. Published by the American Marketing Association since its founding in 1936, JM has played a significant role in shaping the content and boundaries of the marketing discipline. Christine Moorman (T. Austin Finch, Sr. Professor of Business Administration at the Fuqua School of Business, Duke University) serves as the current Editor in Chief.
https://www.ama.org/jm
About the American Marketing Association (AMA)
As the largest chapter-based marketing association in the world, the AMA is trusted by marketing and sales professionals to help them discover what is coming next in the industry. The AMA has a community of local chapters in more than 70 cities and 350 college campuses throughout North America. The AMA is home to award-winning content, PCM® professional certification, premiere academic journals, and industry-leading training events and conferences.
https://www.ama.org
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-15
Researchers have discovered a new and more efficient computing method for pairing the reliability of a classical computer with the strength of a quantum system.
This new computing method opens the door to different algorithms and experiments that bring quantum researchers closer to near-term applications and discoveries of the technology.
"In the future, quantum computers could be used in a wide variety of applications including helping to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, developing artificial limbs and designing more efficient pharmaceuticals," said Christine Muschik, a principal investigator at the Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC) and a faculty member in physics and astronomy at the University of Waterloo.
The research team from ...
2021-06-15
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 7:30 p.m. EDT, Monday, June 14, 2021)--A protein that is critical in cancer cell metabolism has been imaged for the first time with a newly developed radiopharmaceutical, 18F-DASA-23. Imaging with this novel agent has the potential to improve the assessment of treatment response for patients, specifically those with brain tumors. This study was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting.
Tumor cells go through various changes to survive and prosper in the body. One of the key changes they make is modifying a master switch, known as pyruvate kinase ...
2021-06-15
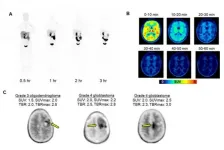
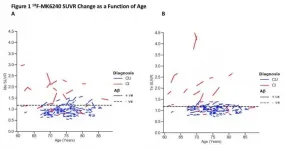
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 7:30 p.m. EDT, Monday, June 14, 2021)--A novel positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer has been shown to effectively measure increases in brain tau--a distinguishing characteristic of Alzheimer's disease--before any symptoms of the disease are observed. With the potential to measure increases in tau over a long period of time, this tracer offers an important tool to assess the effectiveness of Alzheimer's disease treatments in clinical trials. This research was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting.
Tau is a protein commonly ...
2021-06-15
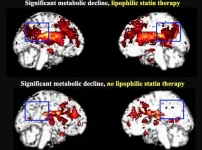
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 7:30 p.m. EDT, Monday, June 14, 2021)--In patients with mild cognitive impairment, taking lipophilic statins more than doubles their risk of developing dementia compared to those who do not take statins. According to research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting, positron emission tomography (PET) scans of lipophilic statin users revealed a highly significant decline in metabolism in the area of the brain that is first impacted by Alzheimer's disease.
Statins are medications used to lower cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart attack or stroke. They are the most commonly used drugs in the developed world, and nearly 50 percent of Americans over age 75 use a statin. Different types ...
2021-06-15
The use of 'ice' flavoured e-cigarettes may be common and positively associated with conventional smoking and nicotine dependence among young adults, suggests research published online in the journal Tobacco Control.
And it's unclear where these' hybrid' vapes, combining fruit/sweet and cooling flavours, fit into current or future regulatory frameworks, which apply restrictions according to distinct flavour categories, point out the study authors.
'Ice' flavoured e-cigarettes--marketed as a combination of fruity/sweet and cooling flavours, such as 'blueberry ice' or 'melon ice'--recently entered the US market. Previous research ...
2021-06-15
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. A third dose of COVID-19 vaccine increased antibody levels in organ transplant recipients with a suboptimal response following standard 2-dose vaccination
Study is the first to report on response to a third vaccine ...
2021-06-15
KINGSTON, R.I. - June 14, 2021 - The rarest frog in Rhode Island may not be as rare as scientists once thought after a study by University of Rhode Island researchers using a seldom-used methodology turned up many more of the endangered animals than they expected.
Eastern spadefoots - often called spadefoot toads, though they are actually frogs - have long been considered highly secretive and difficult to find outside of their one- or two-day annual breeding periods on rainy nights. In some years, they don't breed at all. But after scientists reported just 50 sightings of the frogs over the previous 70 years, the Rhode Island researchers observed 42 spadefoots ...
2021-06-14
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed a way to dynamically switch the surface of liquid
metal between reflective and scattering states. This technology could one day be used to create electrically controllable mirrors or illumination devices.
Liquid metals combine the electrical, thermal and optical properties of metals with the fluidity of a liquid. The new approach uses an electrically driven chemical reaction to create switchable reflective surfaces on a liquid metal. No optical coatings nor polishing steps, which are typically required to make reflective optical components, are necessary to make the liquid metal highly ...
2021-06-14
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- While the United States faces a nationwide nursing shortage, a recent study at the University of Missouri found rural Missouri counties experience nursing shortages at a greater rate than the state's metropolitan counties. In addition, the study found rural Missouri counties have a higher percentage of older nurses nearing retirement, which could have a severe impact on the future of the state's nursing workforce.
Anne Heyen, an assistant teaching professor in the MU Sinclair School of Nursing, analyzed workforce data of nearly 136,000 licensed Missouri nurses to identify the age and geographical disparities ...
2021-06-14
DARIEN, IL - More veterans are receiving important sleep care, especially those living in rural areas where access to sleep medicine specialists can be difficult. The Veterans Health Administration's TeleSleep Program launched telehealth services in 2017 to support the testing, diagnosis, and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea and other sleep disorders. More than one million veterans who received care from VHA in 2020 have sleep apnea.
"The implementation of these services has been very successful," said Dr. Kathleen Sarmiento, program lead for the Office of Rural Health TeleSleep ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Can encroachment benefit hotel franchisees?
News from the Journal of Marketing