Reduced microbial stability linked to soil carbon loss in active layer under alpine permafrost degra
2021-06-16
(Press-News.org) Chinese researchers have recently discovered links between reduction in microbial stability and soil carbon loss in the active layer of degraded alpine permafrost on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (QTP).
The researchers, headed by Prof. CHEN Shengyun from the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources (NIEER) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and XUE Kai from University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, conducted a combined in-depth analysis of soil microbial communities and their co-occurrence networks in the active permafrost layer along an extensive gradient of permafrost degradation.
The QTP encompasses the largest extent of high-altitude mountain permafrost in the world. This permafrost is different than high-latitude permafrost and stores massive soil carbon. An often ignored characteristic of permafrost is that the carbon pool in the active layer soil is more active and directly affected by climate change, compared to deeper layers.
Triggered by climate warming, permafrost degradation may decrease soil carbon stability and induce massive carbon loss, thus leading to positive carbon-climate feedback. However, microbial-mediated mechanisms for carbon loss from the active layer soil in degraded permafrost still remain unclear.
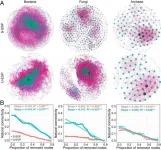
In this study, the researchers found that alpine permafrost degradation reduced the stability of active layer microbial communities as evidenced by increased sensitivity of microbial composition to environmental change, promoted destabilizing network properties and reduced resistance to node or edge attacking of the microbial network.
They discovered that soil organic carbon loss in severely degraded permafrost is associated with increased microbial dissimilarity, thereby potentially contributing to a positive carbon feedback in alpine permafrost on the QTP.
INFORMATION:
The results were published in PNAS in an article entitled "Reduced microbial stability in the active layer is associated with carbon loss under alpine permafrost degradation".
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Strategic Priority Research Program (A) of CAS and the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-16
Greater Helsinki -- Transitioning to low-carbon energy production is the biggest climate challenge to overcome. Many countries are already looking to adopt clean heating solutions more widely, with the International Energy Agency projecting that by 2045 nearly half of global heating will be done with heat pumps. To ensure speedy uptake, governments are likely to offer subsidies to ensure these energy-efficient options actually make their way into homes and offices.
A new study from Aalto University assesses the impact of heat pumps on energy consumption as well as how ...
2021-06-16
Research published in the journal ACS Materials and Interfaces has provided new understanding of how false-negative results in Lateral Flow Tests occur and provides opportunity for simple improvements to be made.
Lateral Flow Devices were introduced late in 2020 on a global scale to help detect novel coronavirus infection in individuals, with test results produced rapidly in half an hour or less. However, their potential has been somewhat hindered by inadequate sensitivity, with a high number of false-negative results.
Using X-ray fluorescence imaging from Diamond Light Source, researchers from King's College London ...
2021-06-16
Researchers from the University of Kent's School of Psychology have found that when people are presented with the idea of a Covid-19 "immunity passport", they show less willingness to follow social distancing and face covering guidelines. However, this willingness seems to return when people read more cautious information about Covid-19 immunity.
PhD students Ricky Green and Mikey Biddlestone and Professor Karen Douglas asked participants from the UK and USA to imagine they had either recovered from Covid-19 or were currently infected. Participants asked to imagine ...
2021-06-16
Several different causes of ageing have been discovered, but the question remains whether there are common underlying mechanisms that determine ageing and lifespan. Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing and the CECAD Cluster of Excellence in Ageing research at the University Cologne have now come across folate metabolism in their search for such basic mechanisms. Its regulation underlies many known ageing signalling pathways and leads to longevity. This may provide a new possibility to broadly improve human health during ageing.
In recent decades, ...
2021-06-16
In an international study published by the journal Environment International, the University of Surrey led an international team of air pollution experts in monitoring pollution hotspots in 10 global cities: Dhaka (Bangladesh); São Paulo (Brazil); Guangzhou (China); Medellín (Colombia); Cairo (Egypt); Addis Ababa (Ethiopia); Chennai (India); Sulaymaniyah (Iraq); Blantyre (Malawi); and Dar-es-Salaam (Tanzania).
Surrey's Global Centre for Clean Air Research (GCARE) set out to investigate whether the amount of fine air pollution particles (PM2.5) drivers inhaled is connected to the duration drivers spend in pollution hotspots and socio-economic indicators such ...
2021-06-16
2 June 2021, Singapore - The human fetal immune system begins to develop early during gestation, however, factors responsible for fetal immune-priming remain elusive. Using multiple complementary approaches, Dr Florent Ginhoux from A*STAR's Singapore Immunology Network (SIgN), Professor Jerry Chan from KK Women's and Children's Hospital (KKH), Professor Salvatore Albani from the SingHealth Duke-NUS Translational Immunology Institute, with collaborators from Cambridge University explored potential exposure to microbial agents in-utero. The team identified live microbes across fetal organs that stimulate activation of fetal T-cells during the second trimester of gestation. Study published in scientific journal, Cell, on 24 June 2021.
The team profiled microbes ...
2021-06-16
Do you like the thick brush strokes and soft color palettes of an impressionist painting such as those by Claude Monet? Or do you prefer the bold colors and abstract shapes of a Rothko? Individual art tastes have a certain mystique to them, but now a new Caltech study shows that a simple computer program can accurately predict which paintings a person will like.
The new study, appearing in the journal Nature Human Behaviour, utilized Amazon's crowdsourcing platform Mechanical Turk to enlist more than 1,500 volunteers to rate paintings in the genres of impressionism, cubism, abstract, and color field. The volunteers' answers were fed into a computer program and then, after this training period, the computer ...
2021-06-16
Chatbots hold promise for dementia patient or caregiver support, but are still in their infancy, finds a paper published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research. None of the interactive digital apps tested by medical researchers and a computer scientist performed well on all testing criteria, and all the apps contained linguistic biases and usability challenges. The authors conclude that until developers produce evidence-based chatbots that have undergone end user evaluation it will be hard to evaluate their potential to adequately educate and support dementia patients and their caregivers.
"Dementia care is complex and no two cases of dementia are alike. Chatbots have the potential of providing ...
2021-06-16
Ozone is a pollutant at ground level, but very high in the atmosphere's "ozone layer," it absorbs damaging ultraviolet radiation. Past studies have examined ozone levels in the Southern Hemisphere, but little is known about levels of the molecule in Antarctica over long periods. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology have analyzed more than 25 years of Antarctic data, finding that concentrations near the ground arose from both natural and human-related sources.
Ozone gas has a sharp or acrid scent that sometimes accompanies smog or summer storms. It forms when sunlight ...
2021-06-16
Microplastic pollution of waterways has become a huge concern, with the tiny pieces of plastic entering food webs and potentially having harmful effects on animals and people. In addition, microplastics can act as breeding grounds for antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Now, researchers reporting in Environmental Science & Technology have analyzed antibiotic-resistance genes (ARGs) on five types of microplastics at different locations along the Beilun River in China, finding much higher abundances in urban than rural regions.
In rivers, major sources of microplastics include textile fibers from laundering, water bottle fragments, and films from bags and wrappers. Also prevalent in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Reduced microbial stability linked to soil carbon loss in active layer under alpine permafrost degra