(Press-News.org) Boston - New study results indicate that different comorbid conditions affecting individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 may impact how long they continue to receive positive SARS-CoV-2 polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test results. Individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 who are aged 60+, have three or more chronic medical conditions, particularly diabetes, obesity, rheumatologic disease, or an organ transplant, have positive PCR tests for longer periods of time compared to younger individuals without these comorbidities. However, the data showed no significant difference in the duration of positive PCR tests results by the degree of immunocompromise or for individuals receiving chemotherapy or steroids to treat COVID-19.
Published online in Open Forum Infectious Diseases and led by researchers at Boston Medical Center, this study is the largest sample size to date of SARS-CoV-2 PCR retesting in both immunocompromised and non-immunocompromised patients, allowing for the comparison between these two groups.
"There are limited data on how long immunocompromised individuals continue to test positive for COVID-19 after initial infection," said Rachel Epstein, MD, MScE, an infectious diseases physician at Boston Medical Center and the study's corresponding author. "This study challenges whether the current recommendations to consider retesting severely immunocompromised individuals and use negative SARS-CoV-2 PCR test results to end isolation is necessary."
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), severely immunocompromised individuals are likely to have prolonged positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR test results. The conditions that cause immunocompromised status represented in the CDC definition include: people on chemotherapy or high dose steroids; those with untreated HIV; those with a primary immunodeficiency; or those who recently received an organ transplant.
The researchers examined data from 3,758 individuals who were retested using the SARS-CoV-2 PCR test following an initial positive result. The individuals were separated into groups by age as well as immunocompromised severity:
Severe - active chemotherapy, HIV with a CD4 count less than 200, organ transplant in the last year, or chronic high-dose steroids (7.4 percent of study group)
Moderate - solid organ transplant recipient greater than 1 year prior, HIV with a CD4 count greater than 200, and others taking chronic biologic medications (4.2 percent of study group)
Not immunocompromised (88.4 percent of study group)
The median length of time for severely immunocompromised patients to receive a negative SARS-CoV-2 PCR test result was 22 days; for moderately and non-immunocompromised individuals, the time was 20 and 16 days, respectively. For individuals who had a solid organ transplant, are older than 60, have diabetes, obesity or rheumatologic disease, as well as those with more than three comorbid conditions, it took longer for a negative SARS-CoV-2 PCR test result.
"Retesting individuals to end isolation precautions can delay care, and may not be necessary even for most severely immunocompromised people, particularly as most transmission studies demonstrate that it is highly unlikely for someone to transmit infection more than 20 days into their illness," said Epstein, an assistant professor of medicine and pediatrics at Boston University School of Medicine. The authors note that retesting recommendations should perhaps consider a combination of conditions or include only certain groups of extremely immunocompromised individuals. There have been a few cases in the literature showing positive COVID1-9 test results months out from initial infection in patients who have undergone a solid organ or bone marrow transplant or received chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
Additional studies that directly measure transmission or transmissibility from individuals with a positive PCR test result more than 20 days into illness with COVID-19 would be helpful to better inform current CDC guidelines.
INFORMATION:
About Boston Medical Center
Boston Medical Center (BMC) is a private, not-for-profit, 514-bed, academic medical center that is the primary teaching affiliate of Boston University School of Medicine. It is the largest and busiest provider of trauma and emergency services in New England. BMC offers specialized care for complex health problems and is a leading research institution, receiving more than $166 million in sponsored research funding in fiscal year 2019. It is the 13th largest funding recipient in the U.S. from the National Institutes of Health among independent hospitals. In 1997, BMC founded Boston Medical Center Health Plan, Inc., now one of the top ranked Medicaid MCOs in the country, as a non-profit managed care organization. Boston Medical Center and Boston University School of Medicine are partners in Boston HealthNet - 12 community health centers focused on providing exceptional health care to residents of Boston. For more information, please visit http://www.bmc.org.
EAST LANSING, Mich. - The original Star Trek television series took place in a future when space is the final frontier, but humanity hasn't reached that point quite yet.
As researchers like Michigan State University entomologists Sarah Smith and Anthony Cognato are reminding us, there's still plenty to discover right here on Earth.
Working in Central and South America, the duo discovered more than three dozen species of ambrosia beetles -- beetles that eat ambrosia fungus -- previously unknown to science. Smith and Cognato described these new species on June 16 in the journal ZooKeys.
The Spartans also selected ...
Researchers from Skoltech and their colleagues from the UK have managed to create a stable giant vortex in interacting polariton condensates, addressing a known challenge in quantized fluid dynamics. The findings open possibilities in creating uniquely structured coherent light sources and exploring many-body physics under unique extreme conditions. The paper was published in the journal Nature Communications.
In fluid dynamics, a vortex is a region where a fluid revolves around a point (2D) or a line (3D); you've clearly seen one in your sink ...
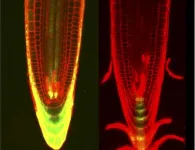
Ikoma, Japan - Humans pride themselves on being able to multitask, especially under pressure. But it turns out that we aren't the only ones who are organized: researchers from Japan have discovered that plants balance genome maintenance with organ growth by organizing different responses to DNA damage.
In a study published in Science Advances, a research team led by Nara Institute of Science and Technology has revealed that plants use combined control of the plant hormones cytokinin and auxin to organize DNA damage responses while maintaining growth.
Plants are highly adaptable organisms that never stop growing, thanks largely to the functions carried out by their roots. Because of the essential role that roots play in plant growth, ...
A new study using cells, transgenic mouse models, and cultured human lung tissue provides evidence that the ability to trigger programmed cell death (apoptosis) may enable highly pathogenic coronaviruses to spread within their hosts so successfully. Targeting this process may reduce the severity of coronavirus diseases, the study goes on to show. While scientists have been aware that highly pathogenic coronaviruses leave substantial cell death in their wake as they infiltrate the body, the importance of apoptosis to the internal spread of coronavirus infections ...
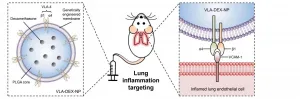
Nanoengineers at the University of California San Diego have developed immune cell-mimicking nanoparticles that target inflammation in the lungs and deliver drugs directly where they're needed. As a proof of concept, the researchers filled the nanoparticles with the drug dexamethasone and administered them to mice with inflamed lung tissue. Inflammation was completely treated in mice given the nanoparticles, at a drug concentration where standard delivery methods did not have any efficacy.
The researchers reported their findings in Science Advances on June 16.
What's special ...
Parenting is one of life's greatest joys, right? Not for everyone. New research from Michigan State University psychologists examines characteristics and satisfaction of adults who don't want children.
As more people acknowledge they simply don't want to have kids, Jennifer Watling Neal and Zachary Neal, both associate professors in MSU's department of psychology, are among the first to dive deeper into how these "child-free" individuals differ from others.
"Most studies haven't asked the questions necessary to distinguish 'child-free' individuals -- those who choose not to have children -- from other types of nonparents," Jennifer Watling Neal said. ...
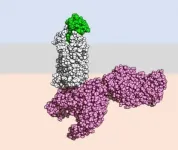
Chemokine receptors, located at the surface of many immune cells, play an important role in their function. Chemokines are small proteins that bind to these receptors and control the movement and behaviour of white blood cells. However, despite the importance of this family of receptors, their activation mechanism remains poorly understood. In Switzerland, a research consortium from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), the Biozentrum of the University of Basel, and the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) in Villigen has succeeded in decoding the activation mechanism of the CCR5 receptor, a member of this family implicated in several diseases such as HIV/AIDS, cancer, and the respiratory ...
New research published this week challenges a popular belief that intermittent fasting diets such as alternate day fasting or the '5:2' are the most effective ways to lose weight.
Over recent years, diets which see people fast on a few days each week have increased in popularity, reinforced by images of people's miraculous weight transformations, and backed by celebrity endorsements.
However, evidence to date about the effectiveness of fasting compared with more traditional diets which aim to reduce calorie intake over the course of a full week has been limited.
Published in the prestigious journal Science Translational Medicine, the new study from a team of physiologists at the University of Bath builds this evidence and indicates that there is 'nothing ...
PHILADELPHIA (June 16, 2021) - The current Medicare reimbursement policy for nurse practitioners (NPs) allows NPs to directly bill Medicare for services that they perform, but they are reimbursed at only 85% of the physician rate. A growing number of states are granting full practice authority to nurse practitioners. Even more states have loosened practice restrictions due to COVID-19. Both of these reasons illustrate why payment parity is essential.
In an article in The Online Journal of Issues in Nursing, Alycia Bischof, MSN, APRN, PNP-BC, Senior Lecturer at the ...
The long relationships between stars and the planets around them - including the Sun and the Earth - may be even more complex than previously thought. This is one conclusion of a new study involving thousands of stars using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory.
By conducting the largest survey ever of star-forming regions in X-rays, a team of researchers has helped outline the link between very powerful flares, or outbursts, from youthful stars, and the impact they could have on planets in orbit.
"Our work tells us how the Sun may have behaved and affected ...