(Press-News.org) NEW YORK (June 17, 2021)--New York City neighborhoods that had higher levels of socioeconomic disadvantage experienced more COVID-19 infections and deaths, according to Mount Sinai scientists who created a neighborhood-level COVID-19 inequity index.
The index measured factors that fueled inequities in the residents' lives, such as employment and commuting patterns, population density of their neighborhood, food access, socioeconomic status, and access to health care. This allowed the scientists to compare between neighborhoods the contributions of these social factors in facilitating disease transmission during the first wave of the pandemic in a study published in Nature Communications in June.
"Much of the early rhetoric around COVID-19 disparities centered on comorbidities which, due to health disparities, may have explained why communities of color were suffering higher mortality. But we were seeing more people of color getting infected in the first place," said Daniel Carrión, PhD, MPH, first author and postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Environmental Medicine and Public Health at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. "Our research team wanted to add to the literature outlining how structural racism is related to neighborhood disadvantage, and how that disadvantage is related to increased COVID-19 infections and mortality."
The COVID-19 inequity index showed that the disparities were considerably worse based on neighborhood racial and ethnic composition; Black neighborhoods had the highest average inequity index, followed by Latinx communities, while white neighborhoods had the lowest. The authors believe one of the reasons for these disparities is the diminished capacity to socially isolate based on where someone lives.
This study showed that areas with higher COVID-19 inequity indices had higher subway ridership after New York State introduced stay-at-home orders. This implies that the residents had less capacity to socially distance, the researchers said, possibly due to their jobs as essential workers or because they lived in denser housing.
The researchers believe their approach to identifying social factors that are associated with viral spread may be useful throughout the United States to pinpoint potential areas for targeted public health intervention.
"The social factors in the COVID-19 inequity index are upstream neighborhood characteristics--they were already in place before the pandemic," said Allan Just, PhD, senior author on the study and Assistant Professor of Environmental Medicine and Public Health at Icahn Mount Sinai. "In the near term, this speaks to the importance of place-based interventions in Black, Indigenous, and people of color (BIPOC) communities to reduce disease incidence and mortality, such as improved and targeted vaccine availability for these communities. This also supports the need to look at social factors in pandemic preparedness."
The team analyzed many forms of publicly available data, including census, New York City subway ridership, New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene infections and mortality data, and other datasets available through New York City's and New York State's open data portals.
Many neighborhood-level social variables are closely related; for example, median income can be strongly associated with education or even food access. This can be a challenge for traditional statistical approaches, so the team employed a new statistical framework designed to deal with these challenges, developed by co-author Elena Colicino, PhD, Assistant Professor of Environmental Medicine and Public Health at Icahn Mount Sinai.
The COVID-19 inequity index included neighborhood-level characteristics, but specifically excluded race and ethnicity as input variables. "Past literature shows that structural racism operates by historically sorting BIPOC people into neighborhoods that do not have the same resources and may facilitate infectious disease transmission," said Dr. Carrión. "We wanted to see if our index reconstructed those racial disparities."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health grants UL1TR001433, P30ES023515, and T32HD049311.
Additional authors include Nicolo Foppa Pedretti, MS, Kodi B. Arfer, PhD, Johnathan Rush, MA, and Nicholas DeFelice, PhD, in the Department of Environmental Medicine and Public Health at Icahn School Mount Sinai.
About the Mount Sinai Health System
The Mount Sinai Health System is New York City's largest academic medical system, encompassing eight hospitals, a leading medical school, and a vast network of ambulatory practices throughout the greater New York region. Mount Sinai is a national and international source of unrivaled education, translational research and discovery, and collaborative clinical leadership ensuring that we deliver the highest quality care--from prevention to treatment of the most serious and complex human diseases. The Health System includes more than 7,200 physicians and features a robust and continually expanding network of multispecialty services, including more than 400 ambulatory practice locations throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, and Long Island. The Mount Sinai Hospital is ranked No. 14 on U.S. News & World Report's "Honor Roll" of the Top 20 Best Hospitals in the country and the Icahn School of Medicine as one of the Top 20 Best Medical Schools in country. Mount Sinai Health System hospitals are consistently ranked regionally by specialty and our physicians in the top 1% of all physicians nationally by U.S. News & World Report.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Twitter and YouTube.
As almost all our private information is digitalized, it is increasingly important that we find ways to protect our data and ourselves from being hacked.
Quantum Cryptography is the researchers' answer to this problem, and more specifically a certain kind of qubit - consisting of single photons: particles of light.
Single photons or qubits of light, as they are also called, are extremely difficult to hack.
However, in order for these qubits of light to be stable and work properly they need to be stored at temperatures close to absolute zero - that is minus ...
AI is used in an array of extremely useful applications, such as predicting a machine's lifetime through its vibrations, monitoring the cardiac activity of patients and incorporating facial recognition capabilities into video surveillance systems. The downside is that AI-based technology generally requires a lot of power and, in most cases, must be permanently connected to the cloud, raising issues related to data protection, IT security and energy use.
CSEM engineers may have found a way to get around those issues, thanks to a new system-on-chip they have developed. It runs on a tiny ...
Bottom Line: Genetic mutations indicative of DNA damage were associated with high red meat consumption and increased cancer-related mortality in patients with colorectal cancer.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Marios Giannakis, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a physician at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
Background: "We have known for some time that consumption of processed meat and red meat is a risk factor for colorectal cancer," ...
The unique mechanical and optical properties found in the exoskeleton of a humble Asian beetle has the potential to offer a fascinating new insight into how to develop new, effective bio-inspired technologies.
Pioneering new research by a team of international scientists, including Professor Pete Vukusic from the University of Exeter, has revealed a distinctive, and previously unknown property within the carapace of the flower beetle - a member of the scarab beetle family.
The study showed that the beetle has small micropillars within the carapace - or the upper section of the exoskeleton - that give the insect both strength and flexibility to withstand damage very effectively.
Crucially, these micropillars are incorporated into highly regular layering in the exoskeleton ...
Sophia Antipolis - 17 June 2021: People living with obesity who attended a non-judgemental and personalised lifestyle modification programme improved their cardiovascular and mental health during just 10 weeks, according to a study presented today at EuroHeartCare - ACNAP Congress 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 Participants lost weight and achieved benefits in anxiety and depression and physical measurements including blood pressure.
"We focus on changing behaviours and improving people's relationship with food," said study ...
The fast-food industry spent $5 billion on advertising in 2019, and the advertisements disproportionately targeted Black and Hispanic youth, according to new research published today by the Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity at the University of Connecticut. The new report, Fast Food FACTS 2021, finds that the industry's annual ad spending in 2019 increased by over $400 million since 2012, and that children and teens were viewing on average more than two fast food TV ads per day.
Frequent and widespread exposure to fast-food marketing increases young people's preferences for, and consumption ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. - The price tag for giving birth in America may bring some families sticker shock - even for those with private insurance.
And when delivering moms require caesarians or their newborns need neonatal care, some families may spend as much as $10,000 out-of-pocket, according to a new Michigan Medicine-led study.
"Childbirth is the most common reason for hospitalization in the U.S.," said lead author Kao-Ping Chua, M.D., Ph.D.,a pediatrician and researcher at University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children's Hospital and the Susan B. Meister Child Health Evaluation and Research Center.
"Our findings show that some privately insured families are shouldering ...
A recent study by Nagoya University researchers revealed that microRNAs in urine could be a promising biomarker to diagnose brain tumors. Their findings, published in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, have indicated that regular urine tests could help early detection and treatment of brain tumors, possibly leading to improved patient survival.
Early diagnosis of brain tumors is often difficult, partly because most people undergo a brain CT or MRI scan only after the onset of neurological deficits, such as immobility of limbs, and incapability of speech. When brain tumors are detected by CT or MRI, in many cases, they have already grown too large to be fully removed, which could lower patients' survival rate. From this perspective, accurate, easy, and inexpensive ...
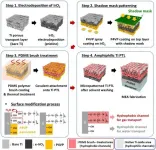
Green hydrogen, a source of clean energy that can be generated without using fossil fuels, has recently gained immense attention as it can be potentially used to promote carbon neutrality. Korean researchers have succeeded in improving the efficiency of unitized regenerative fuel cells that can be used to efficiently produce green hydrogen and generate power.
The unitized regenerative fuel cells boast of hydrogen production and fuel cell modes. They are eco-friendly, cost-effective, and independent energy storage and power generation devices that require less space for ...
SPOKANE, Wash. - Many people likely lost sleep over COVID-19. A study of twins led by Washington State University researchers found that stress, anxiety and depression during the first few weeks of the pandemic were associated with less and lower quality sleep.
In a survey of more than 900 twins taken shortly after COVID-19 lockdown measures began, about half of the respondents reported no change in their sleep patterns, but around a third, 32.9%, reported decreased sleep. Another 29.8% reported sleeping more. In the analysis, the researchers found that any change in sleep was connected to self-reported mental health issues, though it was more strongly associated with decreased ...