A key player in cell death moonlights as a mediator of inflammation
Researchers from Kanazawa University find that gasdermin D, a protein known to be involved in cell death, is also crucial for activation and release of the key immune mediator interleukin-1α
2021-06-18
(Press-News.org) Kanazawa, Japan - Interluekin-1α (IL-1α) is an important part of the immune response, but until now it has been unclear how this molecule is processed from its precursor, pro-IL-1α, and exits the cell during inflammasome activation. Now, researchers from Japan have found that gasdermin D, a protein that was already known to mediate pyroptosis, a form of regulated cell death, plays a crucial role in the maturation and release of IL-1α.
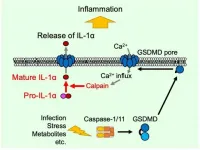
In a study published in March in Cell Reports, researchers from Kanazawa University report that, when the inflammasome (a part of the innate immune system) is activated, gasdermin D forms pores in the cell membrane that allow factors from outside of the cell to flow in, leading to the activation and release of mature IL-1α.
Previous work has shown that inflammasome activation leads to gasdermin D being cut in two by an enzyme, and that one half of the cut protein forms membrane pores. This leads to pyroptosis whereby the pores let water into the cells, causing them to swell and burst.
"We knew that caspase-1 cleaves gasdermin D, and that this enzyme is also important for IL-1α activation," says lead author of the study Kohsuke Tsuchiya. "We therefore suspected that gasdermin D might be involved in the pathway leading to IL-1α release."
To test this possibility, the researchers deleted the gene encoding gasdermin D, and found that this almost completely eliminated IL-1α exit from the cells. Unexpectedly, though, they also saw that virtually no mature IL-1α was present inside these cells.
"This made us think that gasdermin D is important not only for IL-1α release, but also IL-1α maturation," explains Takashi Suda, lead author of the study. "When we looked into this in more detail, we found that gasdermin D did not need to cause cell lysis for these effects to take place. Instead, only its ability to form pores in the membrane was required for both IL-1α maturation and release."
The researchers went on to show that pore formation by gasdermin D allows calcium influx and activation of calpains (a type of proteases), which promotes processing of the pro-IL-1α precursor into mature IL-1α maturation.
"Our findings provide the missing link between caspase-1 activity and IL-1α maturation," says Tsuchiya.
Given that inflammasome activation is a key element of both inflammatory diseases and the response to infection, this study provides important insight into essential functions of the human immune system. Identifying gasdermin D as a regulator of immune function as well as cell death increases our understanding of how inflammasome activation ultimately leads to IL-1α release from immune cells.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-18
COVID-19 has changed the world in unimaginable ways. Some have even been positive, with new vaccines developed in record time. Even the extraordinary lockdowns, which have had severe effects on movement and commerce, have had beneficial effects on the environment and therefore, ironically, on health. Studies from all around the world, including China, Europe and India, have found major drops in the level of air pollution. However, to fully understand the impact of anthropogenic causes, it is important to separate them from natural events in the atmosphere like wind flow.
To demonstrate this point, a new study by researchers at the Research Institute for Humanity and Nature, Japan, uses satellite data and mathematical modeling to explain just ...
2021-06-18
Identifying the causes of human neurodegenerative diseases is a global research priority, warranting frequent reviews of the accumulating knowledge. In doing just that, biologists from the Plant Physiology Laboratory at the University of Guam and neuroscientists from the Experimental Medicine Program at The University of British Columbia have published an update on the reputed environmental toxins that have been suspected of being involved in mammal neurodegeneration. Their summary was published in April in the book Spectrums of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, which is available online ...
2021-06-18
According to a recent Finnish study, higher levels of moderate and vigorous physical activity can curb arterial stiffening already in childhood. However, sedentary time or aerobic fitness were not linked to arterial health. The results, based on the ongoing Physical Activity and Nutrition in Children (PANIC) Study conducted at the University of Eastern Finland, were published in the Journal of Sports Sciences. The study was made in collaboration among researchers from the University of Jyväskylä, University of Eastern Finland, the Norwegian School of Sport sciences, and the University of Cambridge.
Arterial stiffening predisposes to heart diseases, ...
2021-06-18
Tokyo, Japan - In Japan, thousands of homes and businesses and hundreds of lives have been lost to typhoons. But now, researchers have revealed that a new flood forecasting system could provide earlier flood warnings, giving people more time to prepare or evacuate, and potentially saving lives.
In a study published this month in Scientific Reports, researchers from The University of Tokyo Institute of Industrial Science have shown that a recently developed flood forecasting system provides much earlier advance warnings of extreme flooding events than current systems. ...
2021-06-18
Germany is a hotspot for dragonflies and damselflies (Odonata) species in Europe, owing to the range of habitats and climates that it provides. While many recent and mostly small-scale studies suggest long-term declines of insect populations in different parts of Europe, studies of freshwater insects - including dragonflies and damselflies - suggest that some species have increased in occurrence. Researchers of iDiv, FSU and UFZ have now provided a nationwide analysis of the occurrence and distribution of dragonflies and damselflies in Germany between 1980 and 2016. For this, they analysed over 1 million occurrence records on 77 species from different regional ...
2021-06-18
The population on Earth is increasingly growing and people are expected to live longer in the future. Thus, better and more reliable therapies to treat human diseases such as Alzheimer's and cardiovascular diseases are crucial. To cope with the challenge of ensuring healthy ageing, a group of international scientists investigated the potential of biosynthesising several polyamines and polyamines analogues with already known functionalities in treating and preventing age-related diseases.
One of the most interesting molecules to study was spermidine, which is a natural product already present in people's blood and an inducer of autophagy that is an essential cellular process for clearing damaged proteins, e.g., misfolded proteins ...
2021-06-18
URBANA, Ill. - For the most accurate accounting of a product's environmental impact, scientists look at the product's entire life cycle, from cradle to grave. It's a grand calculation known as a life cycle assessment (LCA), and greenhouse gas emissions are a key component.
For corn ethanol, most greenhouse gas emissions can be mapped to the fuel's production, transportation, and combustion, but a large portion of the greenhouse gas calculation can be traced right back to the farm. Because of privacy concerns, however, scientists can't access individual farm management decisions such as fertilizer type and rate.
Nitrogen fertilizer data are an important piece of the calculation because a portion ...
2021-06-18
A decade-long study of the most common forearm fracture in older adults revealed that personalized medicine catering to a patient's individual needs and environment, not age or X-rays, should guide treatment options.
Led by a Michigan Medicine physician, the research team examined treatment outcomes over two years for patients who fractured their distal radius, the larger of two bones in the forearm. They found no one-size-fits all method for treating the fracture, which more than 85,000 Medicare beneficiaries sustain annually.
"Traditionally, surgeons look at these broken bones on X-rays, and they have to assess various ways of fixing it based off fracture anatomy and patient age," said Kevin Chung, M.D., study lead and Charles B. G. De ...
2021-06-18
By combining satellite data and digital models, the researchers have shown that coastal overtopping, and consequently the risk of flooding, is set to further accelerate over the 21st century, by up to 50-fold under a high emission global warming scenario, especially in the tropics. This increase is principally caused by a combination of sea level rise and ocean waves.
Low-lying coastal regions host nearly 10% of the world's population. In addition to ongoing erosion and rising sea levels, these areas and their unique ecosystems are facing destructive hazards, including episodic flooding due to overtopping of natural/artificial protection, as in the case of Hurricane Katrina, ...
2021-06-18
Scientists from the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research and Naval Medical Research Center partnered with researchers at the University of Pennsylvania and Acuitas Therapeutics to develop a novel vaccine based on mRNA technology that protects against malaria in animal models, publishing their findings in npj Vaccines.
In 2019, there were an estimated 229 million cases of malaria and 409,000 deaths globally, creating an extraordinary cost in terms of human morbidity, mortality, economic burden, and regional social stability. Worldwide, Plasmodium falciparum is the parasite species which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A key player in cell death moonlights as a mediator of inflammation
Researchers from Kanazawa University find that gasdermin D, a protein known to be involved in cell death, is also crucial for activation and release of the key immune mediator interleukin-1α