Cellular mechanisms of early mammary gland development unraveled
2021-06-21
(Press-News.org) Helsinki University research group used live tissue imaging for the first time to visualise the emergence of the mammary gland.
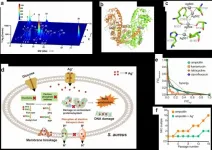
Despite long-standing interest, the cellular mechanisms driving the initiation of mammary gland development have remained elusive for decades, mostly due to technical limitations in studying dynamic cell behaviors in live tissues. Recent advances in microscopic methods and availability of various mouse models allowed the research group of Marja Mikkola from HiLIFE Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki to address this question. This is the first time when live tissue imaging has been used to visualise the emergence of the mammary gland.
Mammary gland is the class-defining organ of mammals, yet we know surprisingly little how its development commences. In their recent study published in Journal of Cell Biology, the research group of Marja Mikkola used time-lapse imaging to show that the growth of the mammary bud is primarily fueled by migration of cells to the bud. In contrast, although increase in cellular size and cell proliferation contribute to this process, the role of these mechanisms remains minor.
"Interestingly, mammary bud cells, unlike most of other skin derivatives such as hair follicle and tooth bud, do not divide for several days, indicating that this might be a unique feature of early mammary gland development" says graduate student Ewelina Trela, the lead author of the study. "However, we do not yet know why this happens", she continues.
Mammary buds use a previously undescribed mechanism for invagination
Tissue invagination, or tissue folding inwards into the underlying stroma, is a fundamental mechanism that occurs to generate the architecture of many organs. In the same piece of work, the authors describe a novel mechanism for tissue invagination.
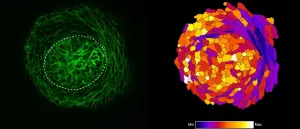
"Using confocal fluorescence microscopy, we found thin and elongated epidermal keratinocytes surrounding mammary bud in a rim like fashion: their appearance and disappearance coincided with the invagination process suggesting that these cells, named ring cells, could be functionally important" details principal investigator Marja Mikkola.
Next, the Mikkola group teamed up with the group of Sara Wickström at HiLIFE and Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki to establish live imaging of the forming mammary bud, which confirmed that ring cells move circumferentially around the mammary bud.
The study also revealed that the ring cells exert contractile force through the actomyosin network, via non-muscle myosin IIA (NMIIA). The functionality of ring cells was impaired in NMIIA deficient mice leading to compromised mammary bud shape. Whether other developing organs utilize a similar cellular mechanism for invagination remains an open question.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-21
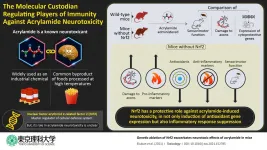
Acrylamide is a toxic chemical compound that affects the nervous system. Not only is it widely used in industries such as paper production, plastics, and wastewater management, but it is also a byproduct of commonly used food processing methods, which makes human exposure to acrylamide inevitable. Therefore, many studies have focused on understanding the toxic effects of acrylamide and our body's response to them. Generally, in response to toxicity, the body's cells release protective factors and antioxidants to remedy the damage. This response is activated by various cellular machinery. One such activator is a protein called "nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2" (Nrf2), ...
2021-06-21
Special diets, exercise programs, supplements and vitamins, there is everywhere something supposed to help us live longer. Whether it actually works has not always been shown, but the average life expectancy of people has increased over the last 150 years. A study by an international team of researchers, including Claudia Fichtel and Peter Kappeler, scientists in the Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology Unit at the German Primate Center (DPZ) - Leibniz Institute for Primate Research in Göttingen, indicates that we probably cannot slow down aging. The comparative studies with humans and non-human primates, indicates that it is not the rate at which humans age that slows ...
2021-06-21
Washington, DC, June 21, 2021 - Depression in youth, between the ages of 10 and 24 years, is both a leading cause of stress and a possible risk factor for future diseases and impairment. Now, a study in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (JAACAP), published by Elsevier, confirms that depression in childhood or adolescence is associated with higher levels of adult anxiety and substance use disorders, worse health and social functioning, less financial and educational achievement, and increased criminality.
The findings are based on the Great Smoky Mountains Study, an ongoing longitudinal ...
2021-06-21
TEL AVIV, Israel and RALEIGH, NC, June 21, 2021, RedHill Biopharma Ltd. (Nasdaq: RDHL) ("RedHill" or the "Company"), a specialty biopharmaceutical company, today announced presentation of the positive Phase 2 safety and efficacy data for oral opaganib (Yeliva®, ABC294640) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia at the World Microbe Forum (WMF) 2021 (poster #: 5574).
Results and post hoc analyses of data from the 40-patient U.S. Phase 2 study were presented in a poster entitled, "Opaganib, an Oral Sphingosine Kinase-2 (SK2) Inhibitor in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Phase 2A Study, in ...
2021-06-21
In 2013, François ENGLERT and Peter HIGGS won the Nobel Prize in Physics for the theoretical discovery of a mechanism that contributes to our understanding of the origin of mass of subatomic particles, which was confirmed through the discovery of the predicted fundamental particle by the A Toroidal LHC Apparatus (ATLAS) and the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) experiments at The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN)'s Large Hadron Collider in 2012. The Higgs mode or the Anderson-Higgs mechanism (named after another Nobel Laureate Philip W ANDERSON), has widespread influence ...
2021-06-21
A Curtin University-led study of ancient bones on South Australia's Kangaroo Island has provided new information about the Island's past fauna and an insight into how species may live there in the future.
Published in Quaternary Science Reviews, the researchers analysed around 2,000 bone fragments with the aim of eventually being able to establish a more complete picture of past biodiversity on the Island.
Lead researcher Dr Frederik Seersholm from Curtin's School of Molecular and Life Sciences said DNA studies on such a large scale have never been done on the Island before.
"We identified 33 species, 10 of which are extinct on the island today. We also found DNA traces from both the ...
2021-06-21
A research team led by Professor Hongzhe SUN, Norman & Cecilia Yip Professor in Bioinorganic Chemistry and Chair Professor from Research Divison for Chemistry and Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, in collaboration with Dr Richard Yi-Ysun KAO, Associate Professor from the Department of Microbiology, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, and Dr Aixin YAN, Associate Professor from School of Biological Sciences, the University of Hong Kong (HKU), discovers that silver (Ag)-based antimicrobials can effectively combat antibiotic resistant Staphylococcus aureus by targeting multiple biological pathways via functional disruption of key proteins and can be further exploited to enhance the efficacy of conventional antibiotics ...
2021-06-21
Microalgae are "simple" organisms of single cells, yet they pack a mighty potential punch when it comes to helping humanity achieve carbon neutrality, according to researchers from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Their metabolic activities play fundamental roles in global carbon cycling and convert carbon dioxide into a wide variety of high-value macromolecules.
Now, the QIBEBT researchers have developed a way to rapidly determine exactly which microalgae -- out of the millions of variations -- can most readily convert carbon dioxide into valuable compounds that can be used for fuels, food and drugs. They published ...
2021-06-21
Fragrances are functional molecules with a pleasant scent that are widely used in aqueous products (cosmetics and detergents) and on surfaces such as textiles, leather and wallpaper. However, maintaining gentle and continuous scent on these items is an ongoing challenge in the field of flavours and fragrances.
Profragrances are delivery systems used to control the release of the volatile compounds in fragrances. They have fragile chemical bonds that can be stimulated by ambient conditions such as light, temperature, pH value and even oxygen. Drawing on these molecular profragrances, ...
2021-06-21
Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from human activities have risen drastically over the last century and a half and are seen as the primary cause of global warming and abnormal weather patterns. So, there has been considerable research focus, in a number of fields, on lowering our CO2 emissions and its atmospheric levels. One promising strategy is to chemically break down, or 'reduce,' CO2 using photocatalysts--compounds that absorb light energy and provide it to reactions, speeding them up. With this strategy, the solar powered reduction of CO2, where no other artificial source of energy is used, becomes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cellular mechanisms of early mammary gland development unraveled