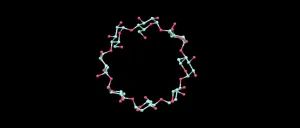
(Press-News.org) Engineers at Tufts University have developed new methods to more efficiently fabricate materials that behave in unusual ways when interacting with microwave energy, with potential implications for telecommunications, GPS, radar, mobile devices, and medical devices. Known as metamaterials, they are sometimes referred to as "impossible materials" because they could, in theory, bend energy around objects to make them appear invisible, concentrate the transmission of energy into focused beams, or have chameleon like abilities to reconfigure their absorption or transmission of different frequency ranges.
The innovation, described today in Nature Electronics, constructs the metamaterials using low-cost inkjet printing, making the method widely accessible and scalable while also providing benefits such as the ability to be applied to large conformable surfaces or interface with a biological environment. It is also the first demonstration that organic polymers can be used to electrically "tune" the properties of the metamaterials.
Electromagnetic metamaterials and meta-surfaces - their two-dimensional counterparts - are composite structures that interact with electromagnetic waves in peculiar ways. The materials are composed of tiny structures - smaller than the wavelengths of the energy they influence - carefully arranged in repeating patterns. The ordered structures display unique wave interaction capabilities that enable the design of unconventional mirrors, lenses and filters able to either block, enhance, reflect, transmit, or bend waves beyond the possibilities offered by conventional materials.
The Tufts engineers fabricated their metamaterials by using conducting polymers as a substrate, then inkjet printing specific patterns of electrodes to create microwave resonators. Resonators are important components used in communications devices that can help filter select frequencies of energy that are either absorbed or transmitted. The printed devices can be electrically tuned to adjust the range of frequencies that the modulators can filter.
Metamaterial devices operating in the microwave spectrum could have widespread applications to telecommunications, GPS, radar, and mobile devices, where metamaterials can significantly boost their signal sensitivity and transmission power. The metamaterials produced in the study could also be applied to medical device communications because the biocompatible nature of the thin film organic polymer could enable the incorporation of enzyme-coupled sensors, while its inherent flexibility could permit devices to be fashioned into conformable surfaces appropriate for use on or in the body.
"We demonstrated the ability to electrically tune the properties of meta-surfaces and meta-devices operating in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum," said Fiorenzo Omenetto, Frank C. Doble Professor of Engineering at Tufts University School of Engineering, director of the Tufts Silklab where the materials were created, and corresponding author of the study. "Our work represents a promising step compared to current meta-device technologies, which largely depend on complex and costly materials and fabrication processes."
The tuning strategy developed by the research team relies entirely on thin-film materials that can be processed and deposited through mass-scalable techniques, such as printing and coating, on a variety of substrates. The ability to tune the electrical properties of the substrate polymers enabled the authors to operate the devices within a much wider range of microwave energies and up to higher frequencies (5 GHz) than was assumed to be possible with conventional non-meta materials ( END
Inkjet printing 'impossible materials'
Engineers develop inexpensive, scalable method to make metamaterials that manipulate microwave energy in ways conventional materials cannot
2021-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How the surfaces of silicone breast implants affect the immune system
2021-06-21
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Every year, about 400,000 people receive silicone breast implants in the United States. According to data from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, a majority of those implants needs to be replaced within 10 years due to the buildup of scar tissue and other complications.
A team led by MIT researchers has now systematically analyzed how the varying surface architecture found in these implants influences the development of adverse effects, which in rare cases can include an unusual type of lymphoma.
"The surface topography of an implant can drastically affect how the immune response perceives it, and this has important ramifications for the [implants'] design," says Omid Veiseh, a former MIT postdoc. "We ...
Scientists develop energy saving technique paving way for a carbon neutral society
2021-06-21
Researchers at the University of Bristol have discovered a method which will allow for faster communication systems and better energy saving electronics.
The breakthrough was made by establishing how to remotely measure the electric field inside a semiconductor device for the first time. A semiconductor is a material, such as Silicon, which can be used in electronic devices to control electric current.
Now, in this new study, published today in Nature Electronics, scientists outline how to precisely quantify this electric field, meaning next generation power and radio frequency electronic devices can be developed which have the potential to be faster, and more reliable, as well as more energy ...
This molecule is made from sugar, shaped like a doughnut, and formed using light
2021-06-21
A process using a light-sensitive chemical can drastically reduce cost and energy consumption to produce gamma-cyclodextrin, a compound that is widely used in manufacturing, according to a Dartmouth study.
The research, published in Chem, demonstrates how a hydrazone template can replace energy-intensive distillation to produce and isolate gamma-cyclodextrin--a water-soluble chemical that attracts other molecules and is used to enhance food, pharmaceuticals, and a wide range of consumer products.
"These compounds are biodegradable, biocompatible, benign and commonly used," said Ivan Aprahamian, a professor of chemistry at Dartmouth. "We are making ...
Protein linked to heart health, disease a potential therapeutic target for dementia
2021-06-21
By the time people with Alzheimer's disease start exhibiting difficulty remembering and thinking, the disease has been developing in their brains for two decades or more, and their brain tissue already has sustained damage. As the disease progresses, the damage accumulates, and their symptoms worsen.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found that high levels of a normal protein associated with reduced heart disease also protect against Alzheimer's-like brain damage - at least in mice. The findings, published June 21 in Neuron, suggest that raising levels ...
Investigational Alzheimer's drug improves biomarkers of the disease
2021-06-21
An investigational Alzheimer's drug reduced molecular markers of disease and curbed neurodegeneration in the brain, without demonstrating evidence of cognitive benefit, in a phase 2/3 clinical trial led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis through its Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network-Trials Unit (DIAN-TU). These results led the trial leaders to offer the drug, known as gantenerumab, to participants as part of an exploratory open-label extension. The researchers continue to monitor changes in measures of Alzheimer's disease in those participants who are receiving the drug.
The DIAN-TU study (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01760005), published June 21 in Nature Medicine, evaluated the effects of two investigational drugs - ...
Projections of US high-tide flooding show rapid increases and extreme months
2021-06-21
In the mid-2030s, multiple United States coastal regions may see rapid increases in the number of high-tide flooding (HTF) days, according to a study led by the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa and published today in Nature Climate Change. The combined effects of sea-level rise (SLR) and natural fluctuations in tidal range are anticipated to cause tipping points in the frequency of HTF.
Coastal locations around the U.S., particularly along the Atlantic coast, are experiencing recurrent flooding at high tide. The impact of HTF accumulates over numerous seemingly minor occurrences, which can exceed the impact of rare extremes over time. These impacts are subtle--for example, the loss of revenue due to recurrent road and business closures--compared with the physical damage of property ...
Targeted therapy could be first line treatment for childhood cancer
2021-06-21
Scientists studying a common childhood cancer have made a major breakthrough which could lead to a cure for some youngsters who would not have survived the condition.
An international study, involving Newcastle University, UK, has for the first time found a genetic marker in tumours from patients with high-risk neuroblastoma.
Research, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, has identified that alterations in the neuroblastoma's ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) gene are associated with a significantly poorer prognosis for children with high-risk disease.
Experts ...
Fertility drugs do not increase breast cancer risk, study finds
2021-06-21
Drugs routinely used during fertility treatments to release eggs do not increase the risk of developing breast cancer, new research has shown.
Researchers from King's College London, in partnership with King's Fertility, analysed studies involving 1.8 million women undergoing fertility treatments. These women were followed up in studies for an average period of 27 years and had no increase in the risk of developing breast cancer.
The research, published today in Fertility and Sterility journal, is the largest study to date assessing whether commonly used fertility drugs are for a cancer risk for women.
Fertility treatments can range from using medications to boost the release of an egg in a women's natural cycle to more complex ...
Significant inequalities observed in popular Liverpool 'mass testing' pilot
2021-06-21
A study by the University of Liverpool has shown that while asymptomatic COVID-19 testing in Liverpool was popular, significant inequalities were evident between those who got tested and those who didn't.
Published in the journal The Lancet Regional Health - Europe, the study found that 43% of residents aged over 5 years (n = 214 525) took up the offer of free testing for people without symptoms of COVID-19 between 6th November 2020 and 31st January 2021. A total of 1.3% of tests were positive, meaning that 5192 individuals who did not know they had the virus were notified ...
Adjuvant-free avian influenza vaccines in the works
2021-06-21
The avian influenza, an acute viral infectious disease that occurs in poultry such as chickens, ducks, and migratory birds, has been reported to be transmittable to humans. It is difficult to control because it spreads among migratory birds that travel to China, Europe, and elsewhere. Once it is transmitted, it spreads rapidly. Disposing infected livestock is not only costly, but also a cause of serious environmental pollution. This is why vaccines against infectious diseases are imperative. To this, a research team in Korea has recently developed a plant-based, adjuvant-free, recombinant protein vaccine that exhibits a strong immune response.
Professor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Inkjet printing 'impossible materials'Engineers develop inexpensive, scalable method to make metamaterials that manipulate microwave energy in ways conventional materials cannot