Loss of circadian regulation allows for increase in glucose production during lung cancer
New study identifies possible therapeutic target to suppress cancer cell growth
2021-06-25
(Press-News.org) Irvine, CA - June 25, 2021 - New research from the University of California, Irvine reveals how the circadian regulation of glucose production in the liver is lost during lung cancer progression, and how the resulting increase in glucose production may fuel cancer cell growth.
The new study titled, "Glucagon regulates the stability of REV-ERBα to modulate hepatic glucose production in a model of lung cancer-associated cachexia," published today in Science Advances, illustrates how the circadian clock is regulated under conditions of stress such as during lung cancer progression and cancer-associated tissue wasting disease called cachexia.
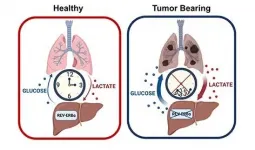
"Our research shows that a critical circadian protein, REV-ERB?, controls glucose production in the liver. During lung cancer progression and specifically under conditions of cachexia, this circadian regulation is lost, resulting in increased glucose production from the liver," said senior author Selma Masri, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Biological Chemistry at UCI School of Medicine. "Based on our findings, we identified that lung tumors are able to provide instructive cues to the liver to increase glucose production, a major fuel source for cancer cells."
This research places the circadian clock as a central regulator of glucose production during lung cancer progression and provides important insight toward the development of novel therapeutics to target REV-ERB? to suppress cancer cell growth.
"We are continuing to investigate the consequence of increased glucose production during lung cancer progression by tracing the metabolic fate of this newly generated glucose to determine if this fuel source can drive the heightened metabolic demand of lung cancer cells," said Amandine Verlande, PhD, and Sung Kook Chun, PhD, postdoctoral scholars in the Masri Laboratory.
The circadian clock is our intrinsic biological pacemaker that maintains physiological homeostasis in all tissues of the body. Under conditions of stress, the biological clock is rewired as an adaptive mechanism to maintain synchrony and equilibrium throughout the body.
INFORMATION:
This research was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health, Concern Foundation, V Foundation for Cancer Research, Cancer Research Coordinating Committee, and shared resources supported through the UCI Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center.
About the UCI School of Medicine
Each year, the UCI School of Medicine educates more than 400 medical students, and nearly 150 doctoral and master's students. More than 700 residents and fellows are trained at UCI Medical Center and affiliated institutions. The School of Medicine offers an MD; a dual MD/PhD medical scientist training program; and PhDs and master's degrees in anatomy and neurobiology, biomedical sciences, genetic counseling, epidemiology, environmental health sciences, pathology, pharmacology, physiology and biophysics, and translational sciences. Medical students also may pursue an MD/MBA, an MD/master's in public health, or an MD/master's degree through one of three mission-based programs: Health Education to Advance Leaders in Integrative Medicine (HEAL-IM), Leadership Education to Advance Diversity-African, Black and Caribbean (LEAD-ABC), and the Program in Medical Education for the Latino Community (PRIME-LC). The UCI School of Medicine is accredited by the Liaison Committee on Medical Accreditation and ranks among the top 50 nationwide for research. For more information, visit som.uci.edu.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-25
After suffering a stroke, patients often are unable to use the arm on their affected side. Sometimes, they end up holding it close to their body, with the elbow flexed.
In a new study, Northwestern University and Shirley Ryan AbilityLab researchers have discovered that, in an attempt to adapt to this impairment, muscles actually lose sarcomeres -- their smallest, most basic building blocks.
Stacked end to end (in series) and side to side (in parallel), sarcomeres make up the length and width of muscle fibers. By imaging biceps muscles with three noninvasive methods, the researchers found that stroke patients had fewer sarcomeres along the length ...
2021-06-25
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Researchers at Mayo Clinic Cancer Center are studying a potential new chimeric antigen receptor-T cell therapy (CAR-T cell therapy) treatment for multiple myeloma. Their findings were published on Friday, June 24, in The Lancet.
"CAR-T cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy that involves harnessing the power of a person's own immune system by engineering their T cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells," says Yi Lin, M.D., a Mayo Clinic hematologist and lead author of the study.
Dr. Lin says the Food and Drug Administration approved ...
2021-06-25
The promise of 5G Internet of Things (IoT) networks requires more scalable and robust communication systems -- ones that deliver drastically higher data rates and lower power consumption per device.
Backscatter radios ? passive sensors that reflect rather than radiate energy ? are known for their low-cost, low-complexity, and battery-free operation, making them a potential key enabler of this future although they typically feature low data rates and their performance strongly depends on the surrounding environment.
Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology, Nokia Bell Labs, and Heriot-Watt University have found a low-cost way for backscatter radios to support high-throughput communication and 5G-speed Gb/sec data transfer using only a single transistor when previously ...
2021-06-25
Three years ago, Arthur Ashkin won the Nobel Prize for inventing optical tweezers, which use light in the form of a high-powered laser beam to capture and manipulate particles. Despite being created decades ago, optical tweezers still lead to major breakthroughs and are widely used today to study biological systems.
However, optical tweezers do have flaws. The prolonged interaction with the laser beam can alter molecules and particles or damage them with excessive heat.
Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have created a new version of optical tweezer technology that fixes this problem, a development ...
2021-06-25
Want a smartphone that stretches, takes damage, and still doesn't miss a call?
A team of Virginia Tech researchers from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and the Macromolecules Innovation Institute has created a new type of soft electronics, paving the way for devices that are self-healing, reconfigurable, and recyclable. These skin-like circuits are soft and stretchy, sustain numerous damage events under load without losing electrical conductivity, and can be recycled to generate new circuits at the end of a product's life.
Led by Assistant Professor Michael Bartlett, the team recently published its findings in END ...
2021-06-25
Scientists from the National University of Science and Technology "MISIS" (NUST MISIS) in cooperation with their colleagues from the Siberian Federal University and the Research and Production Centre of Magnetic Hydrodynamics (Krasnoyarsk) have developed a technology for producing a unique heat-resistant aluminium alloy with improved durability.
According to the researchers, this new alloy could replace more expensive and heavier copper conductors in aircraft and high-speed rail transport. The study results were published in an interdisciplinary, peer-reviewed journal, the Materials Letters. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167577X2100896X)
Researchers have created a method for producing ...
2021-06-25
Night and day, oil tankers, yachts and cargo ships stacked with shipping containers ply the 80-kilometer (50-mile) waterway through the jungles of Panama between the Atlantic and the Pacific Ocean: about 40 ships every 24 hours. But even though the Canal is fed by freshwater rivers that empty through the locks on each end, a system that generally prevents fish and smaller marine invertebrates from hopping from ocean to ocean, some still manage to get through, clinging to the hulls of ships. Other invading species arrive from far-flung ports, dumped with ballast water as ships prepare for transit.
"Panama is a major shipping hub that provides amazing opportunities to test key ideas about marine invasions by studying ...
2021-06-25
A team of engineers and clinicians has developed an ultra-thin, inflatable device that can be used to treat the most severe forms of pain without the need for invasive surgery.
The device, developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge, uses a combination of soft robotic fabrication techniques, ultra-thin electronics and microfluidics.
The device is so thin - about the width of a human hair - that it can be rolled up into a tiny cylinder, inserted into a needle, and implanted into the epidural space of the spinal column, the same area ...
2021-06-25
A new electrode that could free up 20% more light from organic light-emitting diodes has been developed at the University of Michigan. It could help extend the battery life of smartphones and laptops, or make next-gen televisions and displays much more energy efficient.
The approach prevents light from being trapped in the light-emitting part of an OLED, enabling OLEDs to maintain brightness while using less power. In addition, the electrode is easy to fit into existing processes for making OLED displays and light fixtures.
"With our approach, you can do it all in ...
2021-06-25
More corn is grown in the United States than any other crop, but we only use a small part of the plant for food and fuel production; once people have harvested the kernels, the inedible leaves, stalks and cobs are left over. If this plant matter, called corn stover, could be efficiently fermented into ethanol the way corn kernels are, stover could be a large-scale, renewable source of fuel.
"Stover is produced in huge amounts, on the scale of petroleum," said Whitehead Institute Member and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) biology professor Gerald Fink. "But there are enormous technical challenges to using them cheaply to create biofuels and other important chemicals."
And so, year after year, most of the woody corn material is left in the fields to rot.
Now, a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Loss of circadian regulation allows for increase in glucose production during lung cancer
New study identifies possible therapeutic target to suppress cancer cell growth





