Extreme events: Ecosystems offer cost effective protection
2021-06-30
(Press-News.org) Decision-makers around the world are increasingly interested in using ecosystem solutions such as mangroves, coral reefs, sand dunes and forests on steep slopes to help buffer the impacts from hazard events and protect populations. But what evidence exists to show the efficacy of nature-based solutions over man-made protective measures to reduce the impacts of the increasing numbers of hazard events humanity faces due to climate change?
An international, multi-disciplinary team of 28 researchers has examined nearly 20 years' worth of peer-reviewed studies on the impacts of ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction (DRR) efforts to, for the first time, summarize the state of knowledge of ecosystem services and functions for DRR. The team reviewed 529 English-language articles to catalog the extent of knowledge on, and confidence in, ecosystems in reducing disaster risk.
"This is the most extensive and up-to-date assessment of the role nature-based solutions can play for reducing impacts of natural hazards" affirms Dr. Jaroslav Mysiak, director of the research division 'Risk assessment and adaptation strategies' at the CMCC Foundation - Euro-Mediterranean Center on Climate Change. "It complements the recently released European Environment Agency's report in the context of climate change and resilience".
As reported in the article published by the journal Nature Sustainability, researchers assessed the state of knowledge on the role ecosystems play in reducing the disaster risk: from the management of wildfires to the mitigation of flooding in urban areas through the implementation of green design, from the use of vegetation on steep slopes to cost-effectively reduce mountain hazards - such as mudslides and avalanches - to the management of stormwater.
Their review of existing research reveals that persistent droughts, land degradation and desertification are often slow-onset processes in drylands that, over time, may well lead to disaster. Importantly, they found ample evidence of how ecosystem-based approaches in areas susceptible to drought can reduce the impacts of climate change.
The main author of the article Karen Sudmeier, Senior Adviser, Disaster Risk Reduction, United Nations Environment Programme writes in a blog post: "Two decades of research analyzed over six years left us with a number of questions: we know there is evidence that most ecosystems reduce the impacts of hazard events in a cost-effective manner. Now we need to disseminate this evidence in the language that decision-makers speak: how much, how high, how wide? We also need to focus our attention on performance standards, green design blueprints, ecological engineering standard operating procedures and the specs that will provide the ultimate evidence base to draw attention and investment to nature's solutions to increasing numbers of hazard events worldwide. Our research in this growing field has only just begun."
The report, "Scientific evidence for ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction," is available online from Nature Sustainability.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-30
A study analysing the association between a wide variety of prenatal and childhood exposures and neuropsychological development in school-age children has found that organic food intake is associated with better scores on tests of fluid intelligence (ability to solve novel reasoning problems) and working memory (ability of the brain to retain new information while it is needed in the short term). The study, published in Environmental Pollution, was conceived and designed by researchers at the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal)--a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation--and ...
2021-06-30
A scientific breakthrough: Researchers from Tel Aviv University have engineered the world's tiniest technology, with a thickness of only two atoms. According to the researchers, the new technology proposes a way for storing electric information in the thinnest unit known to science, in one of the most stable and inert materials in nature. The allowed quantum-mechanical electron tunneling through the atomically thin film may boost the information reading process much beyond current technologies.
The research was performed by scientists from the Raymond and Beverly Sackler School of Physics and Astronomy and Raymond and Beverly Sackler School of Chemistry. The group includes Maayan Vizner Stern, Yuval Waschitz, Dr. Wei Cao, Dr. Iftach Nevo, Prof. Eran Sela, Prof. Michael Urbakh, ...
2021-06-30
Working out just five minutes daily via a practice described as "strength training for your breathing muscles" lowers blood pressure and improves some measures of vascular health as well as, or even more than, aerobic exercise or medication, new CU Boulder research shows.
The study, published June 29 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, provides the strongest evidence yet that the ultra-time-efficient maneuver known as High-Resistance Inspiratory Muscle Strength Training (IMST) could play a key role in helping aging adults fend off cardiovascular disease - the nation's leading killer.
In the United States alone, 65% of adults over age 50 have ...
2021-06-30
A University of Arkansas researcher and international colleagues found that employed individuals, on average, are 35.3% more likely to be infected with the flu virus.
The findings confirm a long-held assumption about one prevalent way illness spreads and could influence government policy on public health and several issues for private companies, from optimal design and management of physical work spaces to policy decisions about sick leave and remote work.
To track influenza incidence, Dongya "Don" Koh, assistant professor of economics in the Sam M. Walton College of Business, and colleagues relied on nationally representative data from the Medical ...
2021-06-30
A new study shows that colleges students are experiencing significant grief reactions in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The paper, "College Student Experiences of Grief and Loss Amid the COVID-19 Global Pandemic," was recently published in OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying.
"This study aimed to identify the most common non-death losses and grief reactions experienced by undergraduate and graduate college students amid the pandemic," said author Erica H. Sirrine, Ph.D., director of Social Work at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital. "What we found is that students ...
2021-06-30
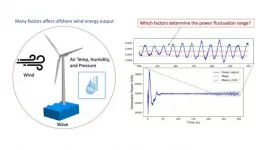
New Brunswick, N.J. (June 28, 2021) - Rutgers researchers have developed a machine learning model using a physics-based simulator and real-world meteorological data to better predict offshore wind power.
The findings appear in the journal Applied Energy.
Offshore wind is rapidly maturing into a major source of renewable energy worldwide and is projected to grow by 13% in the next two decades and 15-fold by 2040 to become a $1 trillion industry, matching capital spending on gas- and coal-fired power generation. In the United States, for instance, New York and New Jersey recently awarded two offshore ...
2021-06-30
When it comes to climate change, not all organisms will lose out. A new Cal Poly study finds that rattlesnakes are likely to benefit from a warming climate.
A combination of factors makes a warming climate beneficial to rattlesnakes that are found in almost every part of the continental United States but are especially common in the Southwest.
Rattlers are experts at thermoregulation. Researchers found that, when given a choice, the snakes prefer a body temperature of 86-89 degrees Fahrenheit, a much warmer temperature than they generally experience in nature. The average ...
2021-06-30
CHICAGO (June 30, 2021) -- Four leading medical specialty societies released a new clinical practice guideline today that includes recommendations for reducing blood loss during heart surgery and improving patient outcomes. The document, a multidisciplinary collaboration among The Society of Thoracic Surgeons, the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, the American Society of ExtraCorporeal Technology, and the Society for the Advancement of Patient Blood Management, is available online in The Annals of Thoracic Surgery and two other journals.
"As medicine evolves and we learn more, it always is important to review past ...
2021-06-30
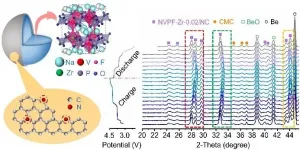
Na3V2(PO4)2F3(NVPF), a cathode material used in sodium-ion batteries (SIB), features ultrafast Na+ migration and high structural stability because of its three-dimensional open framework. However, the poor intrinsic electronic conductivity of NVPF often leads to high polarization, low Coulombic efficiency, and unsatisfactory rate performance, which hinder its commercial application.
Recently, a group led by Prof. Shuangqiang Chen and Prof. Yong Wang from Shanghai University synthesized zirconium-doped NVPF nanoparticles coated with a nitrogen-doped ...
2021-06-30
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have succeeded in developing a method to label mRNA molecules, and thereby follow, in real time, their path through cells, using a microscope - without affecting their properties or subsequent activity. The breakthrough could be of great importance in facilitating the development of new RNA-based medicines.
RNA-based therapeutics offer a range of new opportunities to prevent, treat and potentially cure diseases. But currently, the delivery of RNA therapeutics into the cell is inefficient. For new therapeutics to fulfil ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Extreme events: Ecosystems offer cost effective protection