(Press-News.org) University of California San Diego School of Medicine researchers have identified a possible link between inadequate exposure to ultraviolet-B (UVB) light from the sun and an increased risk of colorectal cancer, especially as people age.
Reporting in the journal BMC Public Health, researchers investigated global associations between levels of UVB light -- one of several types of ultraviolet light that reach the Earth's surface -- in 2017 and rates of colorectal cancer across several age groups in 186 countries in 2018.
Lower UVB exposure was significantly correlated with higher rates of colorectal cancer across all age groups. After other factors, such as skin pigmentation, life expectancy and smoking were considered, the association between lower UVB and risk of colorectal cancer remained significant for people aged 45 and older.
"Differences in UVB light accounted for a large amount of the variation we saw in colorectal cancer rates, especially for people over age 45. Although this is still preliminary evidence, it may be that older individuals, in particular, may reduce their risk of colorectal cancer by correcting deficiencies in vitamin D," said Raphael Cuomo, PhD, assistant professor of anesthesiology at UC San Diego School of Medicine.
Lower UVB exposure may reduce levels of vitamin D, wrote the authors. Vitamin D deficiency has previously been associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer. The authors suggested that future research could look directly at the potential benefits of correcting vitamin D deficiencies to reduce colorectal cancer risk, especially in older age groups.
With improvements in prevention, early detection and treatment, there are more than 1.5 million colorectal cancer survivors living in the United States. Still, an estimated 52,900 people will die this year from the disease, making it the second deadliest cancer among men and women in the U.S. An estimated 149,500 people will be diagnosed with colorectal cancer in 2021.
For the study, researchers used UVB estimates obtained by the NASA EOS Aura spacecraft in April 2017 and data on colorectal cancer rates in 2018 for 186 countries from the World Health Organization's Global Cancer (GLOBOCAN) database. They also collected data for 148 countries on skin pigmentation, life expectancy, smoking, stratospheric ozone (a naturally occurring gas that filters solar radiation) and other factors that might influence health and UVB exposure, derived from previous literature and databases. Countries with lower UVB included Norway, Denmark and Canada; countries with higher UVB included United Arab Emirates, Sudan, Nigeria and India.
The authors caution that other factors may affect UVB exposure and vitamin D levels, such as vitamin D supplements, clothing and air pollution, which were not included in the study. They also caution that the observational nature of the study does not allow for conclusions about cause and effect and that more work is needed to more fully understand the relationship between UVB, vitamin D and colorectal cancer.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors include: Vidya L. Purushothaman, Cedric F. Garland and Timothy K. Mackey, all at UC San Diego.
Disclosures: Mackey is a senior editorial board member of BMC Public Health and is a founder, officer and employee of the startup company S-3 Research LLC, which is funded and currently supported by the National Institutes of Health - National Institute on Drug Abuse through a Small Business Innovation and Research contract for opioid-related social media research and technology commercialization.
Manufacturing - Powered by nature
A team of researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory demonstrated the ability to additively manufacture power poles from bioderived and recycled materials, which could more quickly restore electricity after natural disasters.
Using the Big Area Additive Manufacturing system, the team 3D printed a 55-foot pole designed as a closed cylindrical structure. They evaluated three different composite materials with glass fibers including cellulose ester, recycled polycarbonate and bamboo fiber reinforced polystyrene.
"We developed a modular design that is easy to manufacture, transport and assemble," ORNL's Halil Tekinalp said. "Sections within the pole can ...
BOSTON - A skin pigmentation mechanism that can darken the color of human skin as a natural defense against ultraviolet (UV)-associated cancers has been discovered by scientists at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). Mediating the biological process is an enzyme, NNT, which plays a key role in the production of melanin (a pigment that protects the skin from harmful UV rays) and whose inhibition through a topical drug or ointment could potentially reduce the risk of skin cancers. The study was published online in Cell.
"Skin pigmentation and its regulation are critically important because pigments confer major protection against UV-related cancers ...
A transplant of healthy gut microbes followed by fibre supplements benefits patients with severe obesity and metabolic syndrome, according to University of Alberta clinical trial findings published today in Nature Medicine.
Patients who were given a single-dose oral fecal microbial transplant followed by a daily fibre supplement were found to have better insulin sensitivity and higher levels of beneficial microbes in their gut at the end of the six-week trial. Improved insulin sensitivity allows the body to use glucose more effectively, reducing blood sugar.
"They were much more metabolically healthy," said principal investigator Karen Madsen, professor of medicine in the Faculty of Medicine ...
Researchers at Linköping University have developed a method that may lead to new types of displays based on structural colours. The discovery opens the way to cheap and energy-efficient colour displays and electronic labels. The study has been published in the scientific journal Advanced Materials.
We usually think of colours as created by pigments, which absorb light at certain wavelengths such that we perceive colour from other wavelengths that are scattered and reach our eyes. That's why leaves, for example, are green and tomatoes red. But colours can be created ...
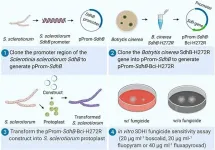
Succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors (SDHIs) are a class of fungicides widely used to control many fungal diseases of crops. The relationship between SDHIs and fungi can be compared to finding the right key for the right lock. However, fungi are adaptable and develop resistance to fungicides often by changing the lock so that the SDHI is no longer able to open the door. Because of this adaptability, it is important to understand the biological mechanisms of fungicide resistance.
A recent collaboration between scientists in Michigan and Massachusetts as ...
However, the majority of these organisms are believed to be in a state a state of 'dormancy' due to environmental stress, such as nutrient-poor conditions. An international team of scientists led by Dagmar Woebken and Stephanie A. Eichorst from the University of Vienna investigated how acidobacteria, which are widespread in soils, can survive under adverse conditions. Two recent studies published in The ISME Journal and mSystems describe these survival strategies.
The living conditions that microorganisms encounter in soils are unpredictable and challenging. Nutrients and oxygen are frequently scarce for long periods. Acidobacteria manage to defy these extreme conditions. They are found in an astonishing diversity in soils worldwide. "Since they are this widespread, ...
The death of cells is well regulated. If it occurs too much, it can cause degenerative diseases. Too little, and cells can become tumours. Mitochondria, the power plants of cells, play a role in this programmed cell death. Scientists from the University of Groningen (the Netherlands) and the University of Pittsburgh (U.S.) have obtained new insights in how mitochondria receive the signal to self-destruct. Their results were published in the Journal of Molecular Biology.
How does a cell kill itself? The details of this process are still unclear. Patrick van der Wel, associate professor ...
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [July 6, 2021] -- New research in the June 2021 issue of JNCCN--Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network assesses the quality of cancer care delivered through extended sites coordinated by some of the country's largest cancer centers. The study was developed to implement strategies for disseminating discoveries and expanding access to the highest quality cancer care as part of AACI's Network Care Initiative, established by former AACI President Stanton L. Gerson, MD, Director of the Case Comprehensive Cancer Center. Results were calculated based on responses to a mixed-methods survey answered by 69 cancer centers between September 2017 and December 2018, at which time 56 reported at ...
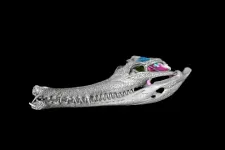
The braincase of crocodylians has a distinctive structure. Unlike evolutionary relatives (birds and squamates), in crocodylians, all braincase bones are rigidly fixed together and form an akinetic structure. In the process of evolution, this made it possible for animals to develop powerful jaws and stronger bite forces, thanks to which crocodylians could gnaw through the hard shell of crayfish and turtles and hunt fish and land animals, including dinosaurs. As a result, they have managed to fill the niche of predators and survive to the present day.
At present, in comparison with other parts of the crocodylian skull, the structure of their braincase has been understudied. This is because, until recently, scientists did not have ...
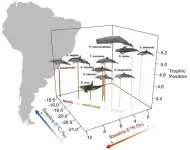
Dolphin species that live together, do not necessarily compete for food
A new molecular method reveals how different species of toothed whales compete for prey and which food they choose in each other's company. Marine scientists from NIOZ recently published their work in the scientific magazine Environmental Research.
Little is still known about the food and food search behaviour of toothed whales. What we know historically, is primarily derived from the stomach content of dead specimens. However, this makes it hard to actively study them in their natural habitat: you can't do more than wait for animals to wash ashore. Consequently, ...