Scientists discover nanoclusters effective for cancer in the second near-infrared synergy therapy
2021-07-13
(Press-News.org) As a minimally invasive method for cancer therapy at precise locations, NIR-induced photothermal therapy (PTT) has drawn extensively attention. The therapeutic mechanism is the use of photothermal agents (PTAs) in the treatment of tumors,and its therapeutic effect happens only at the tumor site where both light-absorbent and localized laser radiation coexist.
The development of PTAs with NIR-II absorbance, ranging from 1000nm to 1700 nm, can efficiently improve their penetrating ability and therapeutic effects because of their high penetration depth in the body. Howerever, several disadvantages are associated with these NIR-II responsive PTAs for their use in biomedical areas. Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), which boast strong absorption effect in NIR-II, can meet this demand. It has attracted much attention for biomedical applications with its noninvasive imaging function and magnetic-induced targeted ability.
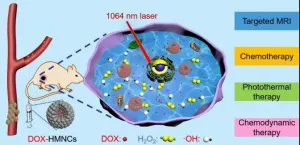
Recently, a research team led by Prof. WANG Hui and Prof. LIN Wenchu of High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported a new type of NIR-II responsive hollow magnetite nanoclusters (HMNCs), which is made of composed of Fe3O4, mesoporous shell and hollow cavity for targeted imaging-guided combined therapy of cancer.
"HMNC absorbed NIR-II laser and converted it into local heat," said Prof. WANG, "therefore we successfully accelerated combination of drug release and chemo-photothermal therapy."
In one-step solvothermal method, they prepared HMNCs with NIR-II absorption at 1066 nm under an external magnetic field (0.5T), which provided photothermal effect on tumor. Besides, as Fe3O4 dissolved in the acid environment, they can convert H2O2 into toxic Hydroxyl radicals, which add chemodynamic effect. What's more, the hollow cavities in HMNCs are good loading places for drug, which also acted as a targeted contrast agent for tumor magnetic resonance imaging.
Further in vivo experiments proved that the combined effect of photothermal, chemo-therapy and chemodynamic therapy of HMNCs has a significant inhibitory effect on mouse tumor growth.
This experiment showed a kind of multifunctional nanocarriers based on NIR-II responsive HMNCs for trimodal cancer therapy.
INFORMATION:
Link to the paper: NIR-II Responsive Hollow Magnetite Nanoclusters for Targeted Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Photothermal/Chemo-Therapy and Chemodynamic Therapy
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the HMNCs for targeted MRI, responsive drug release, NIR-II-induced photothermal treatment and chemodynamic therapy. (Image by WANG Hui)
Contact:
ZHAO Weiwei
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (http://english.hf.cas.cn/)
Email: annyzhao@ipp.ac.cn
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-13
Over the past years, graphene oxide membranes have been mainly studied for water desalination and dye separation. However, membranes have a wide range of applications such as the food industry. A research group led by Aaron Morelos-Gomez of Shinshu University's Global Aqua Innovation Center investigated the application of graphene oxide membranes for milk which typically creates dense foulant layers on polymeric membranes.
Graphene oxide membranes have the advantage to create a porous foulant layer, therefore, their filtration performance can be maintained better than commercial polymeric membranes. The unique chemical and ...
2021-07-13
Clinician well-being is imperative to providing high-quality patient care, yet clinician burnout continues to increase, especially over the last year due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Four leading cardiovascular organizations - the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, the European Society of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation - are calling for global action to improve clinician well-being in a joint opinion paper published today.
"Over the last several decades, there have been significant changes in health care with the expansion of technology, regulatory burden and clerical task loads. These developments have come at a cost to the ...
2021-07-13
A new population-based study looking at nearly 30 years of billing data demonstrates that sex-based differences in Ontario Health Insurance Plan (OHIP) payments exists for Canadian ophthalmologists.
A team led by researchers and clinicians from the Donald K. Johnson Eye Institute, part of the Krembil Research Institute at University Health Network (UHN), studied 22,389 Ontario physicians across three decades and found a significant payment gap between female and male ophthalmologists even after accounting for age, and some practice differences. This disparity was more pronounced among ophthalmologists when compared to other surgical, medical procedural and medical non-procedural specialty groups.
"This is real and robust ...
2021-07-13
DALLAS, July 13, 2021 -- Sharing the results of genetic testing for cardiomyopathy in adolescents ages 13-18 does not appear to cause emotional harm to families or adversely impact family function or dynamics, according to new research published today in Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine, an American Heart Association journal.
Genetic testing for cardiomyopathy in symptomatic children has the potential to confirm a diagnosis, clarify prognosis, determine eligibility for disease-specific cardiomyopathy therapies and even inform risk for other family members. Genetic testing for asymptomatic adults and children also occurs after one of their family members receives positive cardiomyopathy genetic ...
2021-07-13
Philadelphia, July 13, 2021--Adding to the growing body of literature demonstrating the feasibility of correcting lethal genetic diseases before birth, researchers at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have used DNA base editing in a prenatal mouse model to correct a lysosomal storage disease known as Hurler syndrome. Using an adenine base editor delivered in an adeno-associated viral vector, the researchers corrected the single base mutation responsible for the condition, which begins before birth and affects multiple organs, with the potential to cause death in childhood if untreated.
The findings were published ...
2021-07-13
Hair dye, perfume, jewellery. Beautifying to most, but for some they are equivalent to rashes, irritation and reduced quality of life. Together with hay fever and food allergies, allergic contact dermatitis due to exposure to e.g. nickel and perfume ingredients represents the majority of allergic reactions seen among Danes.
Traditionally, researchers have distinguished between immediate and delayed allergic reactions, depending on which parts of the immune system that is responsible for the reaction. E.g., hay fever and food allergies are 'immediate' forms that cause immediate symptoms, whereas it can take days before the skin reacts to things like nickel and perfume. But now a new study ...
2021-07-13
A new paper in The Economic Journal, published by by Oxford University Press, indicates that the presence of adult entertainment establishments may decrease sex crimes, significantly.
The role of entertainment establishments (strip clubs, escort services, adult bookstores, and adult movie theaters) in communities is controversial. Citizens often view them as centers of vice. While some have suggested that these clubs and services may improve behavior if people use them instead of committing sex crimes, such establishments may reinforce the view of women as objects, leading to more violence against them.
This paper exploits a unique data set of high frequency precinct level crime information from New York City, due to its controversial stop-and-frisk policing policy. The researchers ...
2021-07-13
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- New research from Binghamton University, State University of New York suggests that the demographic collapse at the core of the Easter Island myth didn't really happen.
You probably know this story, or a version of it: On Easter Island, the people cut down every tree, perhaps to make fields for agriculture or to erect giant statues to honor their clans. This foolish decision led to a catastrophic collapse, with only a few thousand remaining to witness the first European boats landing on their remote shores in 1722.
But did the demographic collapse at the core of the Easter Island myth really happen? The answer, according to new research by Binghamton ...
2021-07-13
Combining chemotherapy and BRAF oncogene inhibitors is a very effective strategy for fighting metastatic melanoma, the leading cause of death from skin cancer in the world. This has been demonstrated in a study by researchers from the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM), Hospital del Mar, and CIBER Cancer (CIBERONC), in collaboration with the Bellvitge Medical Research Institute (ICO-IDIBELL), which has just been published in the journal Oncogene.
The study, which involved the IMIM's Stem Cells and Cancer Research Group and doctors from the Dermatology and Pathology Departments at Hospital del Mar, analysed what effect ...
2021-07-13
Researchers from University of Bath, University of Melbourne, and King's College London published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that explains a four-stage process that can help firms create pleasurable social atmospheres for consumers.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Social Atmospheres: How Interaction Ritual Chains Create Effervescent Experiences of Place" and is authored by Tim Hill, Robin Canniford, and Giana Eckhardt.
Across the globe, restrictions on live events have affected the experience economy and entertainment industries. Simultaneously, the empty seats and eerie silence in sports ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists discover nanoclusters effective for cancer in the second near-infrared synergy therapy
